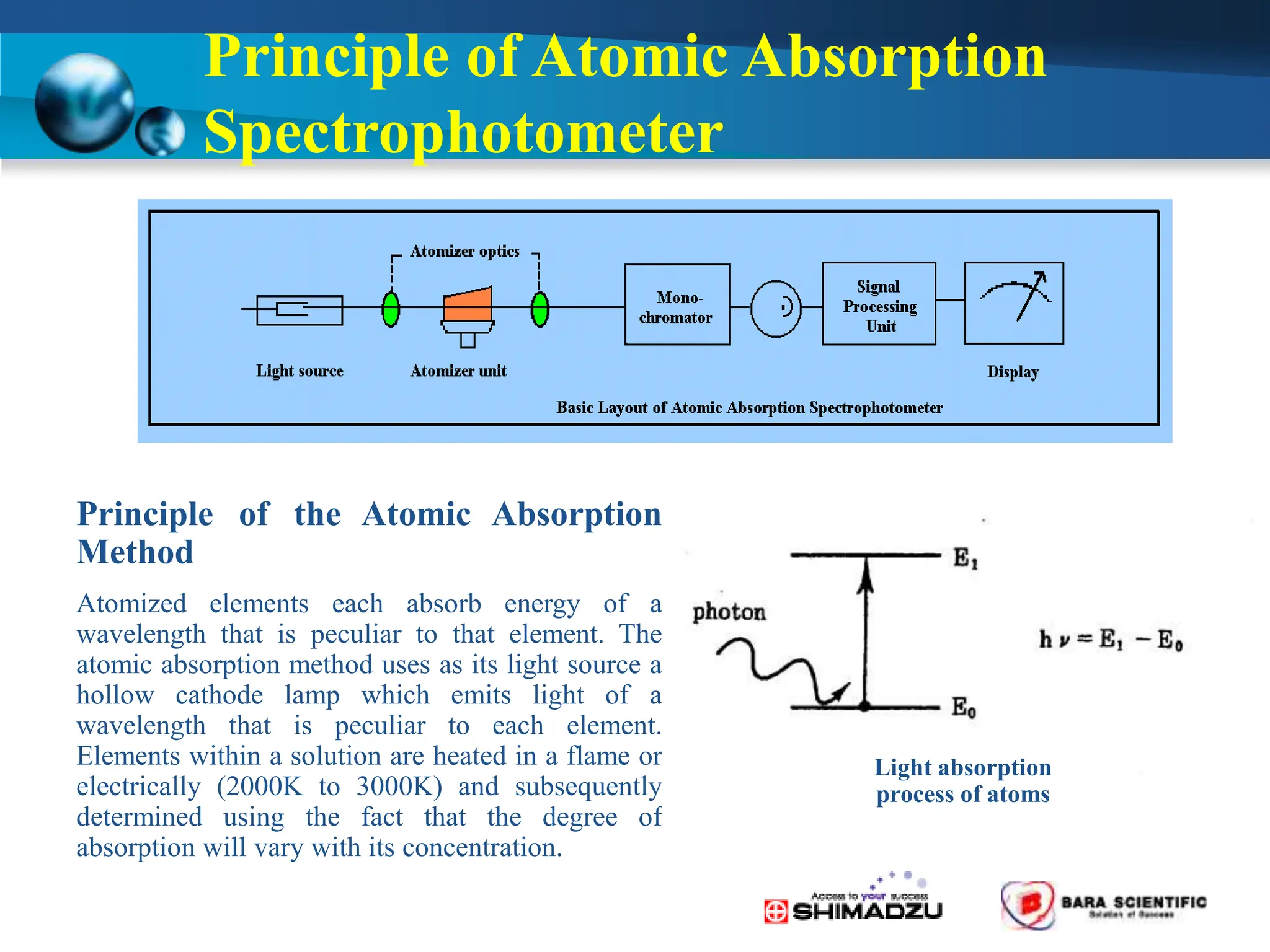
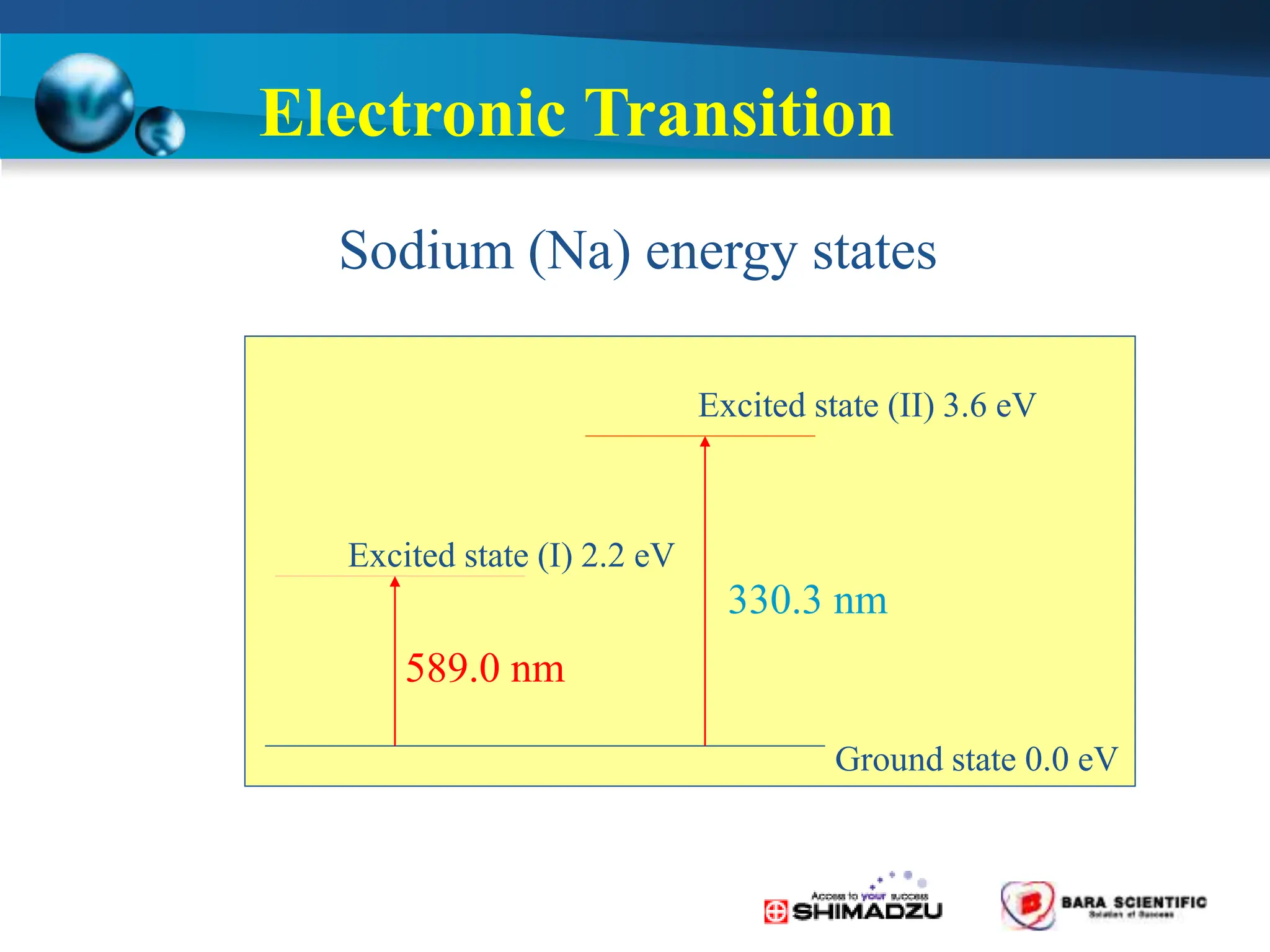
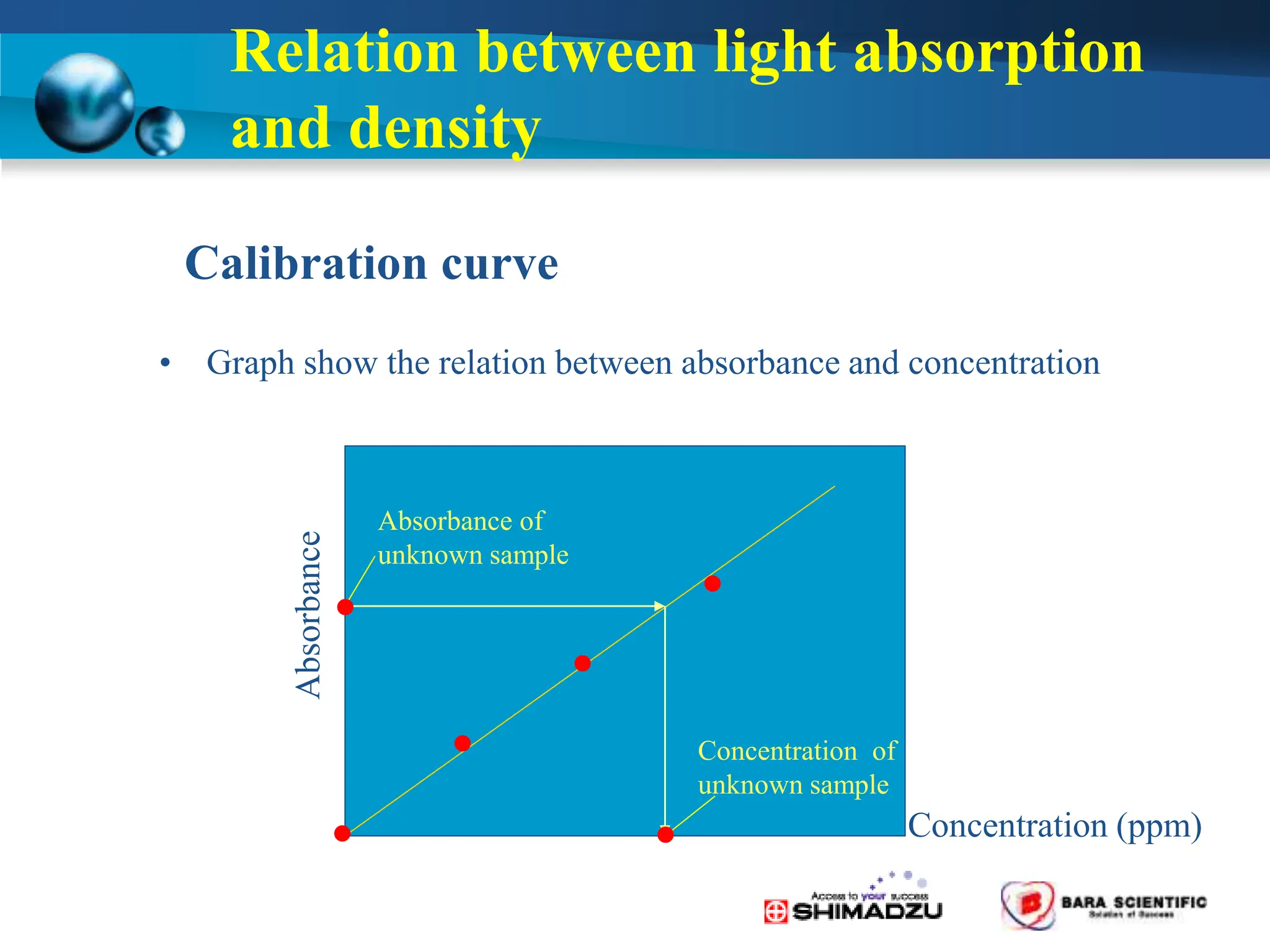
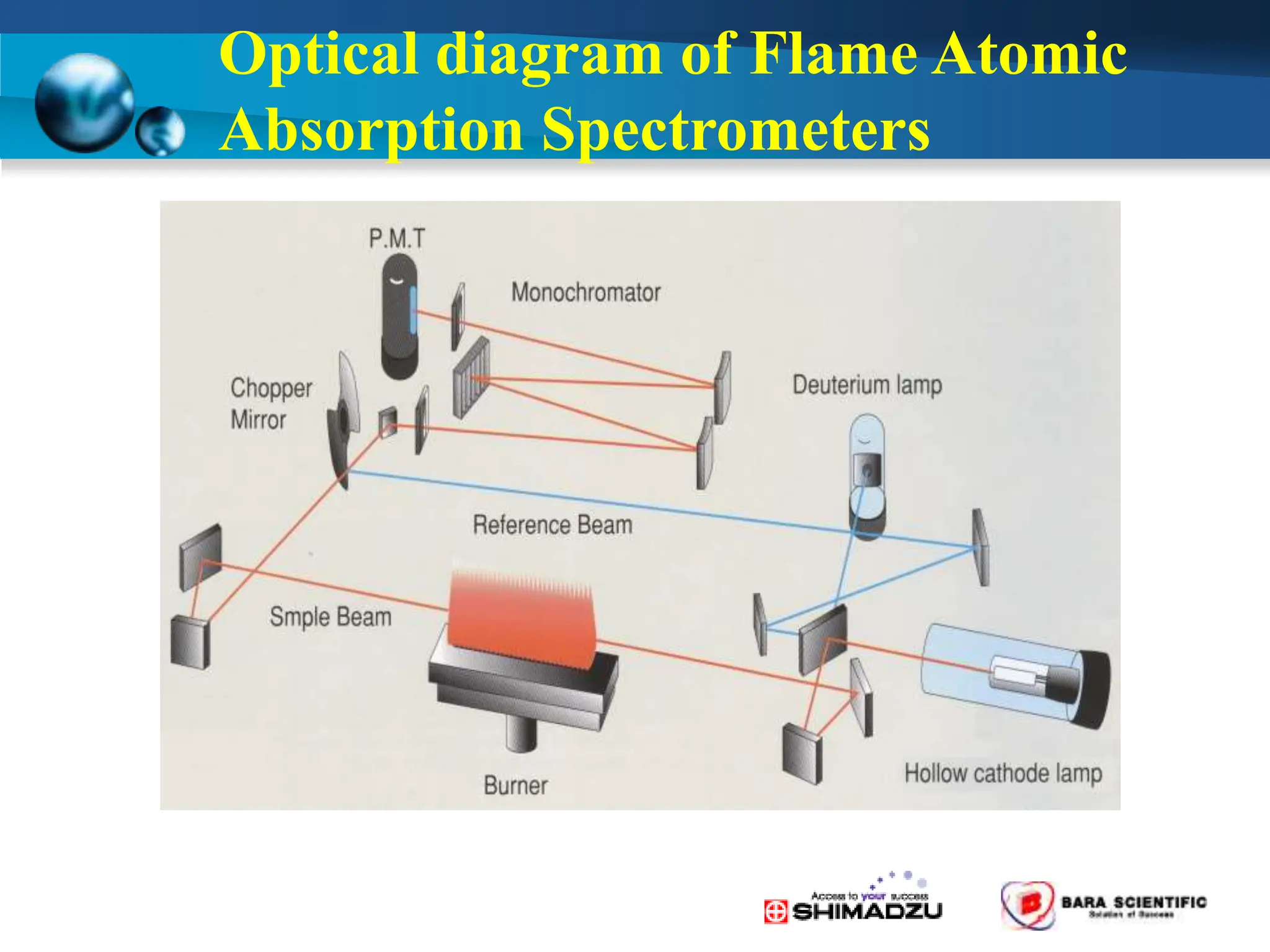
