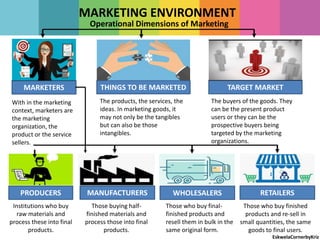
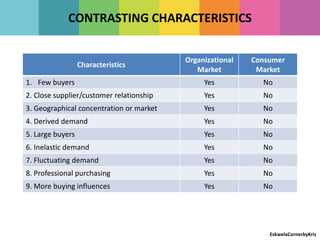
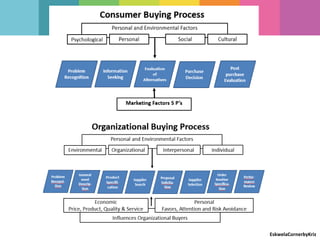
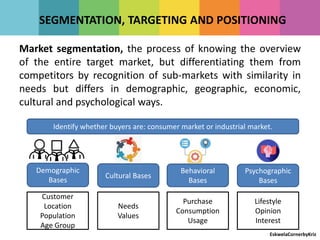
The document outlines the differences between strategic and tactical marketing, emphasizing the importance of marketing research in understanding consumer needs and market conditions. It details the steps involved in marketing research, from data collection to implementing solutions, while highlighting the characteristics of consumer versus organizational markets. Additionally, it discusses market segmentation and the factors that influence effective communication with target customers.