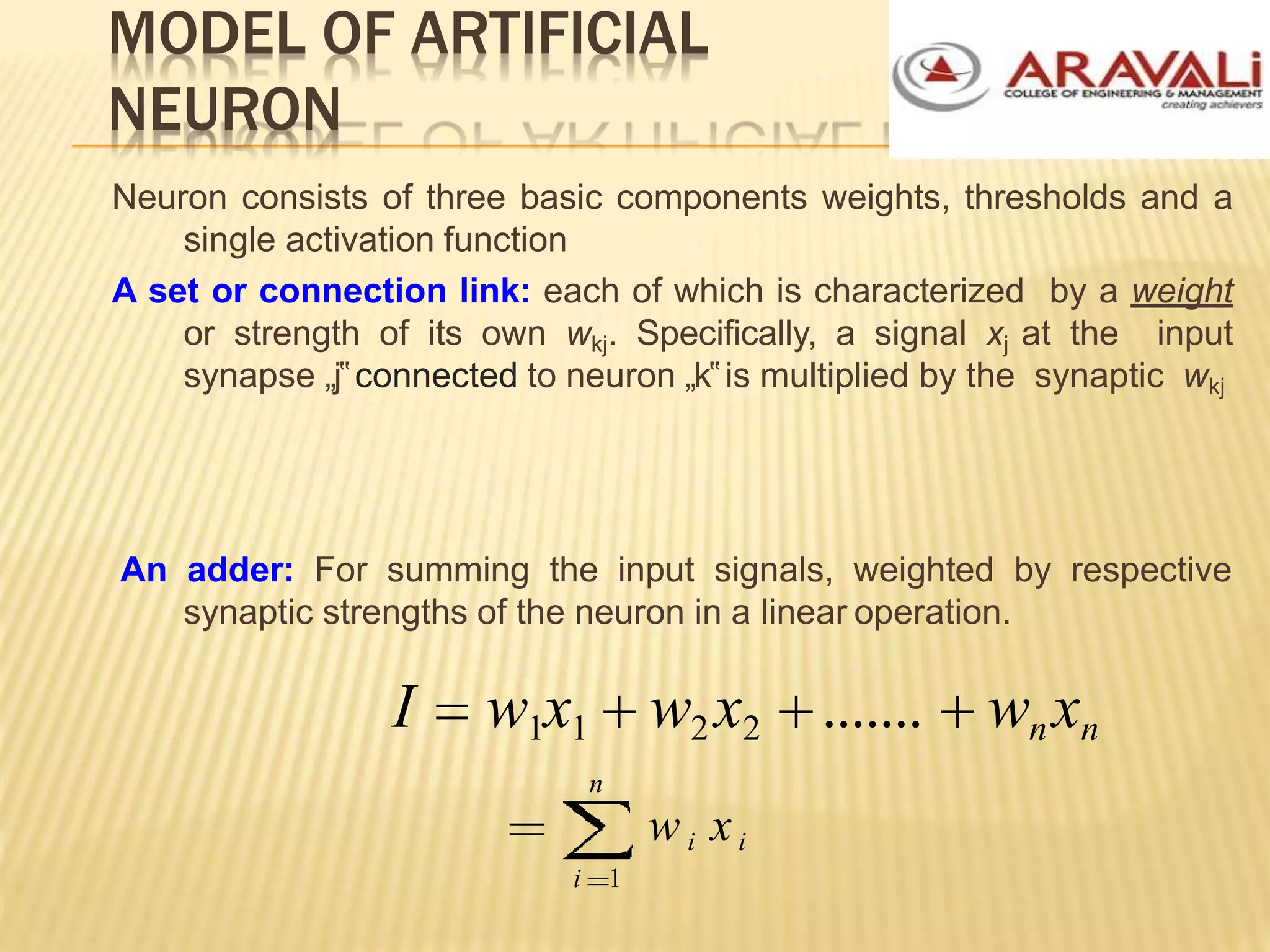
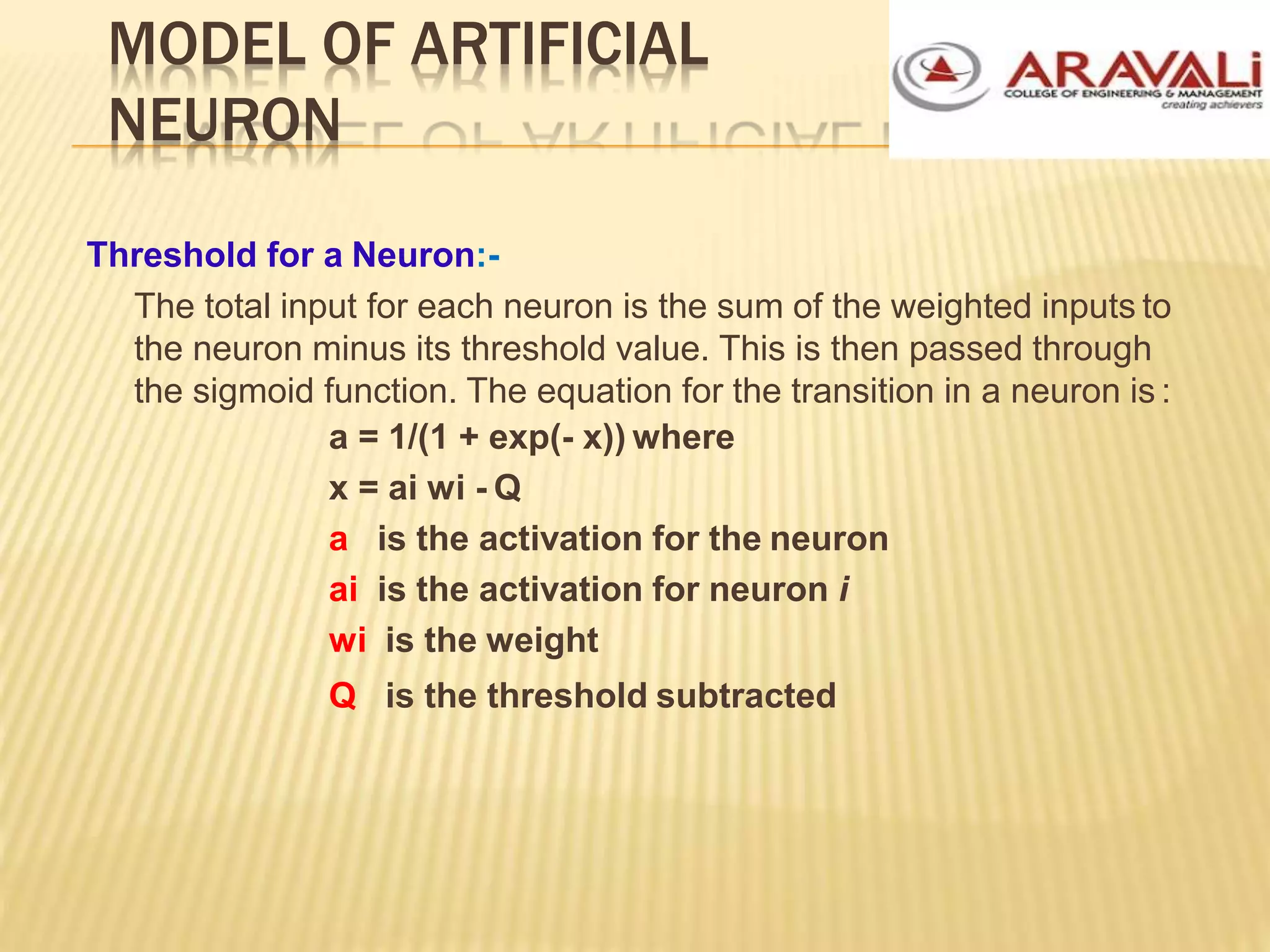
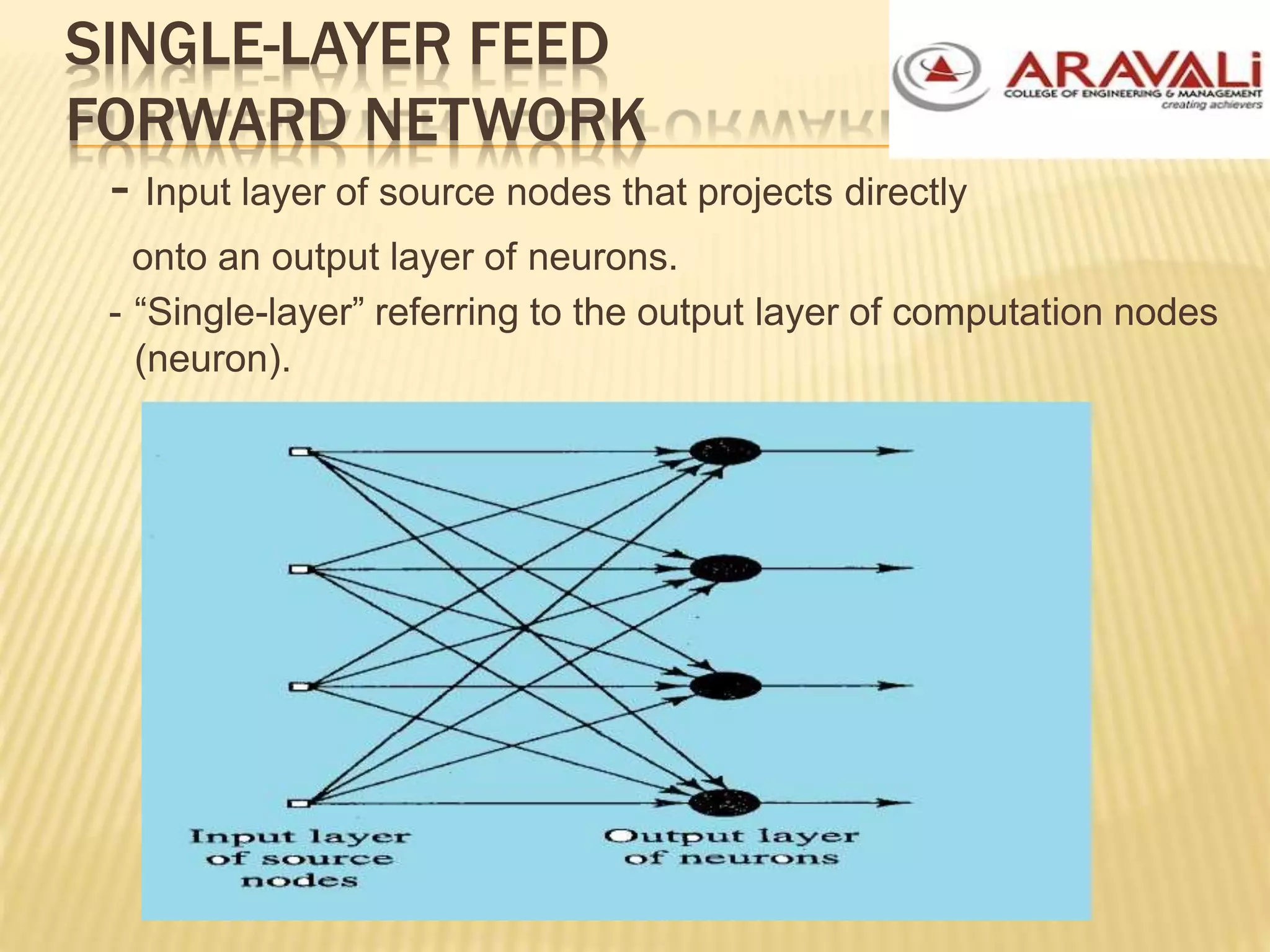
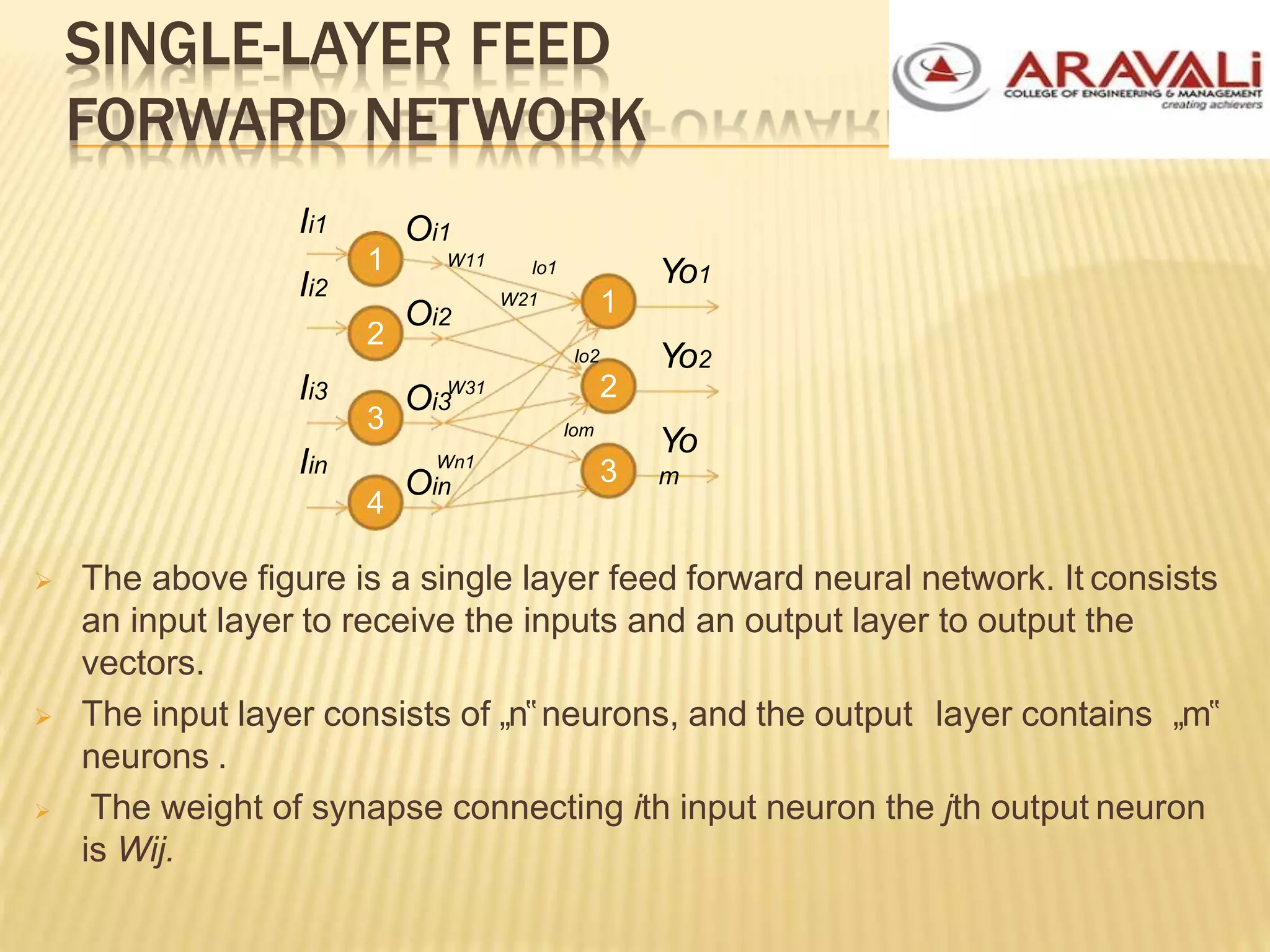
The B.Tech CSE course on machine learning and neural networks covers foundational concepts including artificial neural networks, neuron models, network architectures, and learning methods. It elaborates on the structure of neural networks, activation functions, and various learning techniques such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Additionally, the document discusses real-world applications of neural networks, including character recognition, image compression, and stock market predictions.