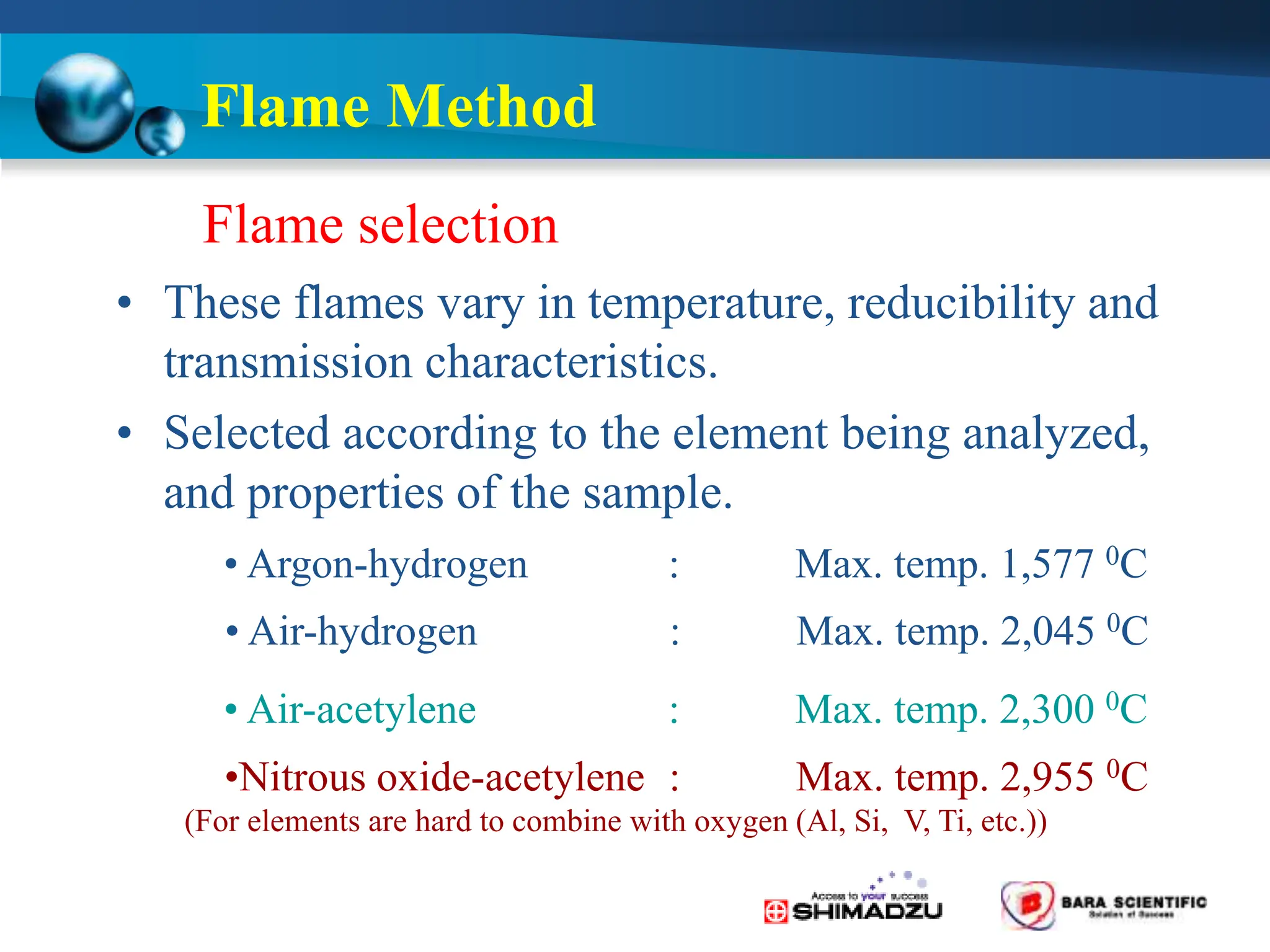
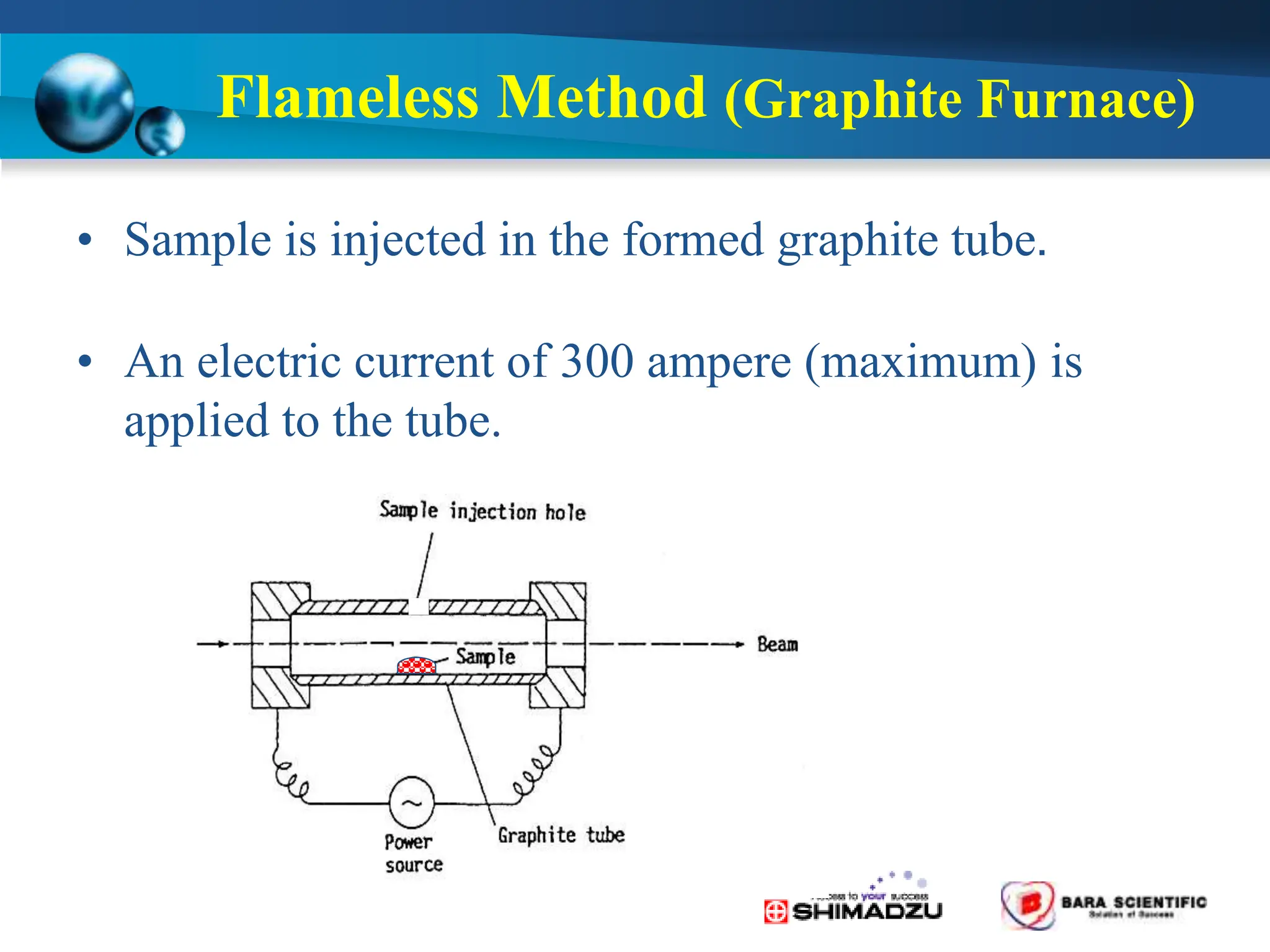
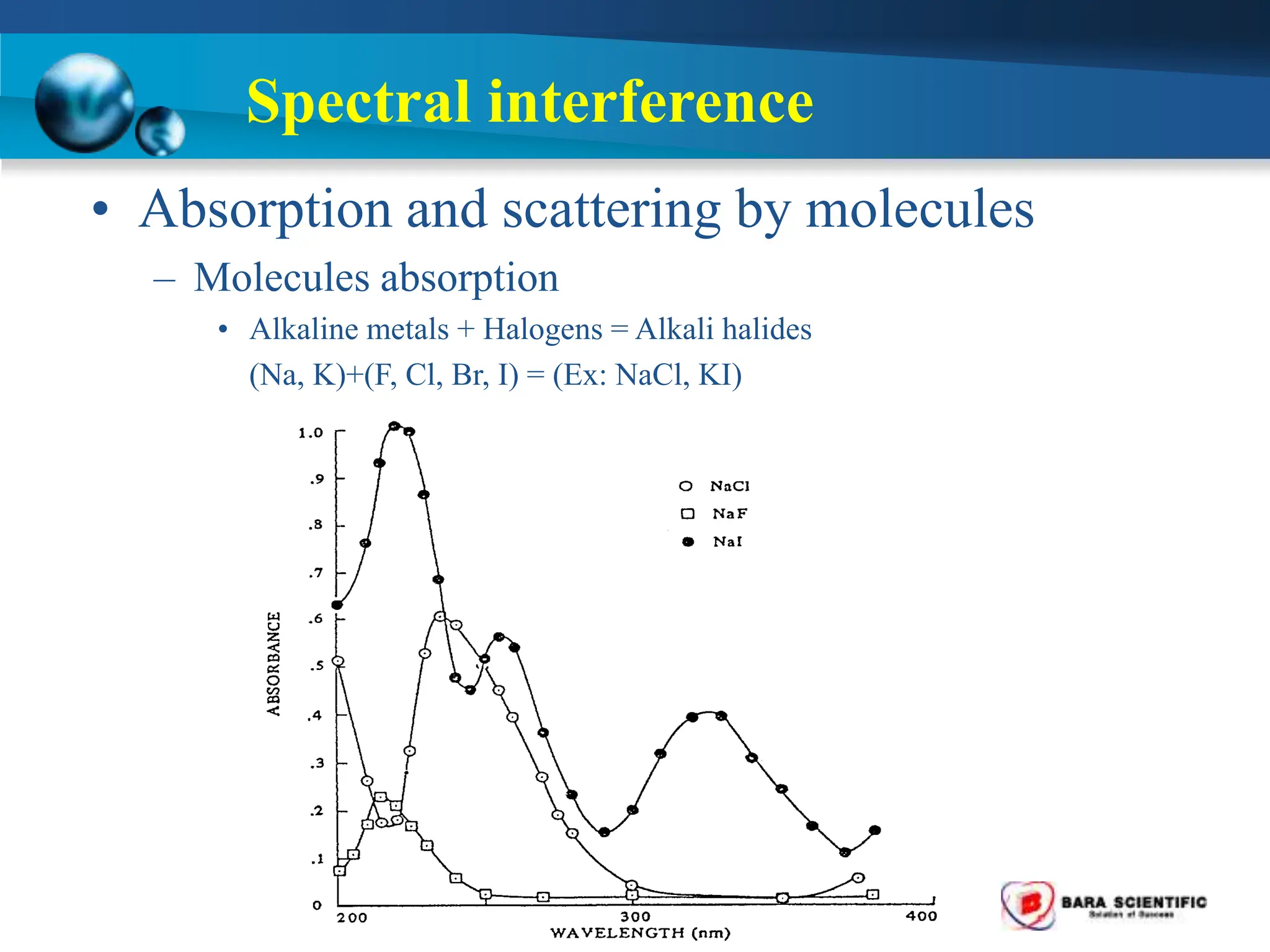
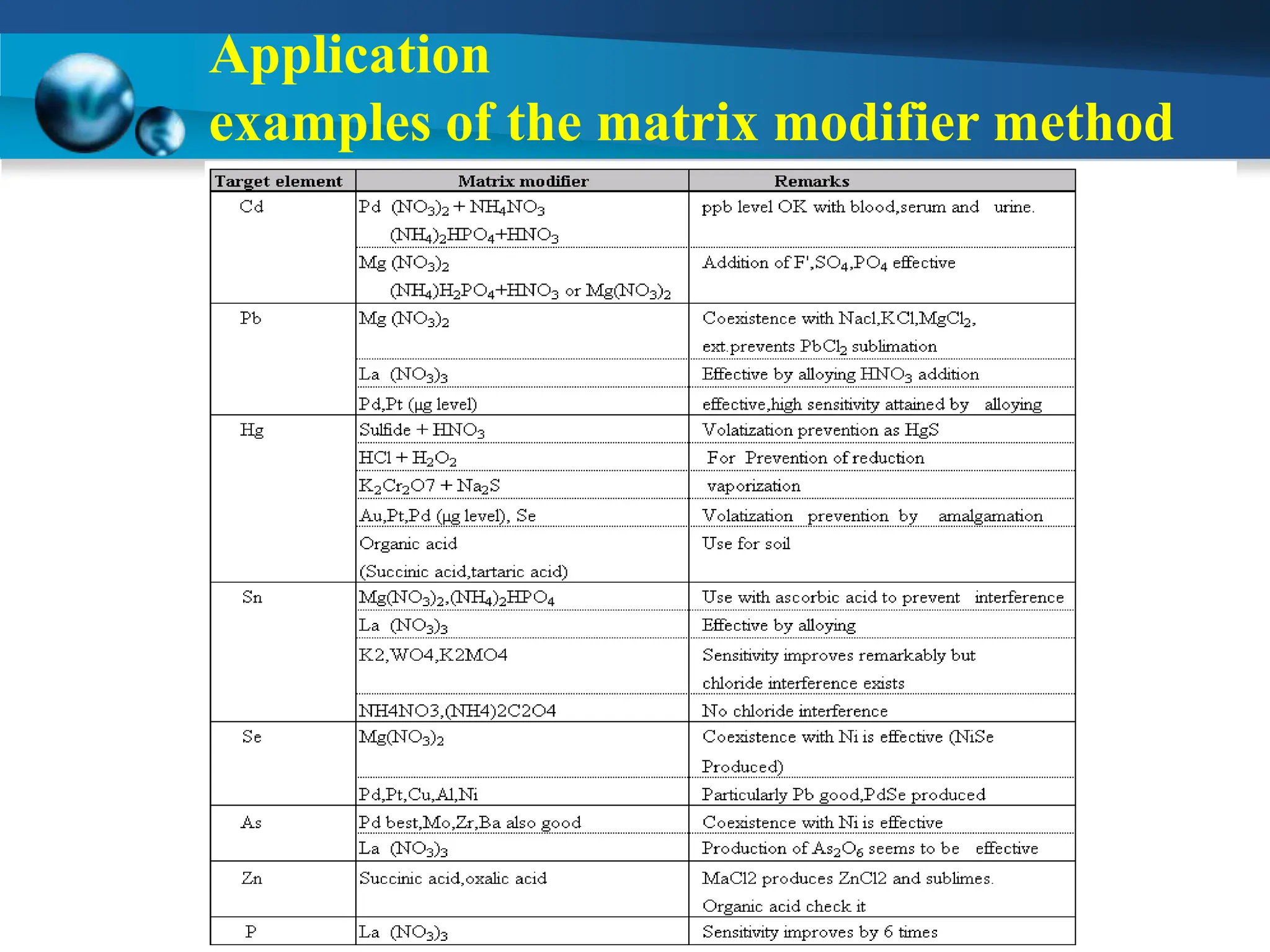
