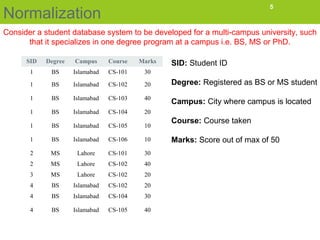
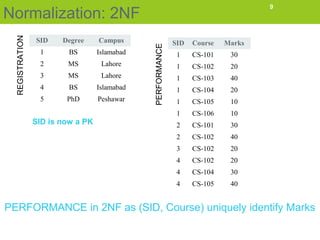
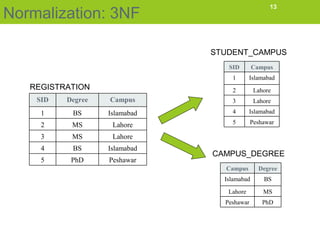
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to eliminate redundancy and ensure data dependencies make sense. The goals are to eliminate storing the same data in multiple tables and only storing related data together. Normalization results in breaking tables into smaller tables and relating them through their primary keys. There are three common normal forms - 1st normal form (1NF), 2nd normal form (2NF), and 3rd normal form (3NF). The document describes transforming a student database from 1NF to 2NF to 3NF to eliminate anomalies like inconsistent changes if data is updated or deleted.