This document discusses principal component analysis (PCA), including the theory behind it and toolkits for implementing it. The theory section explains how PCA transforms correlated variables into uncorrelated principal components to perform dimensionality reduction. It describes minimizing squared error to find the principal components, which are the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix. The document lists toolkits for PCA in languages like C, Java, Perl and MATLAB and provides code examples.




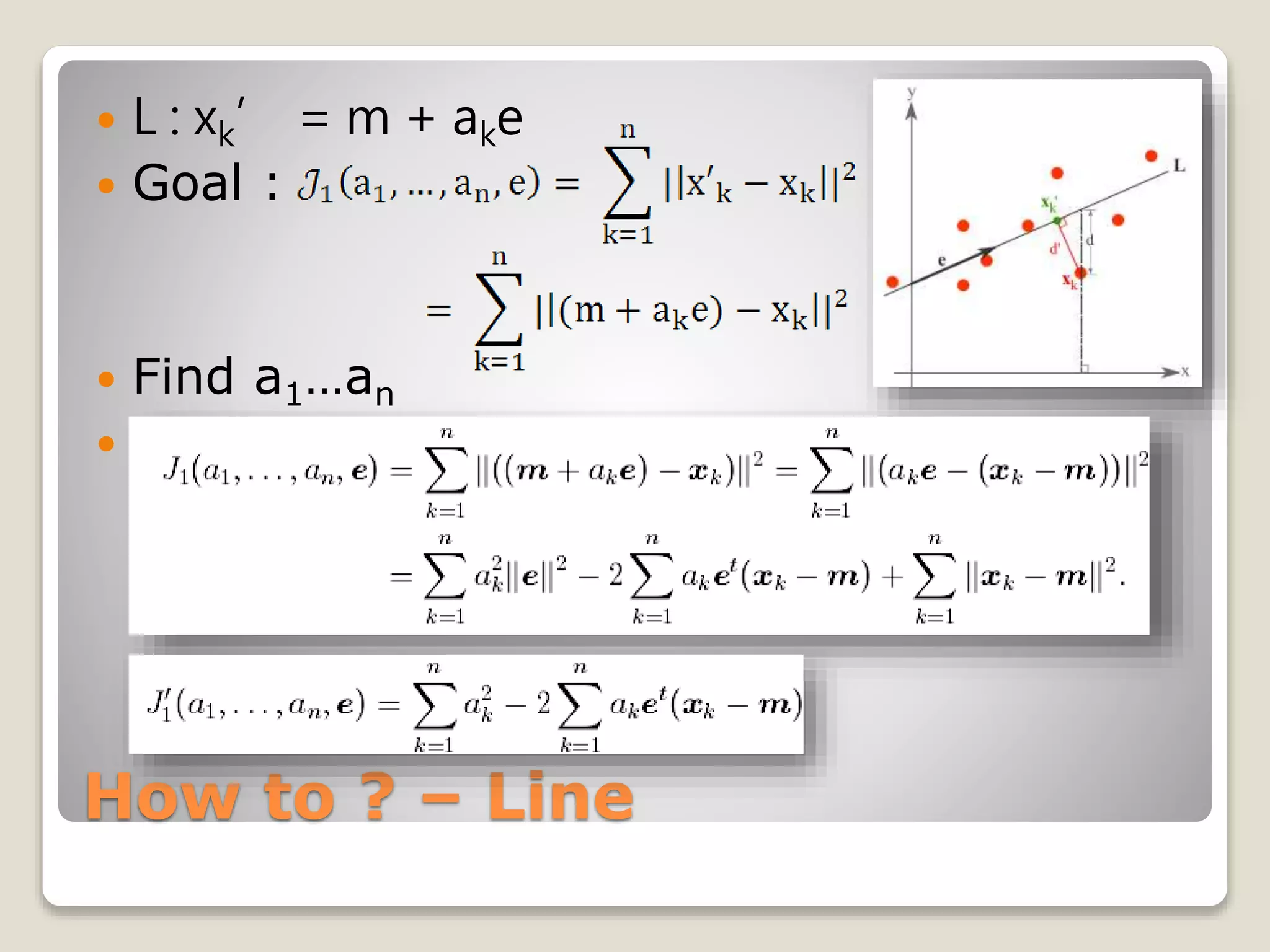
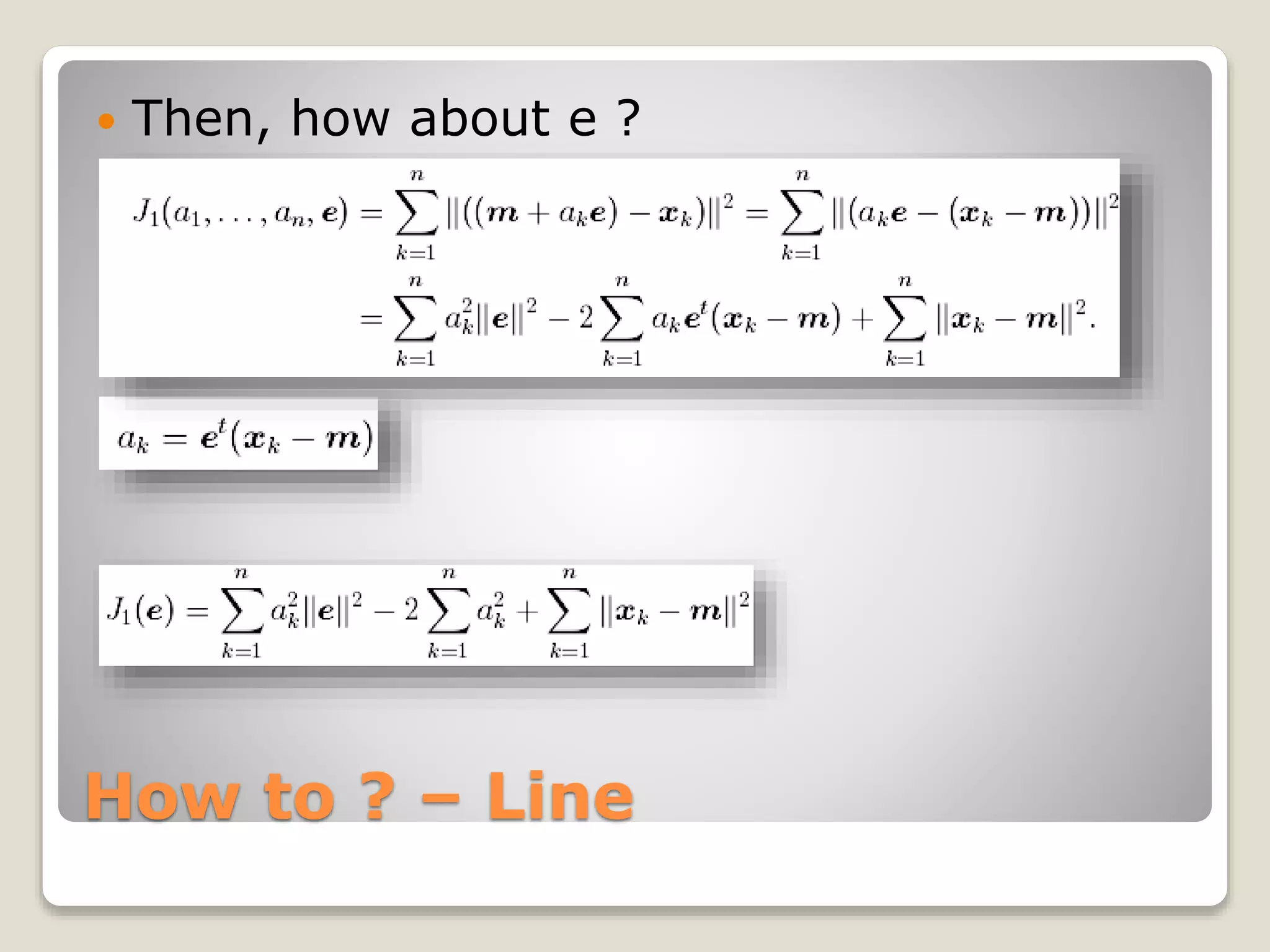
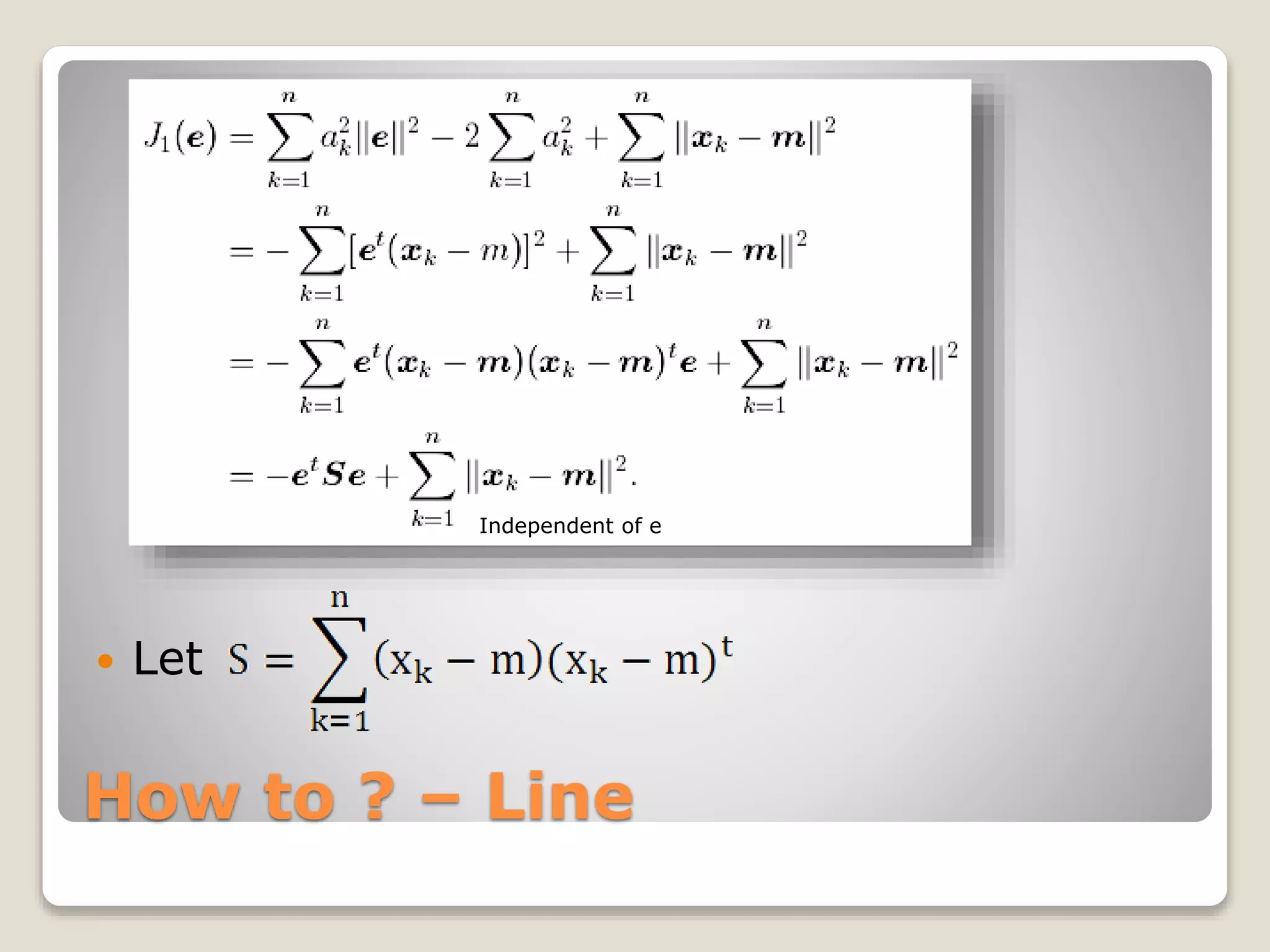