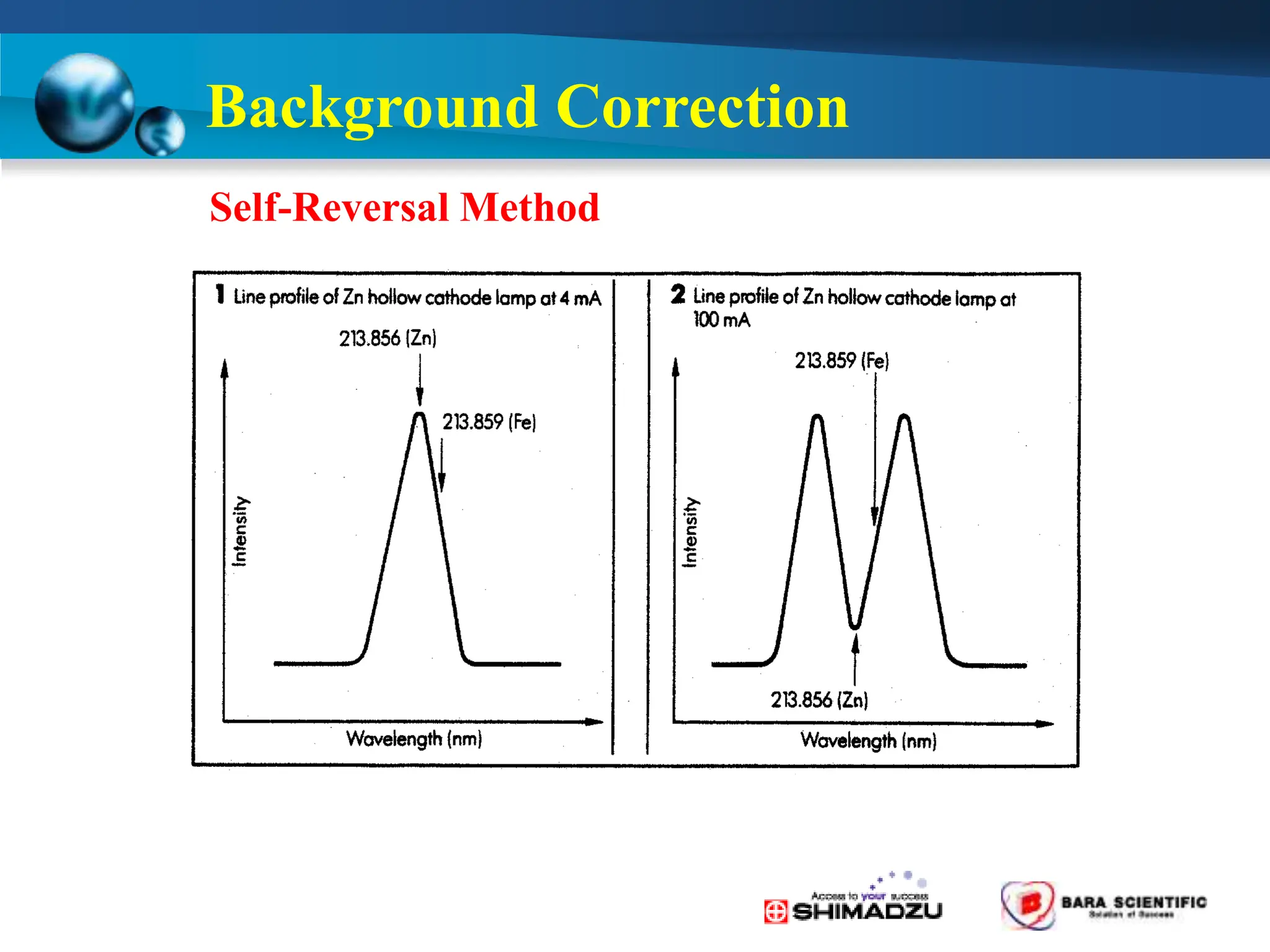
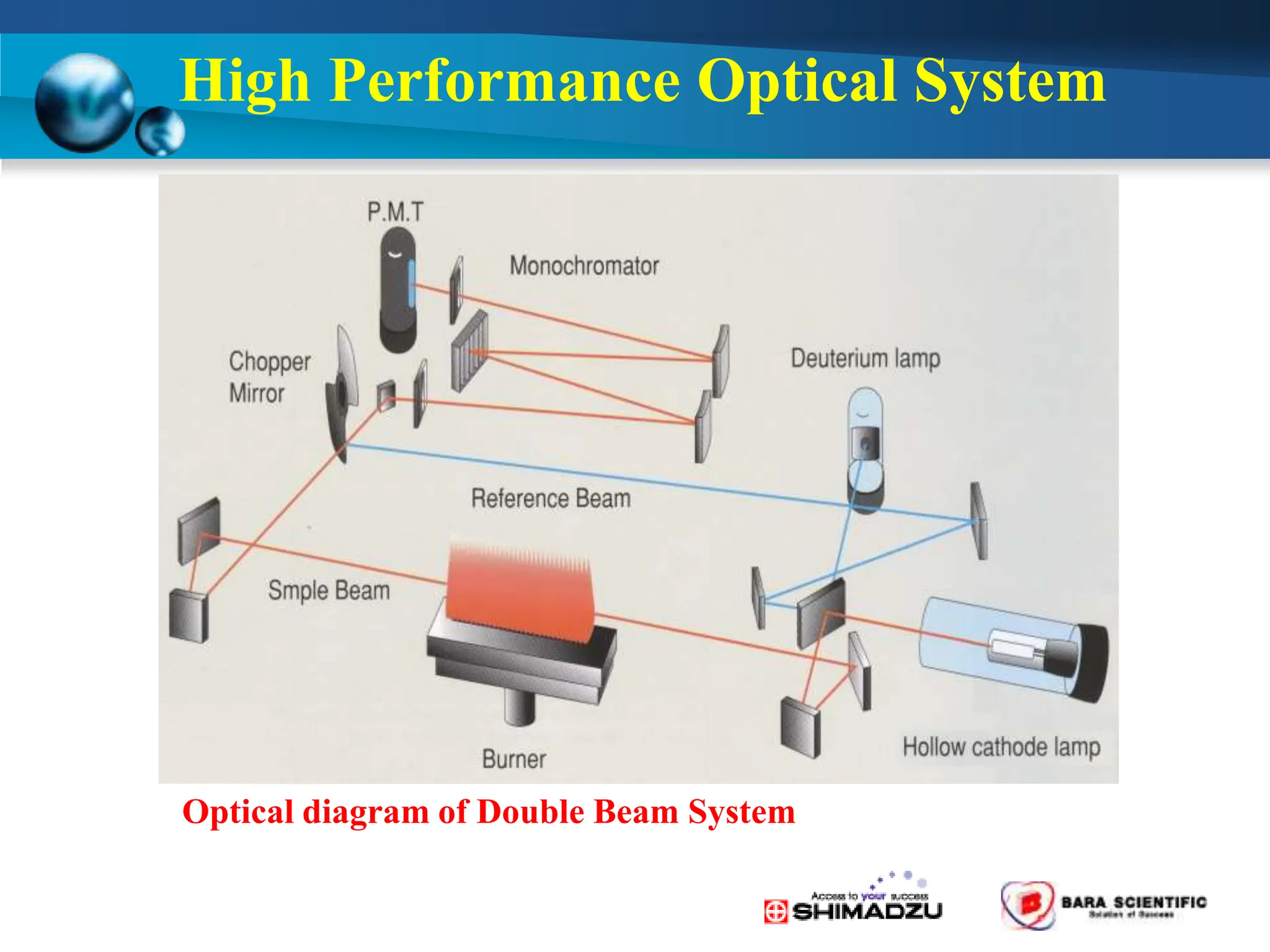
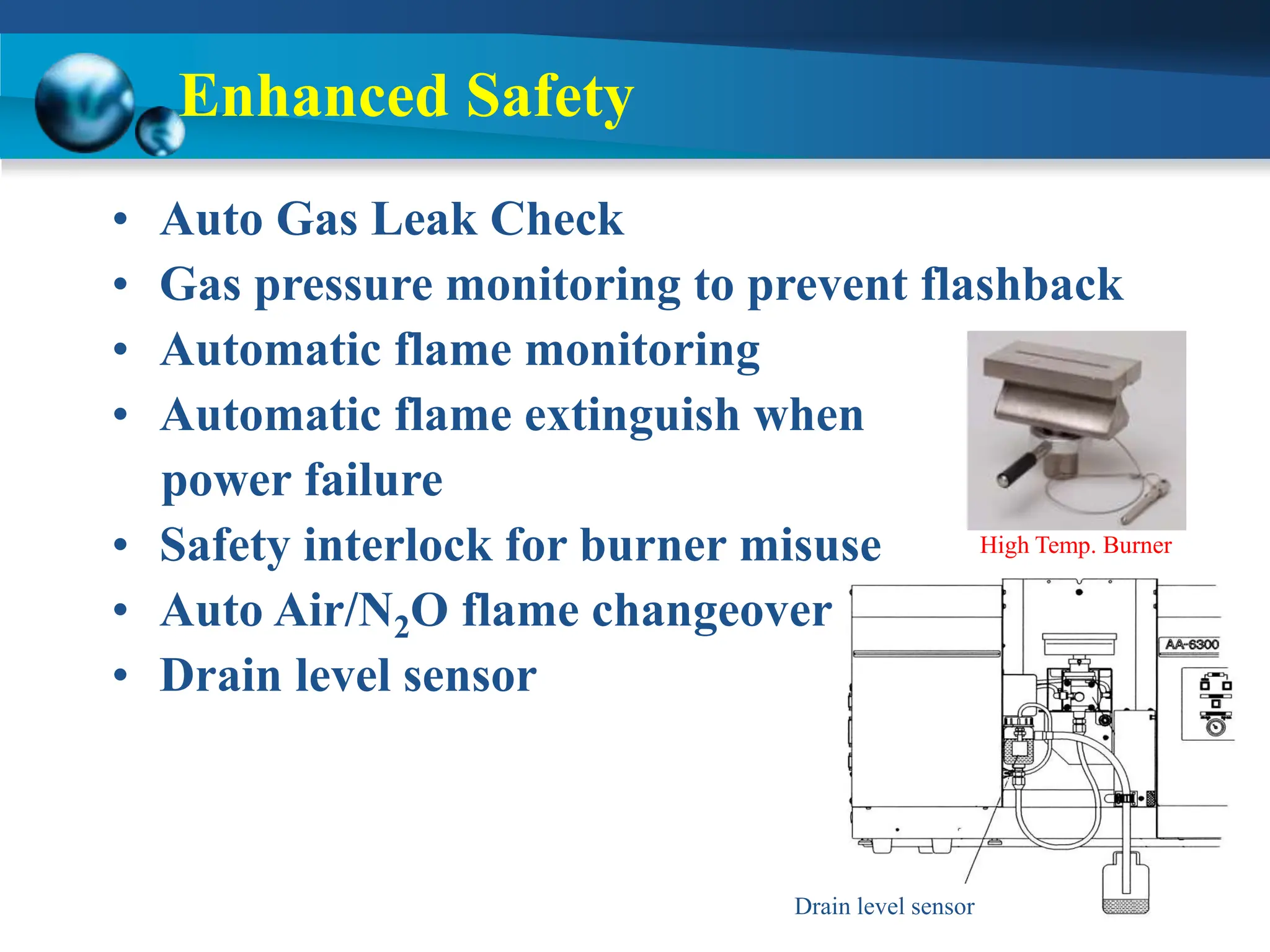
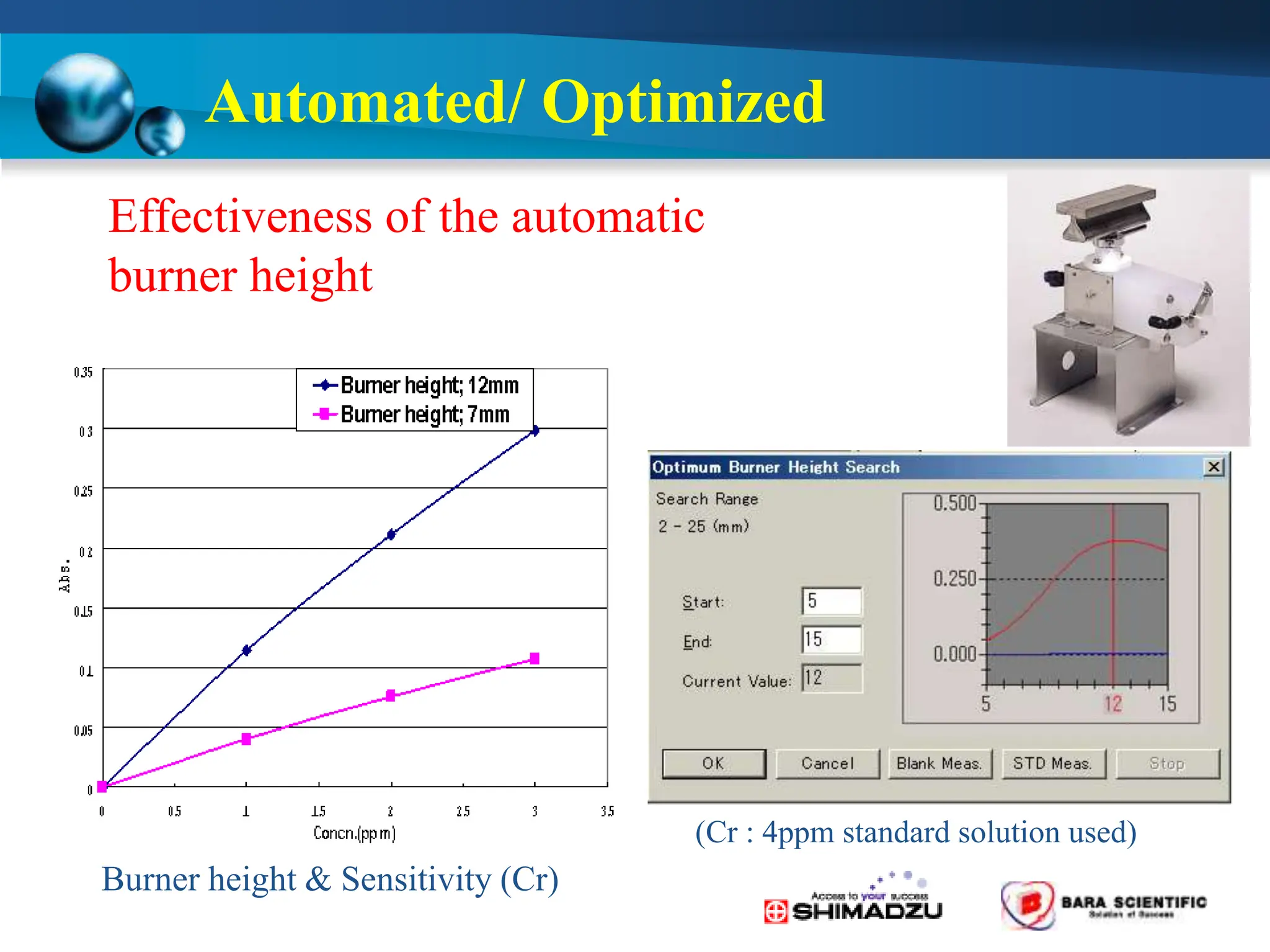
