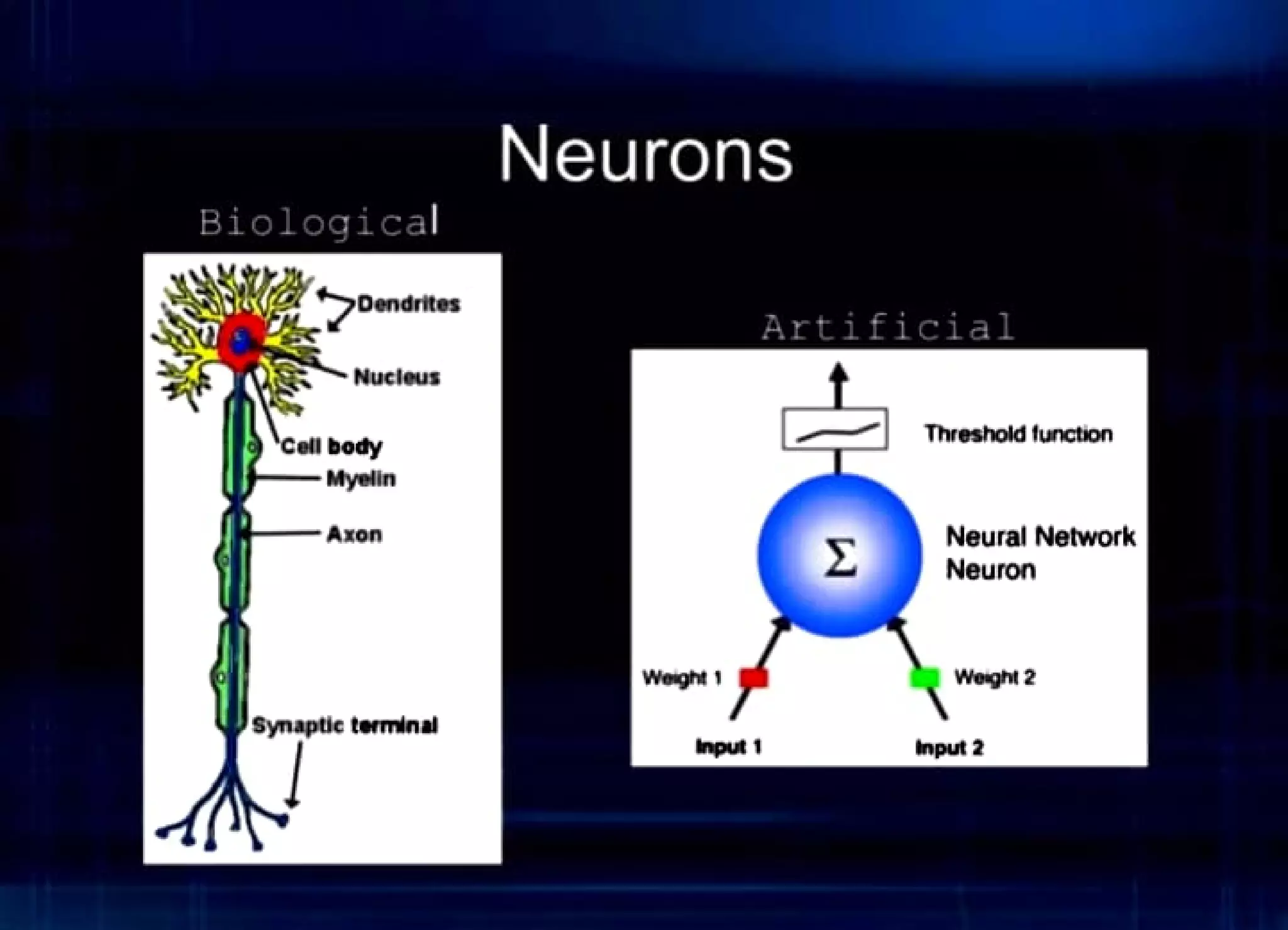
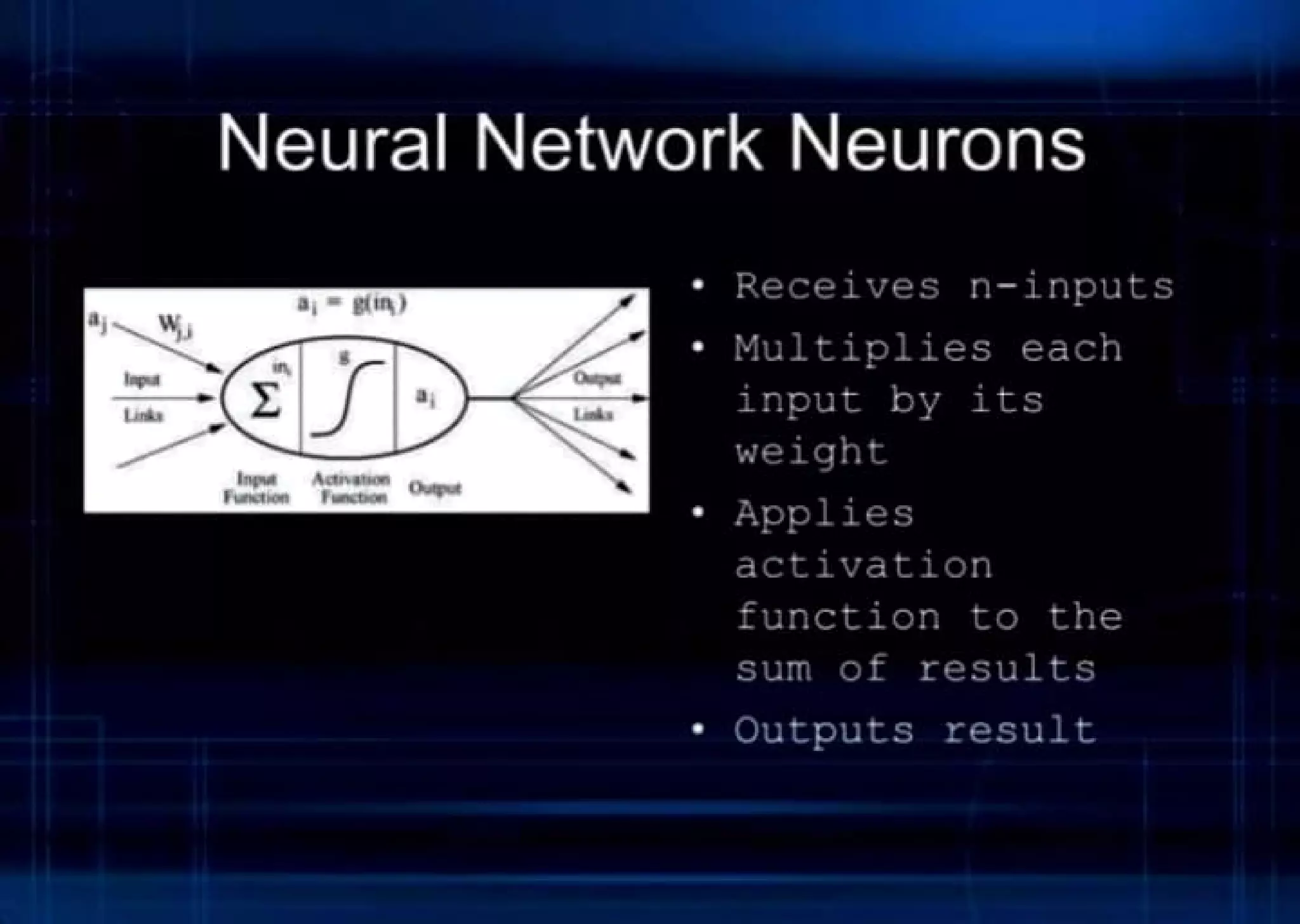
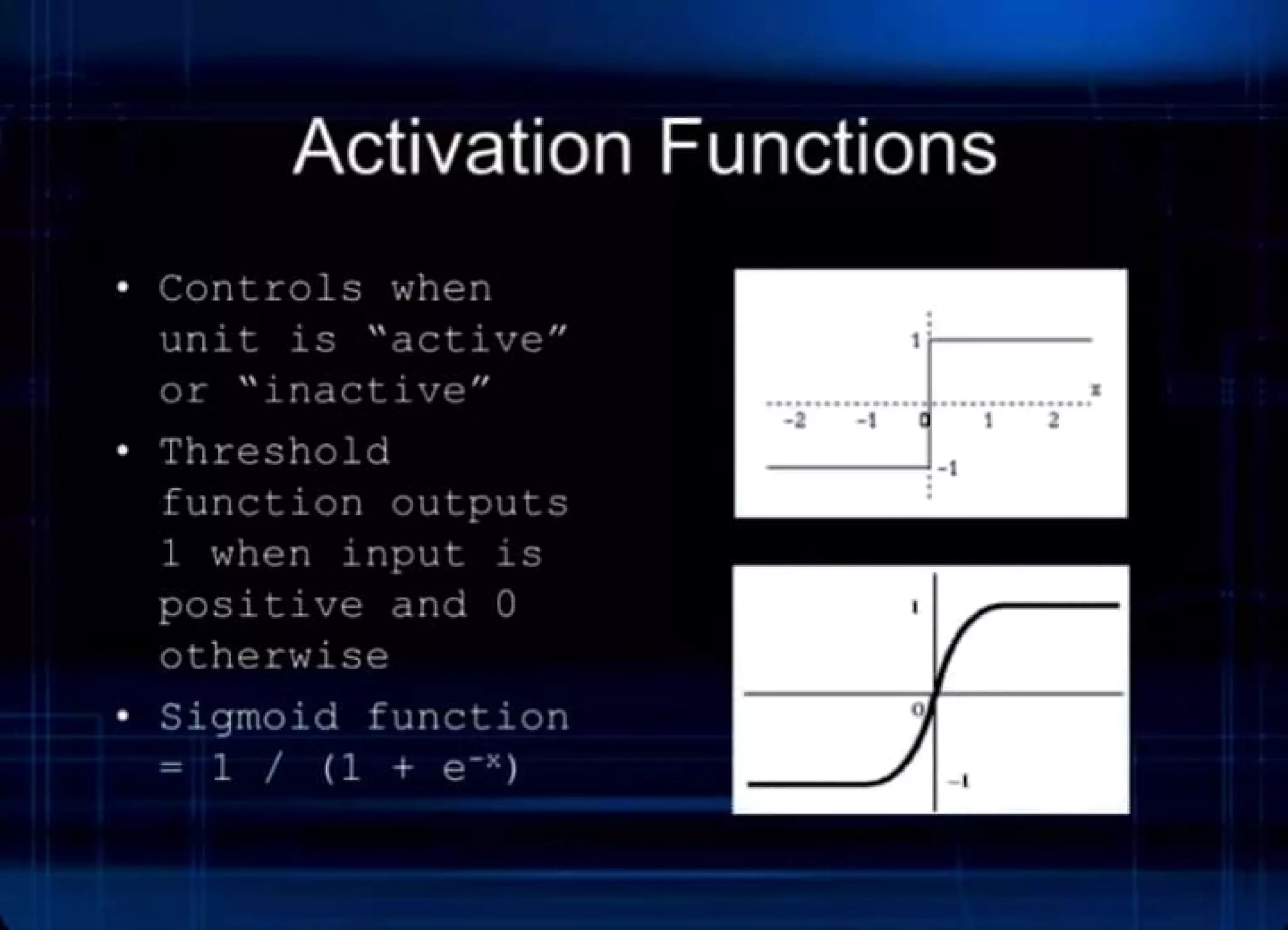
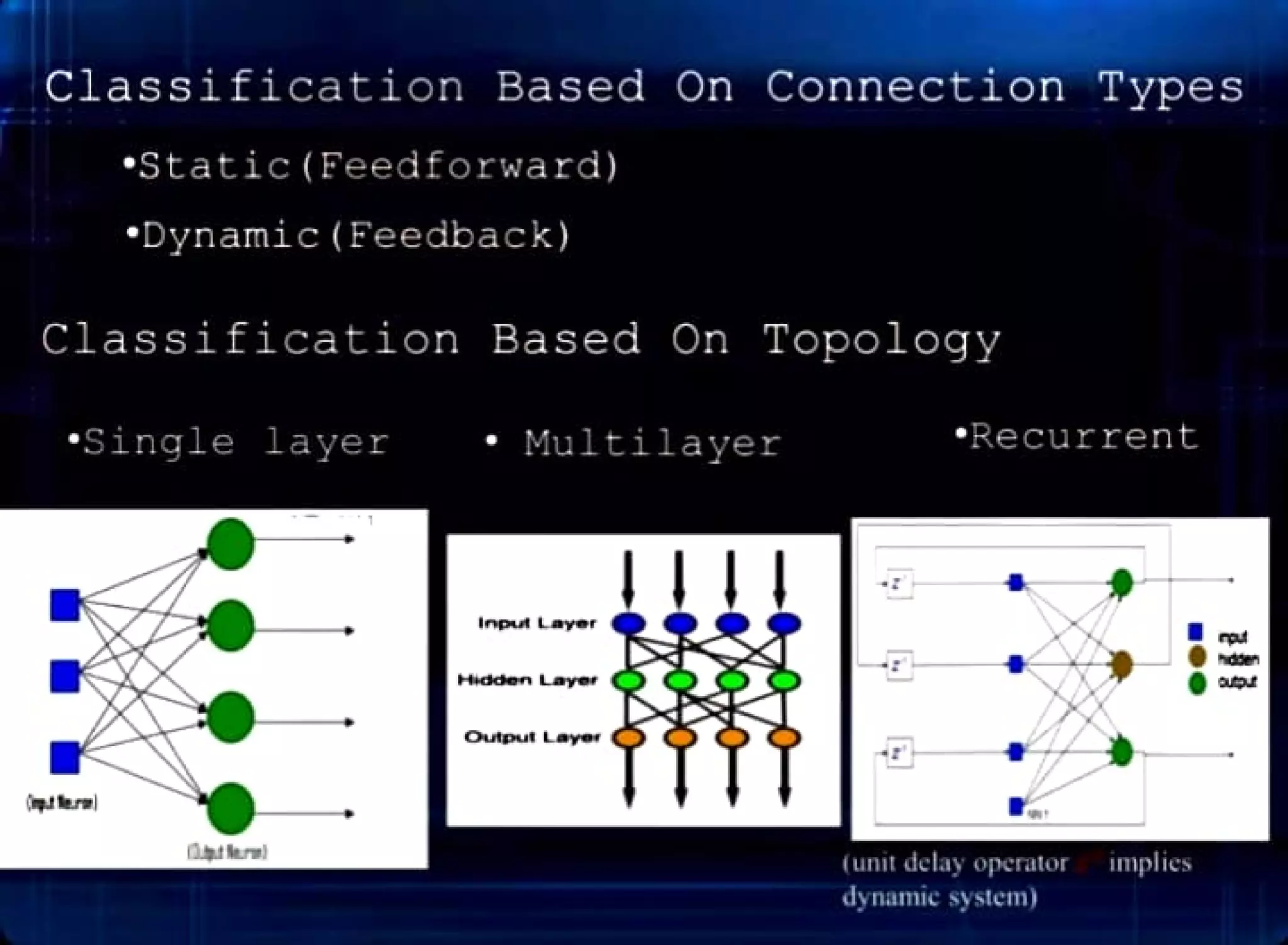
This document provides an introduction to neural networks, including:
- An overview of neurons and how they are connected in a neural network.
- The main types of neural networks including feedforward, feedback, single layer, and multilayer networks.
- How neural networks learn through supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning methods.
- Common applications of neural networks like pattern recognition, control systems, and forecasting.
