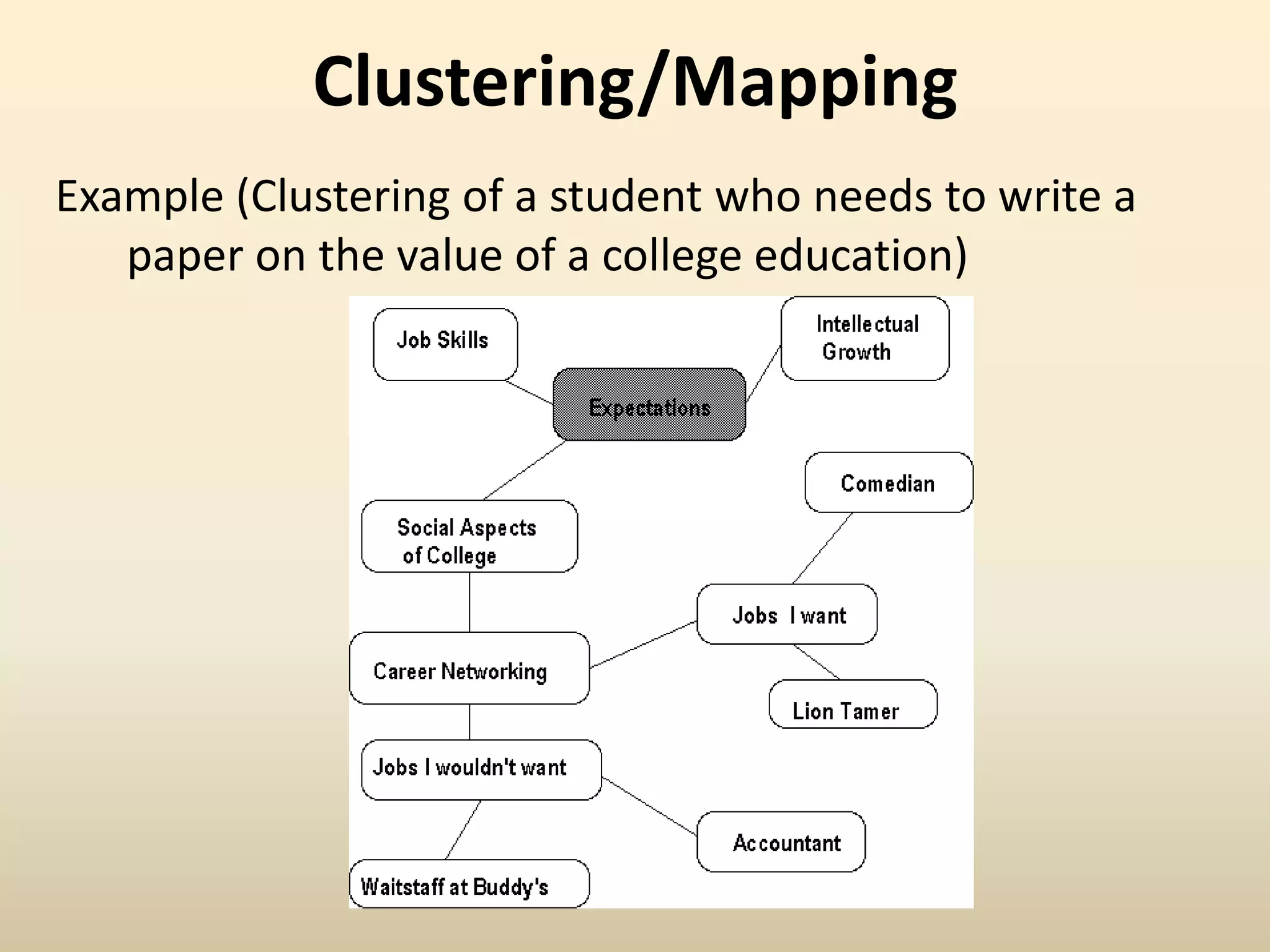
This document discusses pre-writing strategies, which are techniques used in the initial stage of the writing process to generate and organize ideas before writing a draft. It describes four common pre-writing strategies: freewriting, brainstorming/listing, clustering/mapping, and journalistic questions. Examples are provided to illustrate how each strategy can be applied to develop ideas for a paper about the environment.