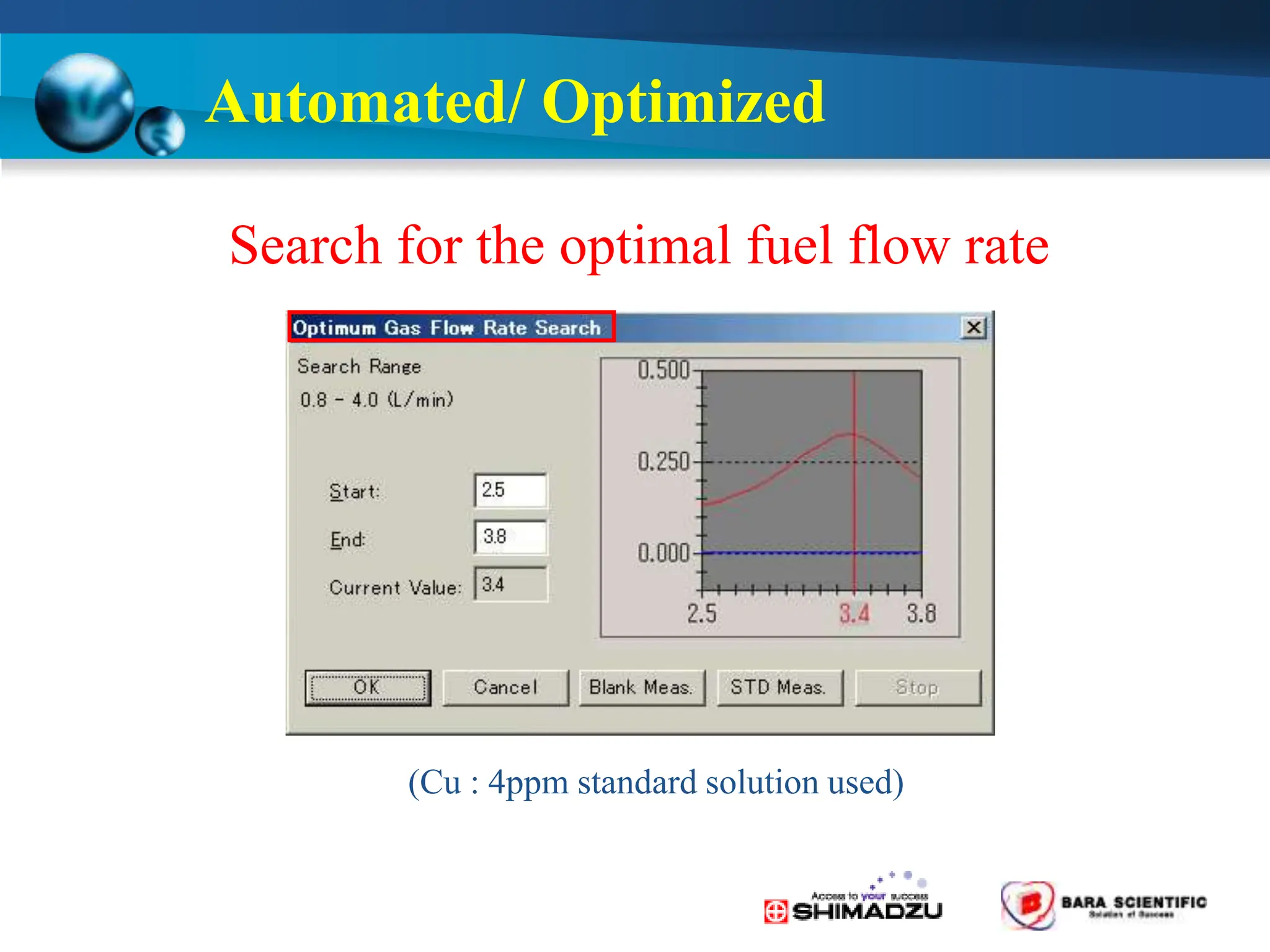
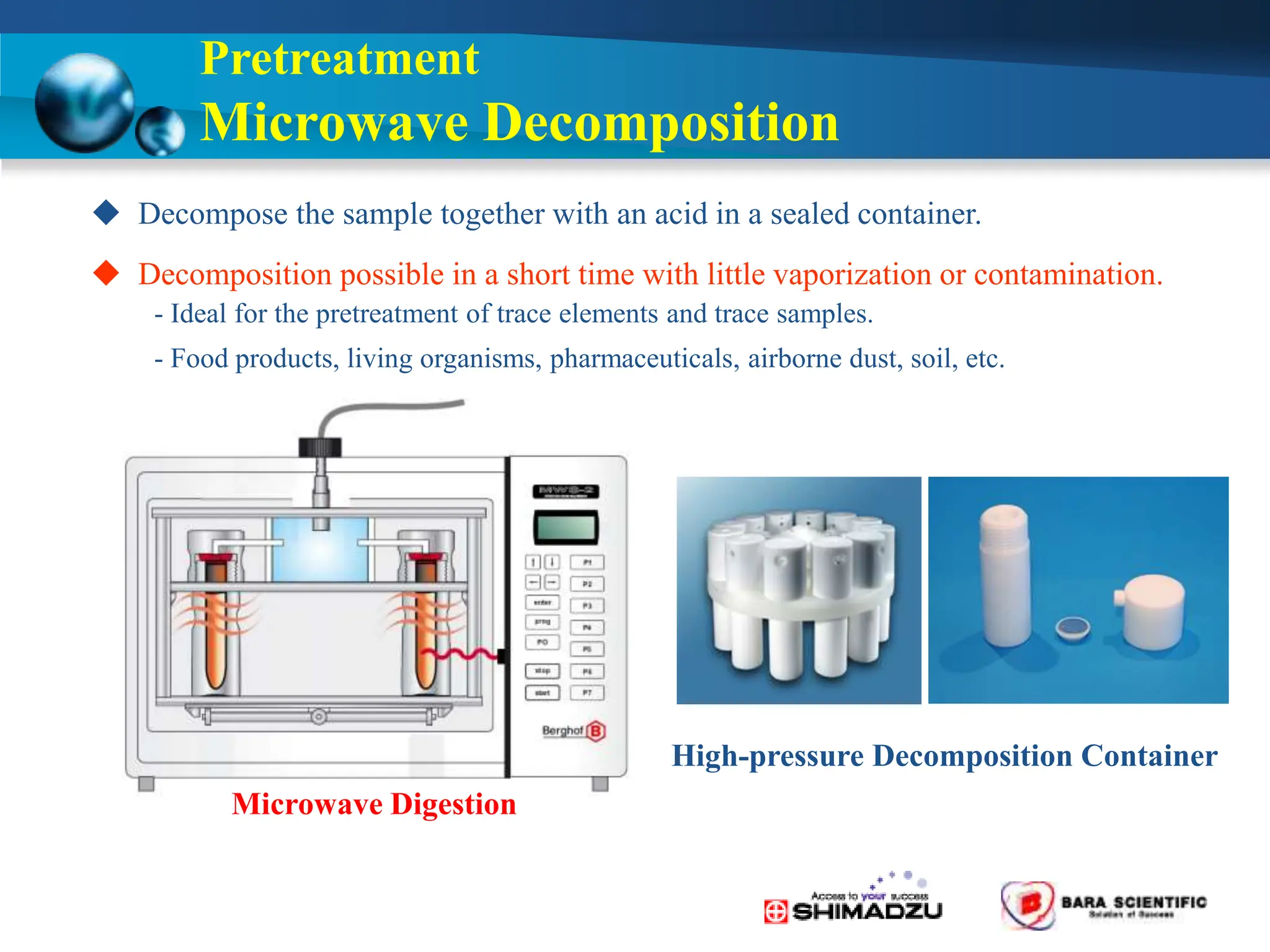
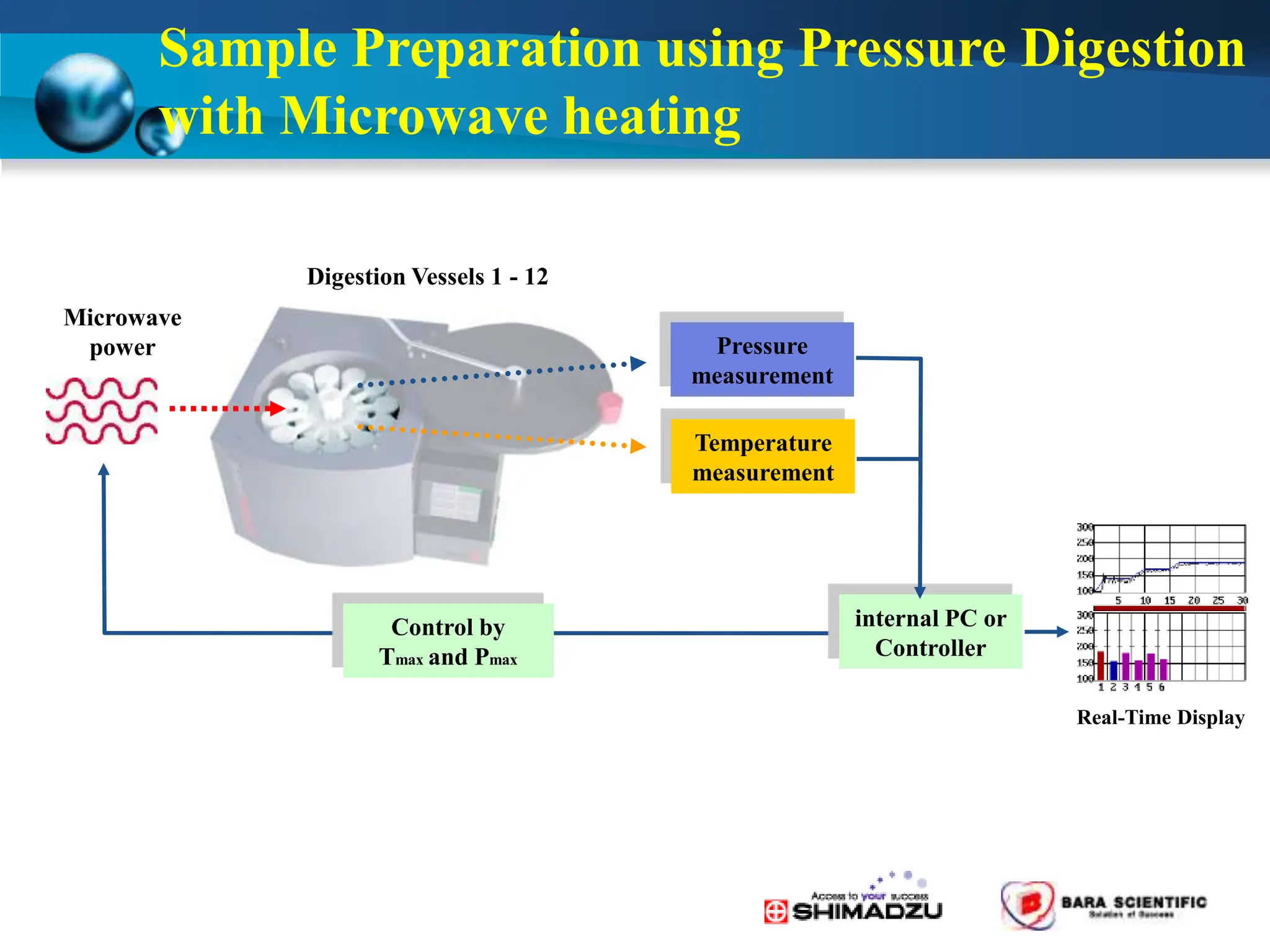
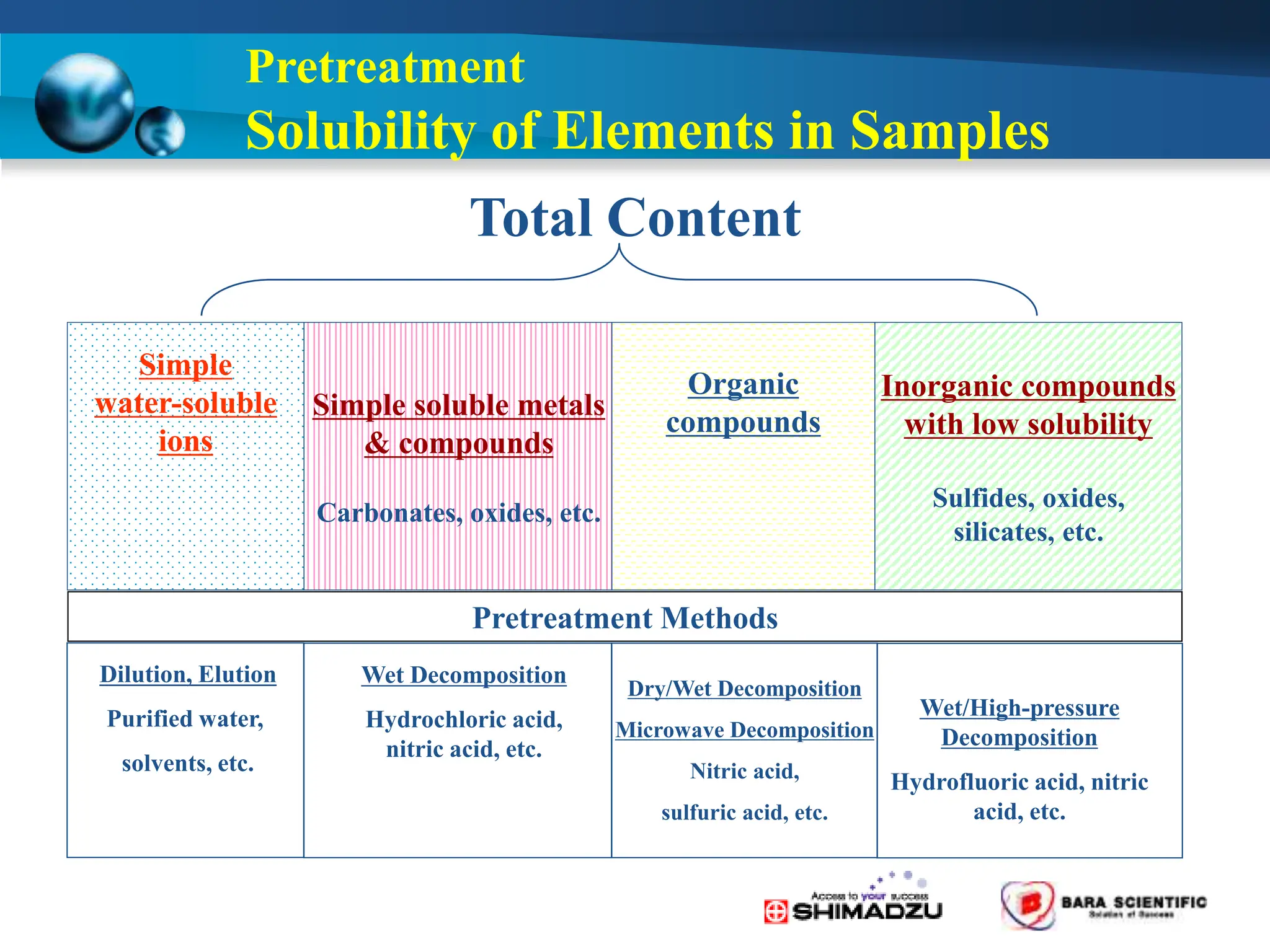