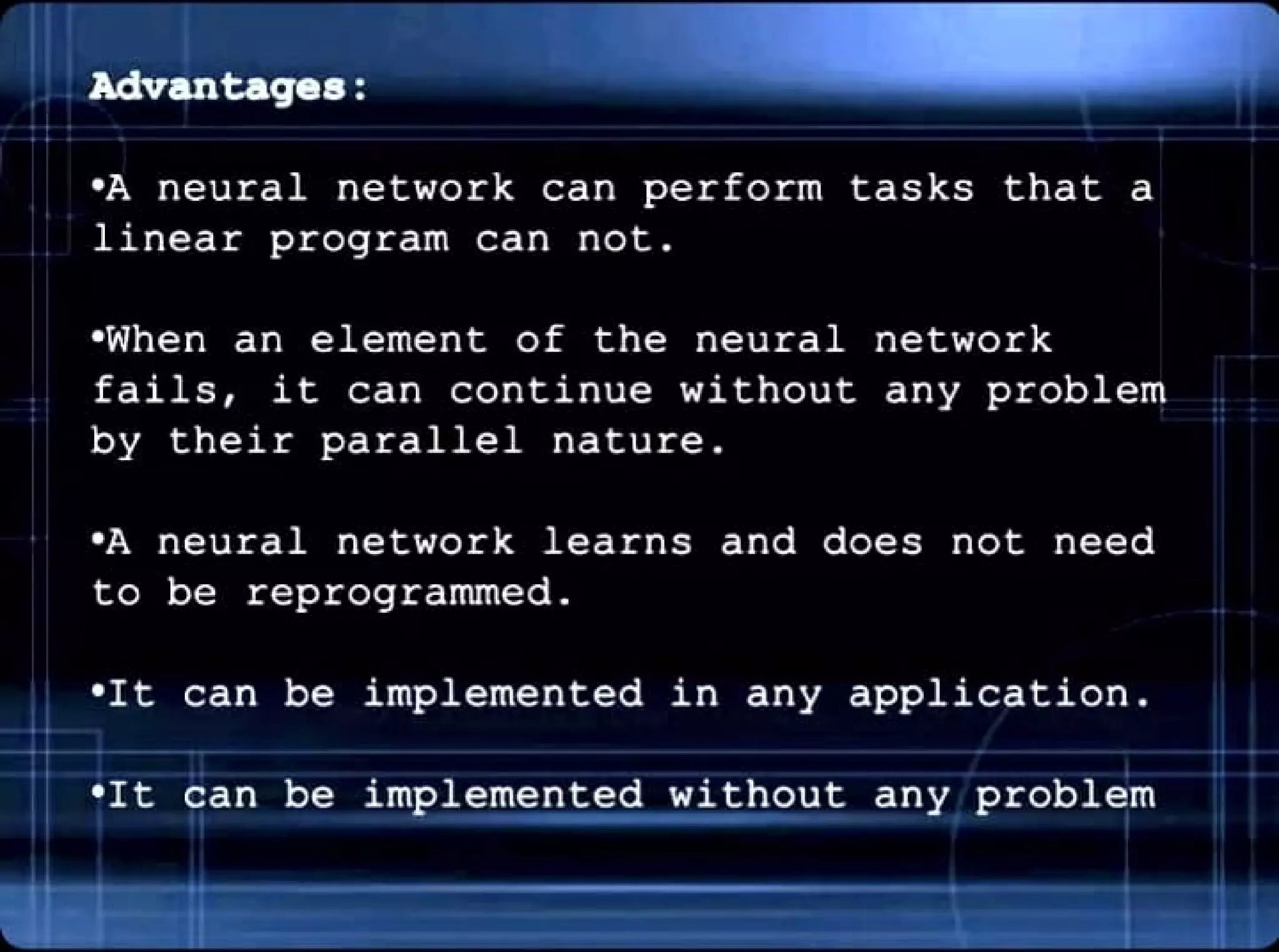
- The advantages of neural networks in tasks linear programs cannot do and their ability to learn without reprogramming. Disadvantages include the need for training and high processing requirements for large networks.