This document discusses comminution mechanisms, which are the ways that particles fracture during size reduction processes. It describes four main mechanisms: shatter (impact fracture), cleavage, attrition, and abrasion. Shatter occurs via high-speed impacts and produces a broad size distribution. Cleavage happens under lower compression and yields a narrower size range. Attrition is particle wear during interactions like grinding. The document explains the factors that influence fracture, such as flaws and applied stress. It also reviews theories of how energy relates to breakage. The goal is to understand particle fracture to improve efficiency of comminution equipment and processes.


![Introduction
• Why comminution?
………..
To create particles in a certain size and
shape
…….…
To increase the surface area available for
next process
………..
To liberate valuable minerals held within
particles[2]
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-3-2048.jpg)
![Introduction
• Grinding and crushing usually account for more than 30
to 50% of the total power used in the concentration
process, but this can rise as high as 70% for hard finely
dispersed and intergrown ores.[1] but about 5 % of all
electricity generated is used in size reduction[2]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-4-2048.jpg)
![Introduction
• Where this 'lost' energy is consumed ?
1. Deforming the particle to its elastic limit
2. Compacting particles after fracture
3. Overcoming friction between particles
4. Elastically deforming milling surfaces
5. Deformation of fractured particles
This energy is dissipated as heat.[4]
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-5-2048.jpg)
![Introduction
• Aim:
• The general goal of the project Mechanisms of
comminution is to enhance understanding of particle
breakage, which shall lead to improved comminution
systems and more efficient utilization of energy for size
reduction and mineral liberation.[3]
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-6-2048.jpg)
![Comminution Theory
• In the crystalline lattice of minerals, these inter-atomic bonds are
effective only over small distances, and can be broken if extended by
a tensile stress. [5]
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-7-2048.jpg)
![Comminution Theory
• The relationship between energy and breakage may be
expressed in the equation:
dE= -K.dx/dxn
• Rittinger: the new surface area produced proportional
to the energy consumed [6]
n=1 E=K(1/x2 – 1/x1)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-8-2048.jpg)
![Comminution Theory
Kick: the same relative reduction in volume is obtained
for constant energy input per unit mass irrespective of the
original size.
n=2 E=K.ln(x1/x2)
Kick's law is reasonably accurate in the crushing range
above about 1 cm in diameter [6]
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-9-2048.jpg)
![Comminution Theory
• Bond: the work input is proportional to the new crack
tip length produced in particle breakage.
n=1.5 E= 2K(1/√x2 -√x1)
• Avilable in the range of conventional rod-mill and ball-
mill grinding.[6]