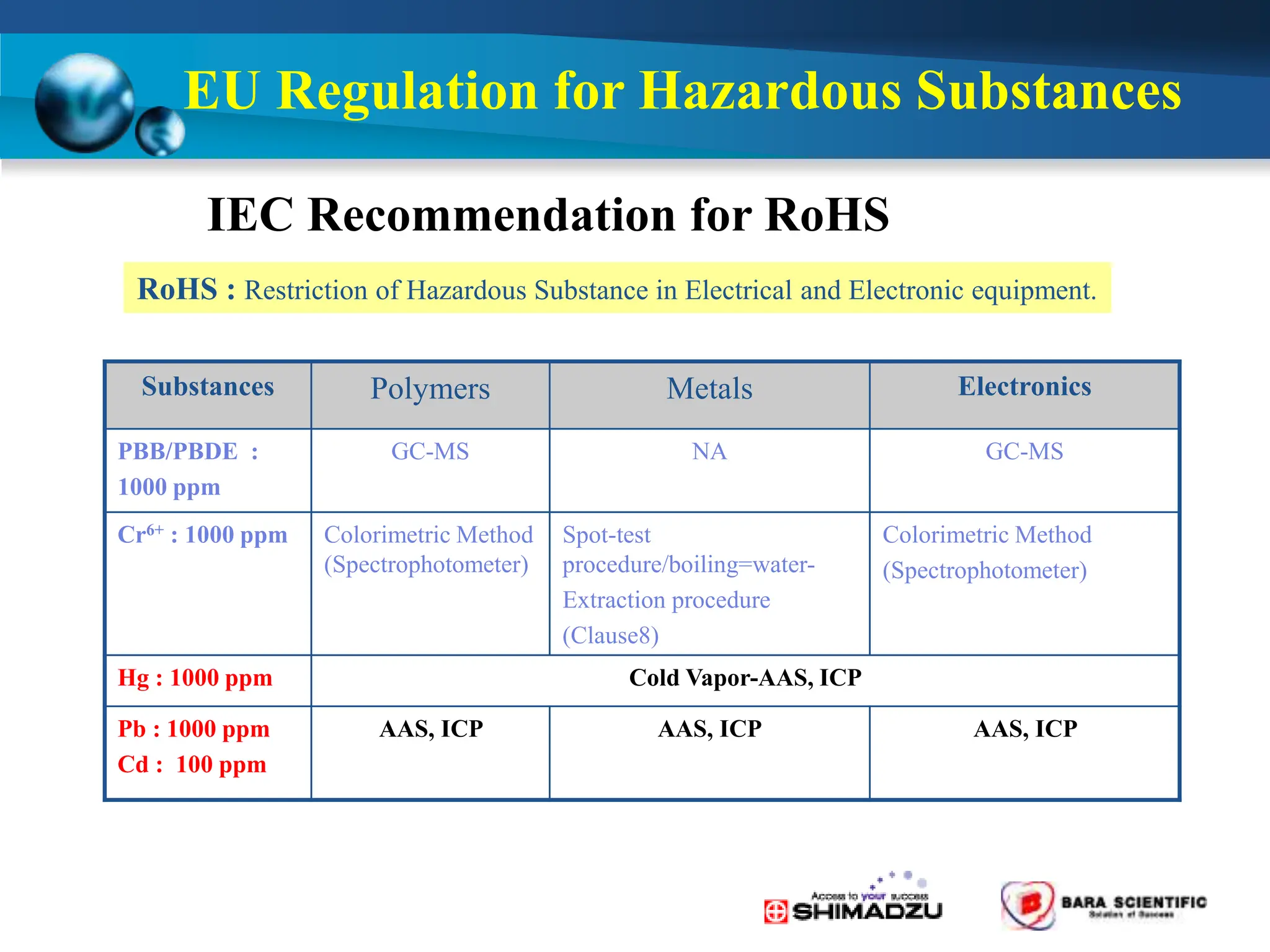
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry is a technique used to determine the concentration of metal elements in samples. It works by heating the sample in a flame or furnace to atomize the elements, and then measuring the absorption of light from a hollow cathode lamp emitting light at the characteristic wavelength of the targeted element. The degree of absorption is directly proportional to the element's concentration based on the Beer-Lambert law. Common applications of AAS include analyzing samples from agriculture, clinical/biochemistry, minerals, food/drugs, and the environment to determine elemental composition.