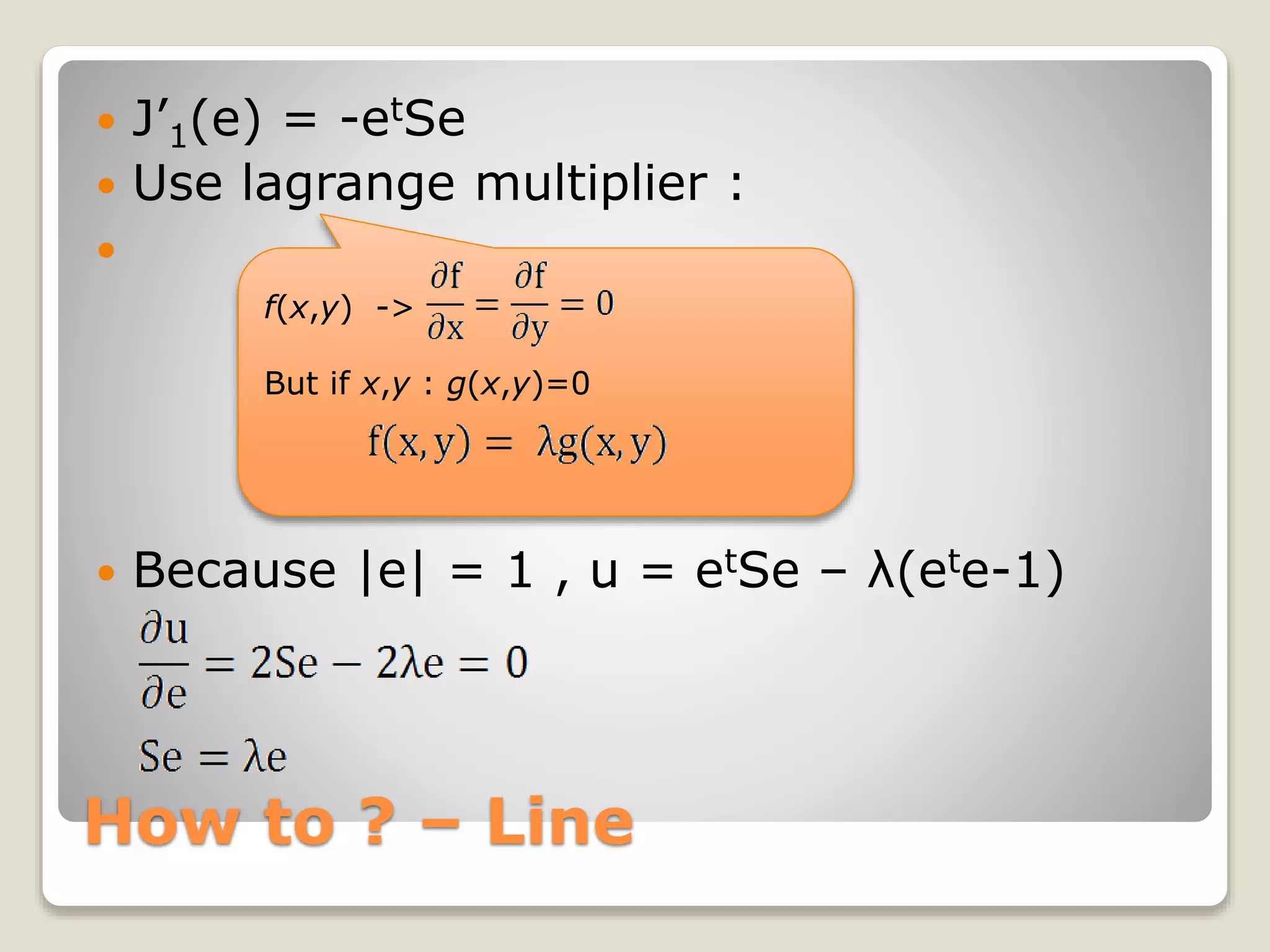
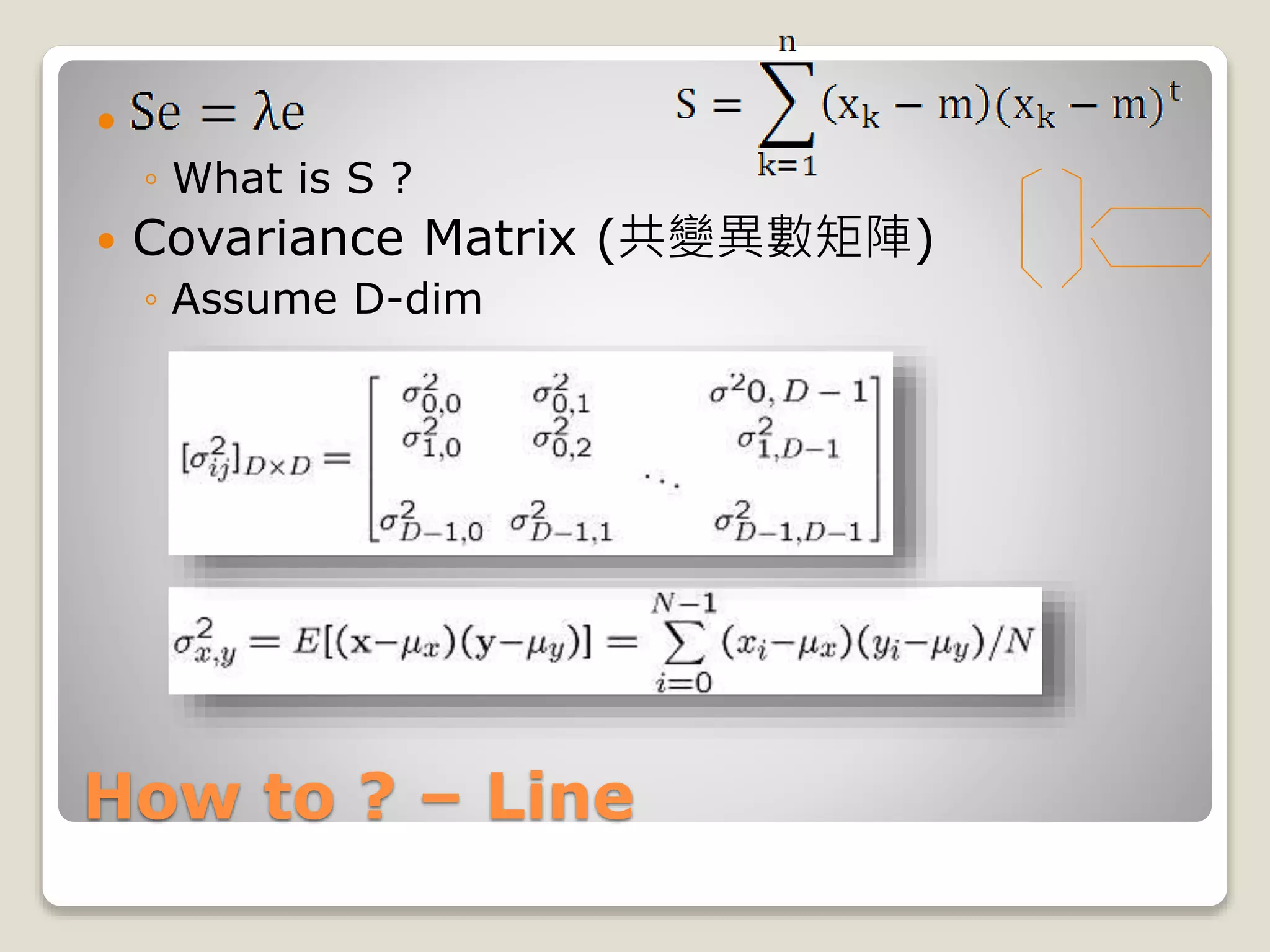
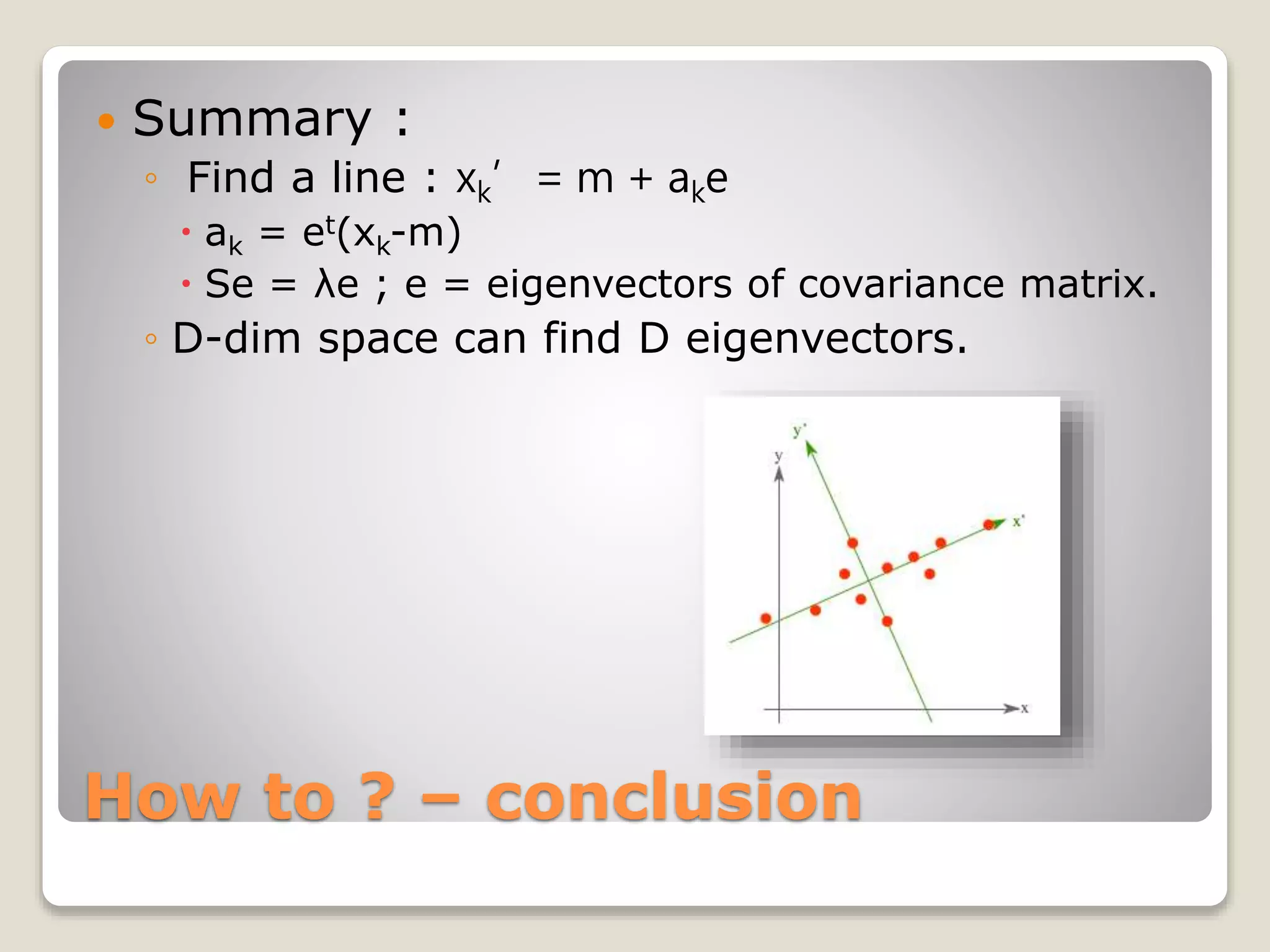
![How to ? – Line
每個部份微分後 [2ak – 2et(xk-m)]
