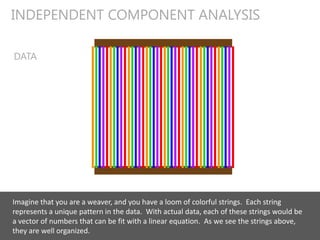
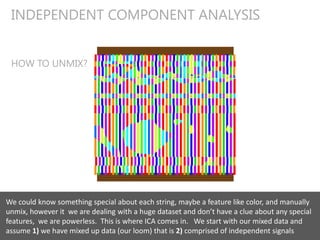
Independent Component Analysis (ICA) is a statistical technique used to separate mixed signals into their independent source components. ICA assumes that the observed mixed data was generated by mixing together statistically independent source signals. ICA uses an "unmixing" matrix to separate the mixed signals by maximizing the statistical independence of the estimated components, with the goal of recovering the original independent source signals. ICA models the probability distribution of each independent source signal using the sigmoid function, and then iteratively updates the unmixing matrix weights to maximize the overall likelihood of the data, until convergence is reached. However, ICA has limitations in that the original source signal order and scaling cannot be determined if the source signals are Gaussian distributed.





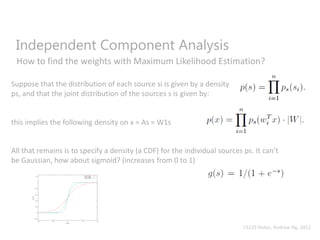



![Why can’t the data be Gaussian?
“Suppose we observe some x = As, where A is our mixing matrix. The distribution of x
will also be Gaussian, with zero mean and covariance
E[xxT ] = E[AssTAT ] = AAT
Now, let R be an arbitrary orthogonal (less formally, a rotation/reflection) matrix, so
that RRT = RTR = I, and let A’ = AR. Then if the data had been mixed according to A’
instead of A, we would have instead observed x’ = A’s. The distribution of x’ is
also Gaussian, with zero mean and covariance
E[x’(x’)T ] = E[A’ssT (A’)T ] = E[ARssT (AR)T ] = ARRTAT = AAT
Hence, whether the mixing matrix is A or A’, we would observe data from a N(0;AAT )
distribution. Thus, there is no way to tell if the sources were mixed using A and A’. So,
there is an arbitrary rotational component in the mixing matrix that cannot be
determined from the data, and we cannot recover the original sources.”
CS229 Notes, Andrew Ng, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/independentcomponentanalysis-150921071543-lva1-app6892/85/Independent-component-analysis-12-320.jpg)
