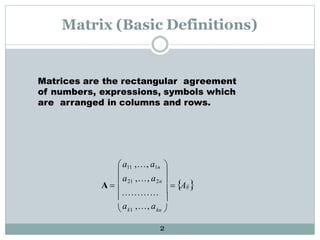
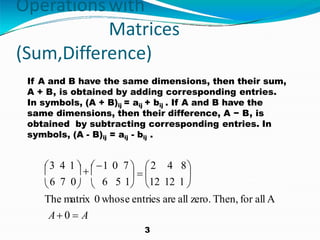
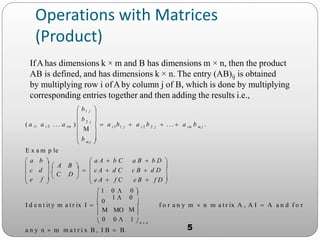
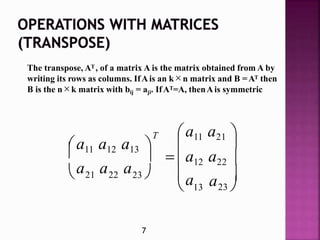
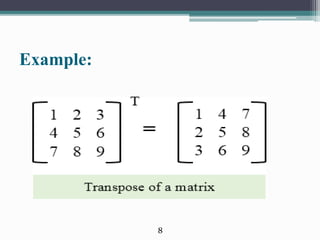
The document presents information on matrices and their applications. It defines what a matrix is as a rectangular arrangement of numbers and expressions in rows and columns. It discusses various operations that can be performed on matrices, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and finding the transpose. Examples are provided to illustrate these operations. The document also lists some fields where matrices are applied, such as geology, statistics, economics, and animation. It provides examples of how matrices are used in tasks like seismic surveys, data analysis, calculating GDP, and 3D animation.