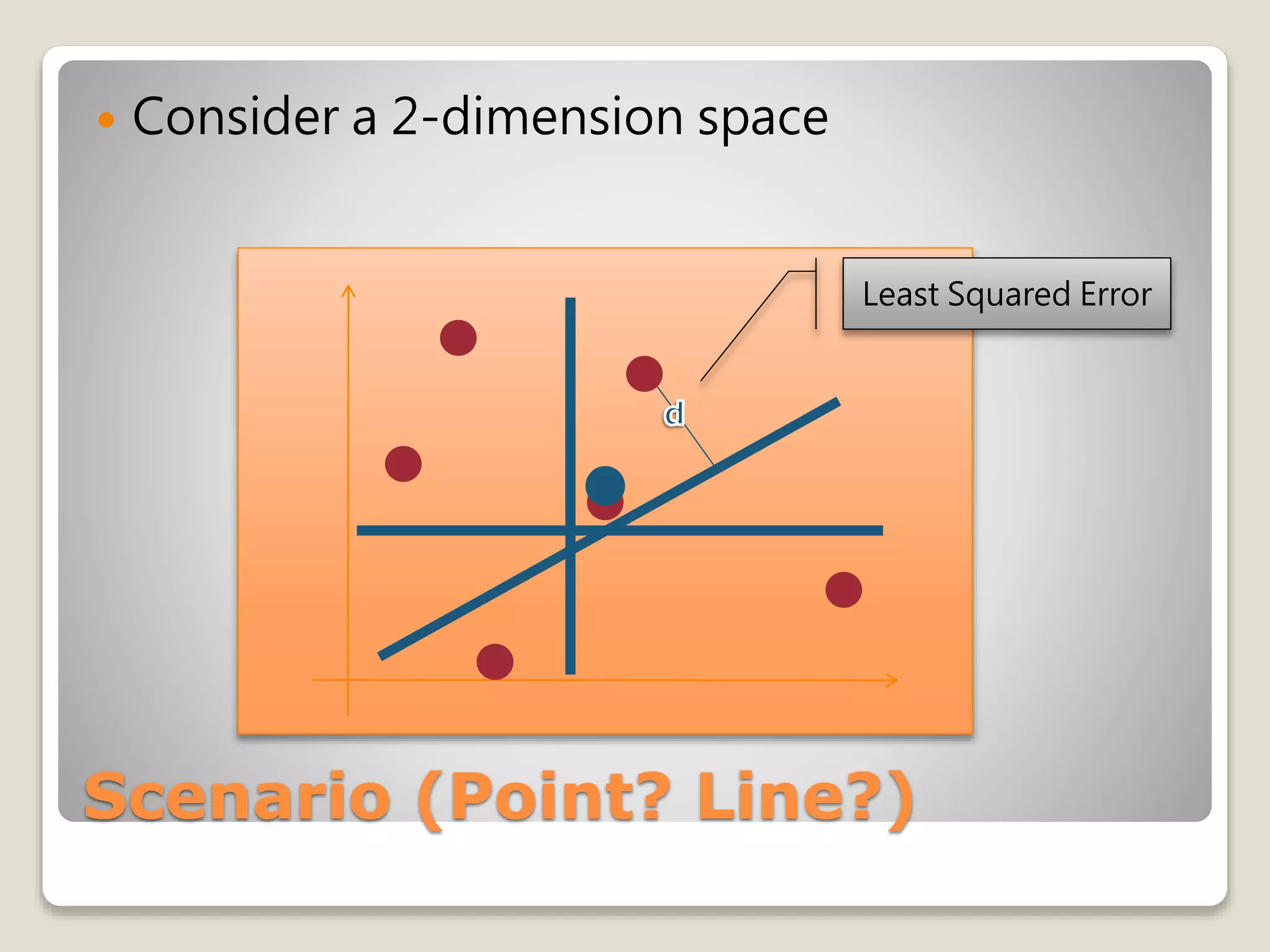
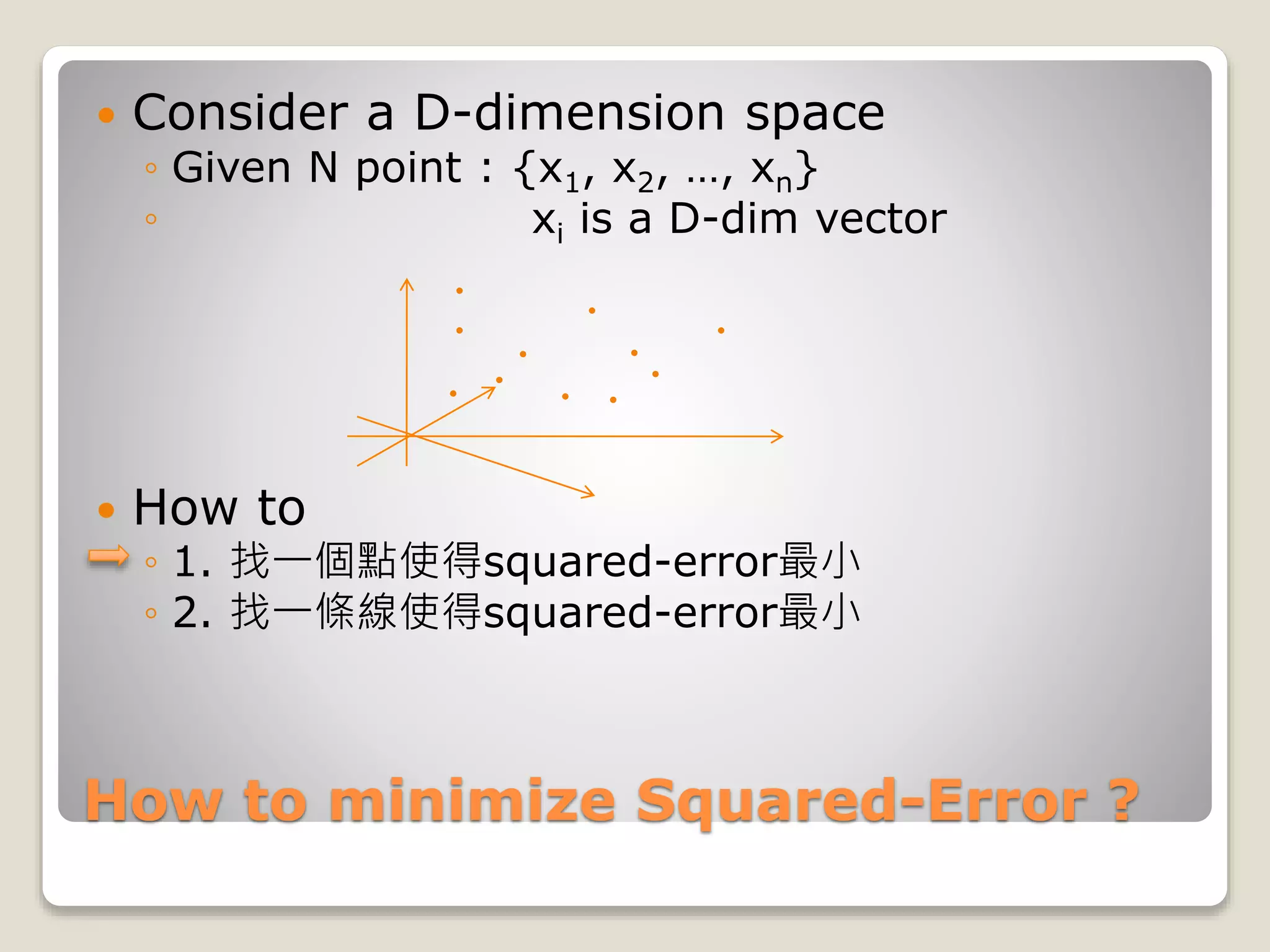
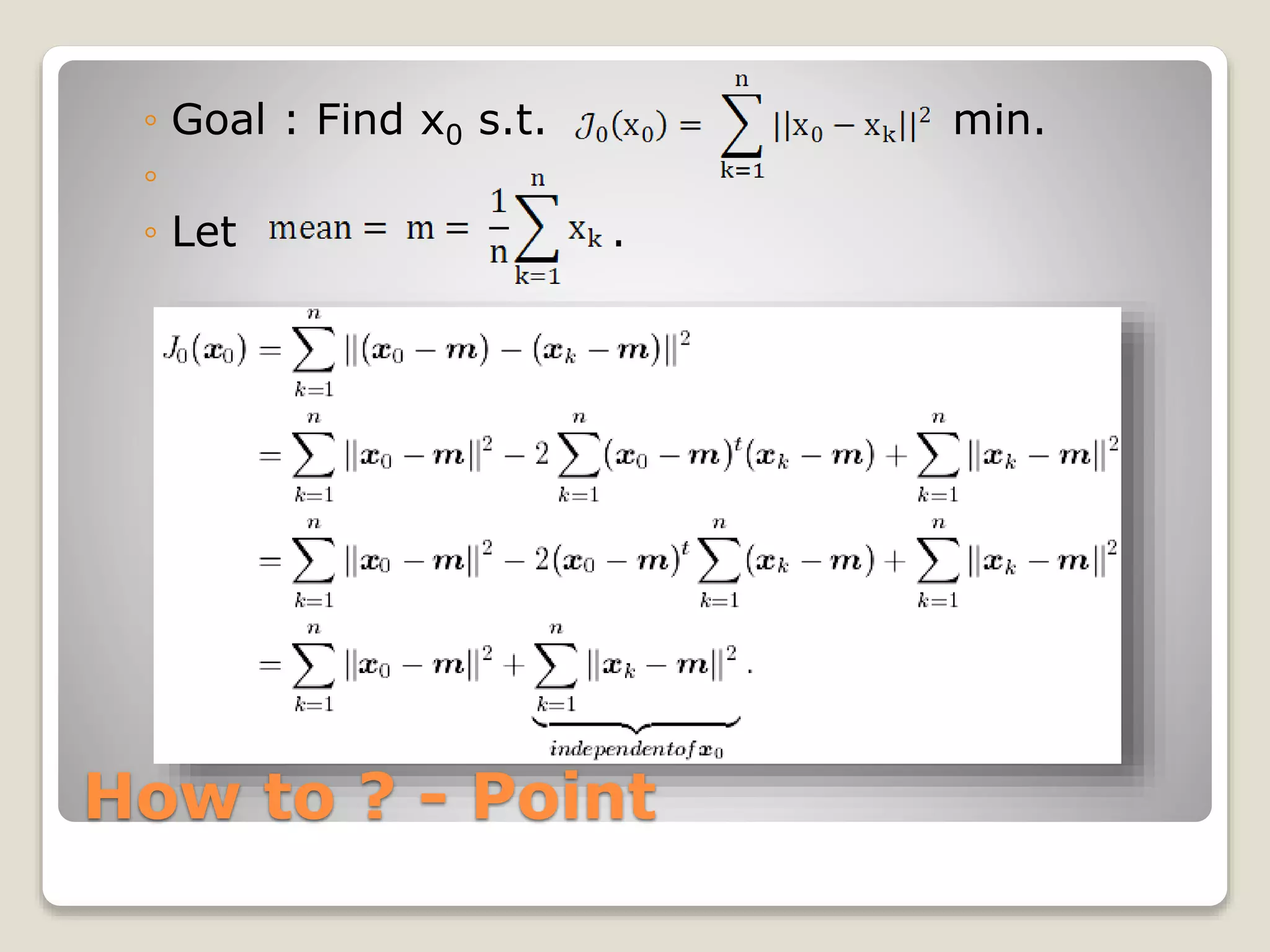
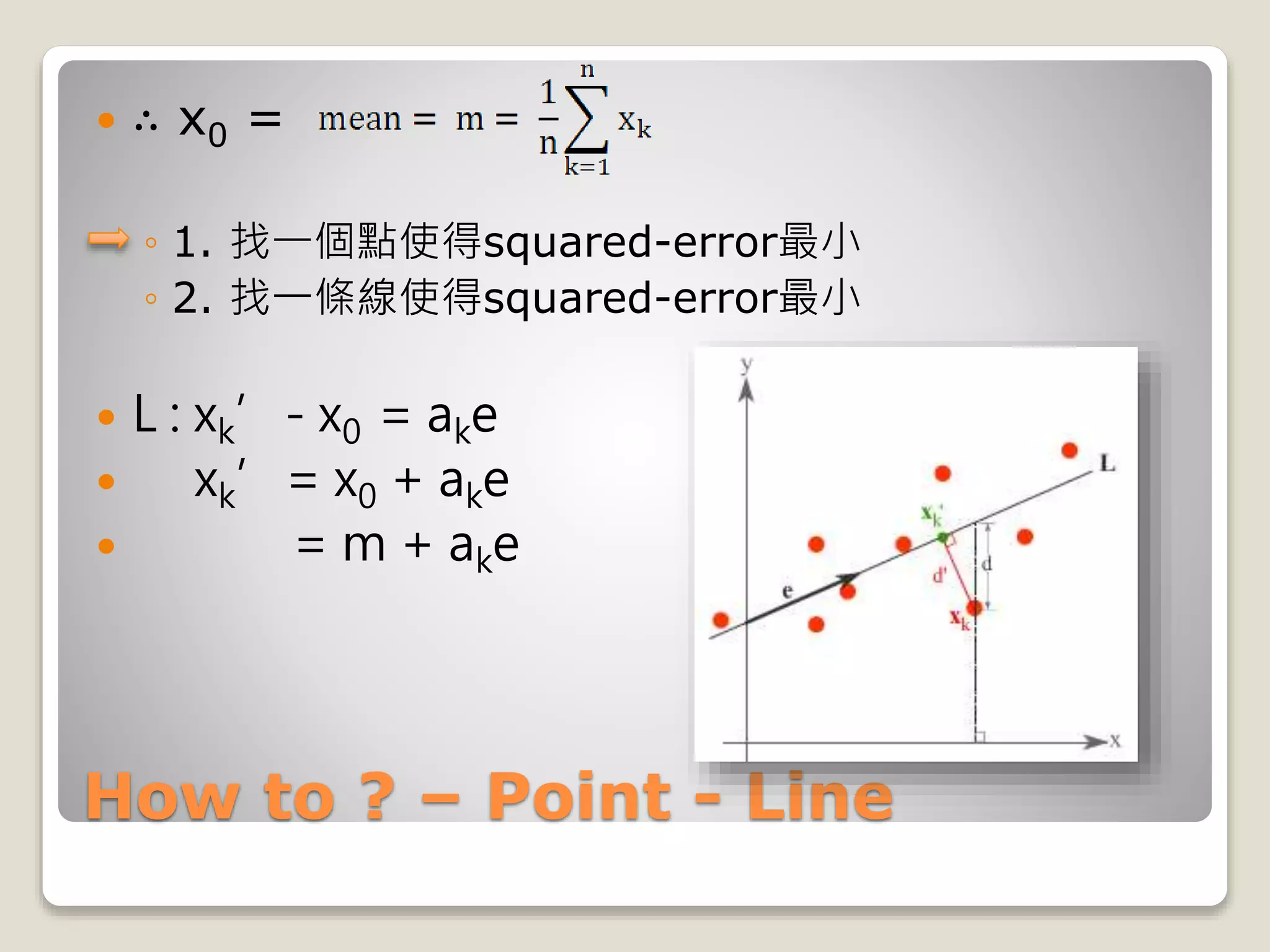
What does it mean ?
xk’ = m + ake](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090504irstudygroup-160501014836/75/PCA-Principal-component-analysis-Theory-and-Toolkits-12-2048.jpg)



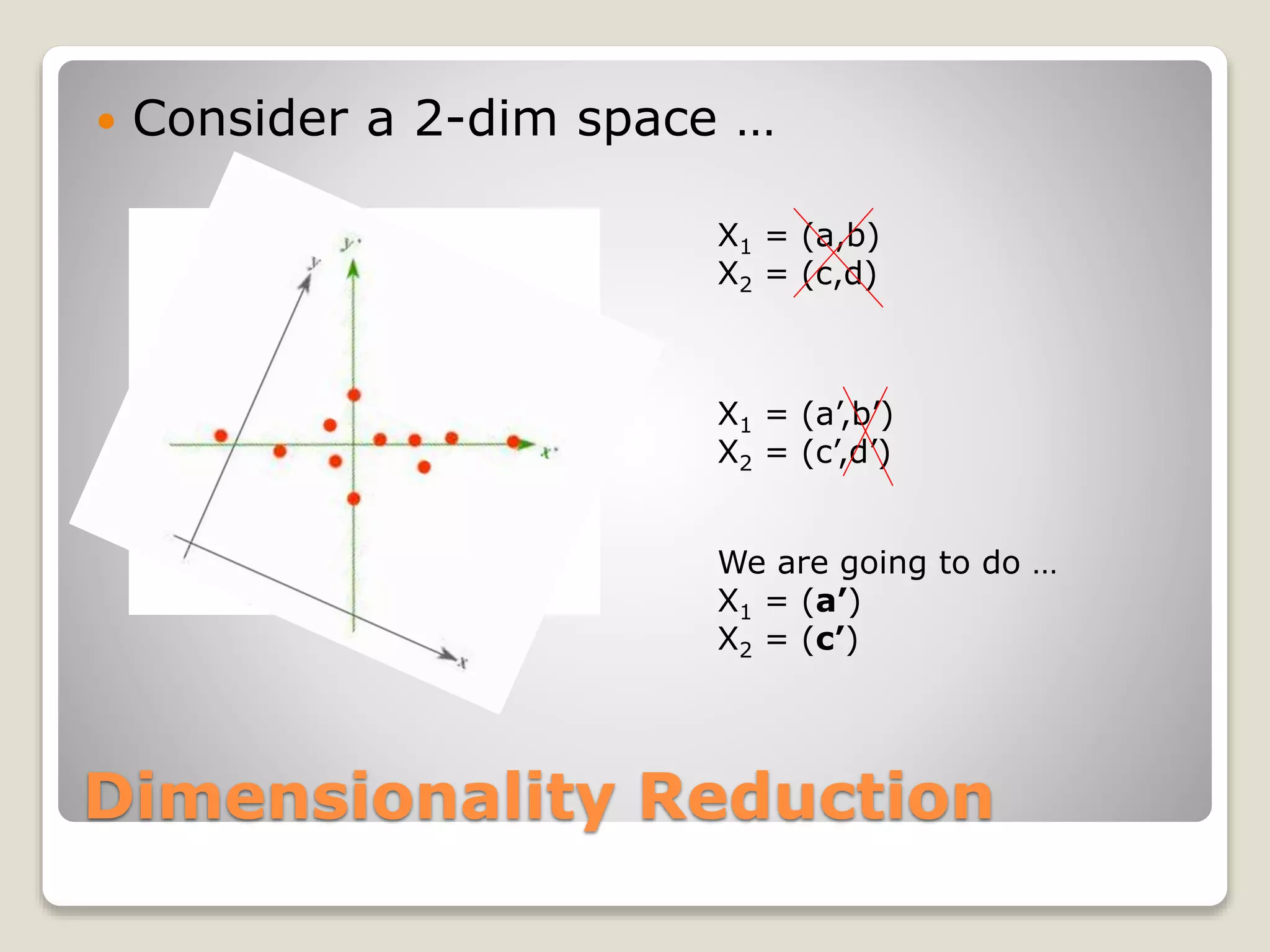
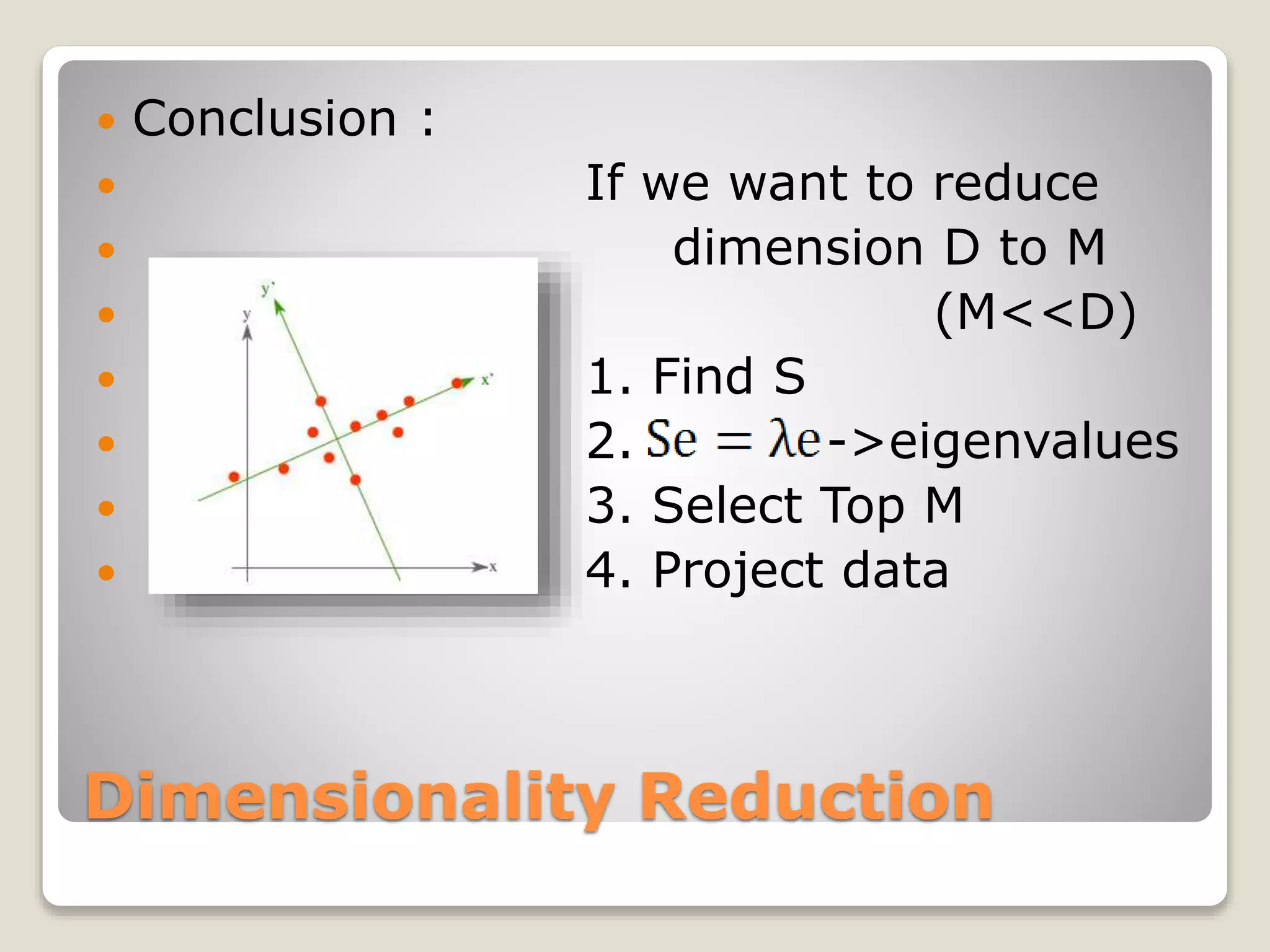
![Dimensionality Reduction
We want to proof :
◦ Axes of the data are independent.
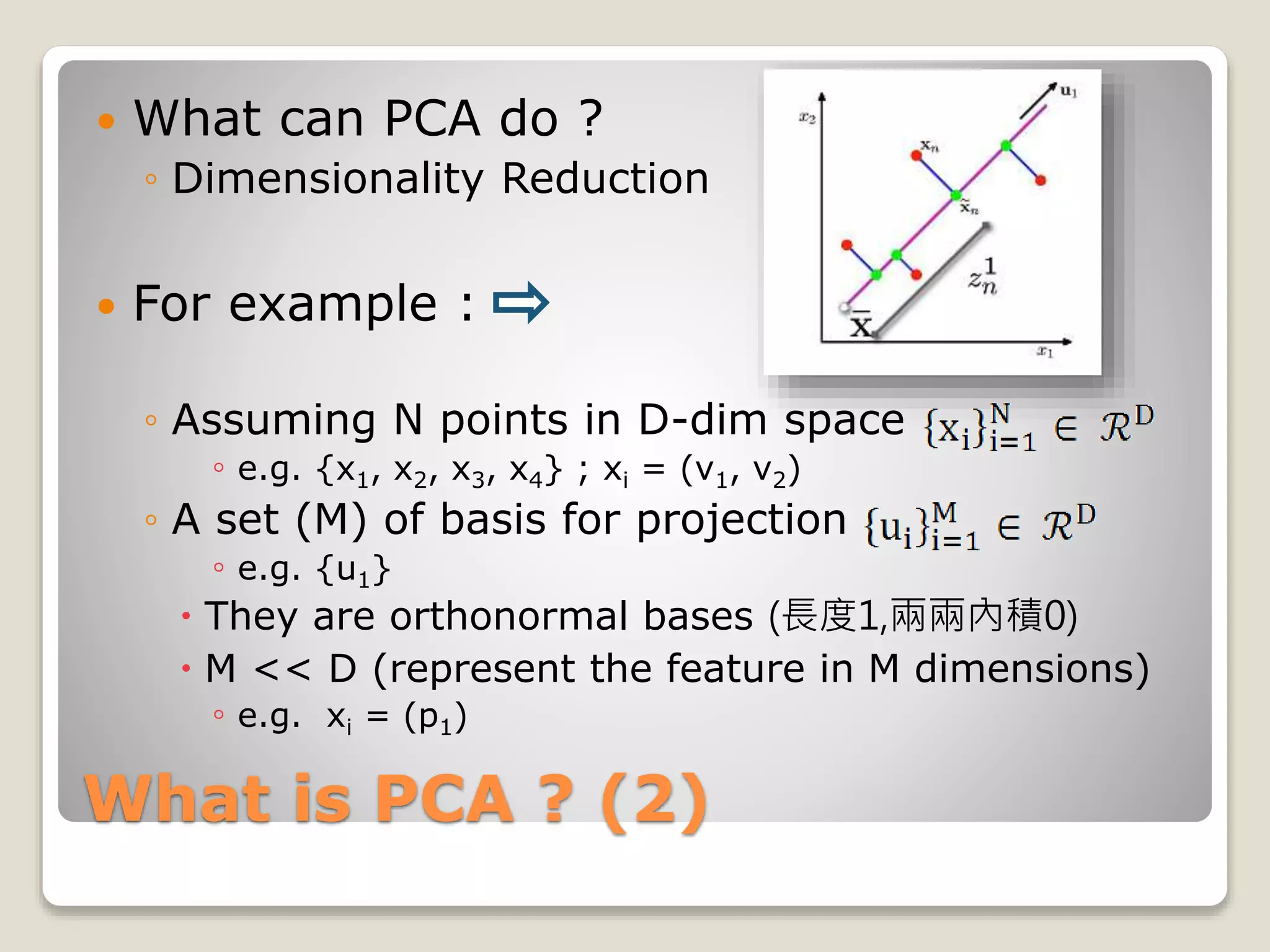
Consider N m-dim vectors
◦ {x1, x2, … ,xn}
◦ Let X=[x1-m x2-m … xn-m]T m = mean
◦ Let E = [e1 e2 … em]
Se = λe
eigen decomposition Eigen vector {e1,…,em}
Eigen value {λ1,…, λm}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090504irstudygroup-160501014836/75/PCA-Principal-component-analysis-Theory-and-Toolkits-22-2048.jpg)
![Dimensionality Reduction
SE = [Se1 Se2 … Sem]
= [λe1 λe2 … λem]
=
= ED
S = EDE-1
E = [e1 e2 … em]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090504irstudygroup-160501014836/75/PCA-Principal-component-analysis-Theory-and-Toolkits-23-2048.jpg)
![Dimensionality Reduction
We want to know new Covariance Matrix
of projected vectors.
Let Y = [y1 y2 … yn]T
E = [e1 e2 … em]
Y = ETX
SY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090504irstudygroup-160501014836/75/PCA-Principal-component-analysis-Theory-and-Toolkits-24-2048.jpg)