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-10-2048.jpg)
![Comminution Theory
[8]
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-11-2048.jpg)
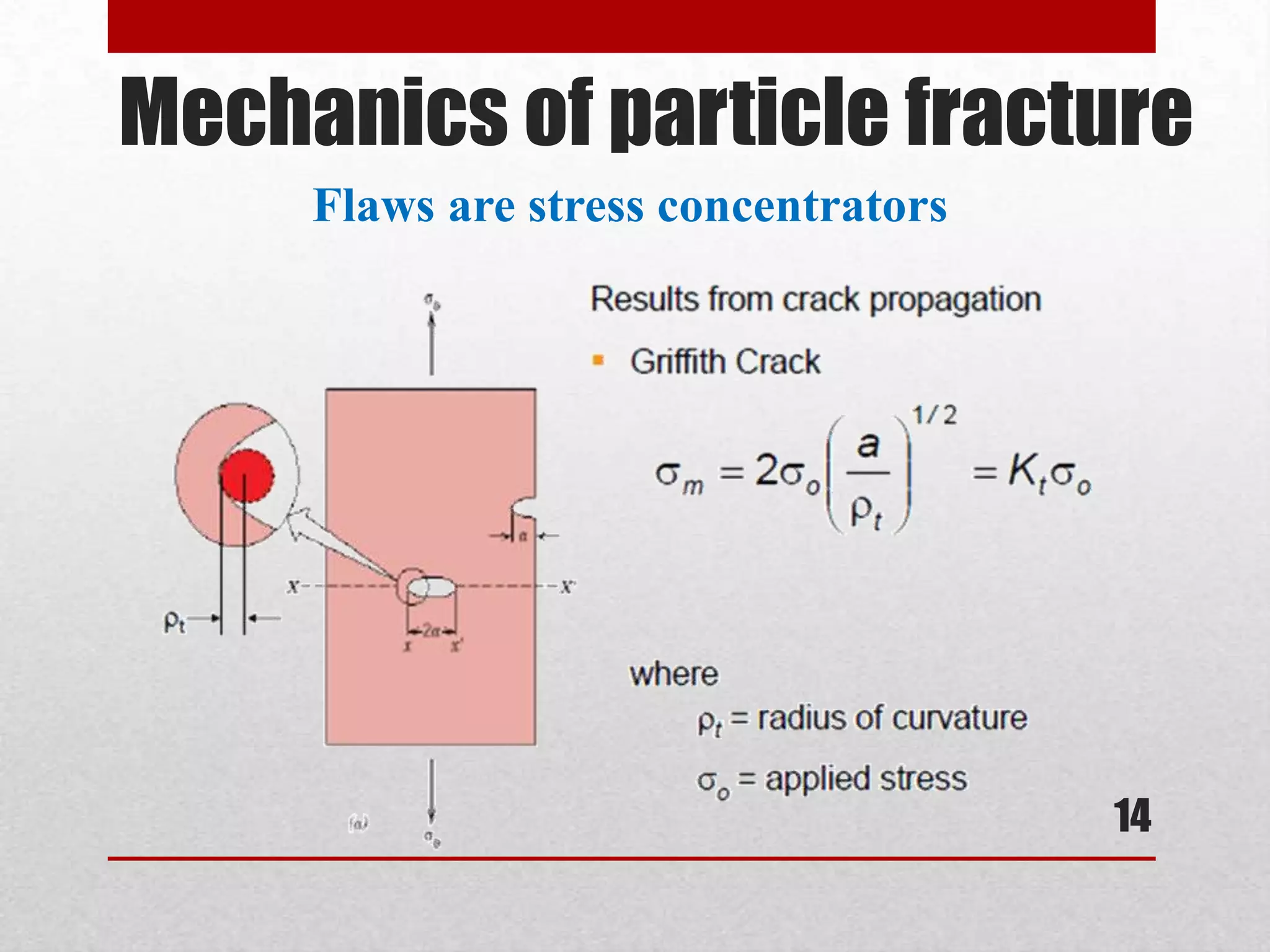
![Mechanics of particle fracture
Flaws are stress concentrators [9]
• Even when rocks are uniformly loaded, the internal stresses are not
evenly distributed[5]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-12-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture
• Griffith showed that materials fail by crack propagation
when this is energetically feasible.[5]
• For crack to propagate:
Strain energy > surface energy created
Requires appropriate crack propagation mechanism[2]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-13-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture
Virtually no stress is
required to bring about
bond breakage, stress is
required to provide the
energy necessary for
crack propagation and
the consequent
production of new
surface. [7]
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-15-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture
• It should be noted that although it is not necessary to
provide enough energy to strain all bonds to the point of
breaking, more energy is required than that which is just
sufficient to provide the free energy of the new surfaces.
Because bonds away from the eventual fracture surfaces
also become strained, hence absorb energy.[7]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-16-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture
• Rumbf:
for smaller particles having fewer flaws, the applied
stress at which fracture occurs is greater.
Irrespective of the distribution and density of flaws, a
greater stress is required to fracture a smaller particle:
strain energy is proportional to volume so the amount of
energy available at a given stress condition decreases as
the particle size decreases.[7]
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-17-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture• The manner in which a particle fractures depends on (i)
the nature of the particle; and (ii) the manner in which the
fracture force is applied.[13]
• Grain boundary fracture: The fracture toughness for
grain boundary cracking is lower than that for random
plane intragranular cracking, because atoms are arranged
irregularly in the grain boundary region.
[12]
18
AB, showing regions of coincidence and non-coincidence
between atoms in the neighbouring grains](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-18-2048.jpg)
![Mechanics of particle fracture
19
• Interfacial fracture: Cracking along these interfaces will
occur preferentially whenever they are present. Like
sedimentary rocks and conglomerates.
• Interphase fracture: interphase fracture is defined as
cracking along the boundary between two different
crystalline phases. [12]
Bonding across the boundary between the different
phases is stronger than that for interfacial boundaries
but not as strong as that across grain boundaries in the
pure, single-phase mineral. [12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-19-2048.jpg)
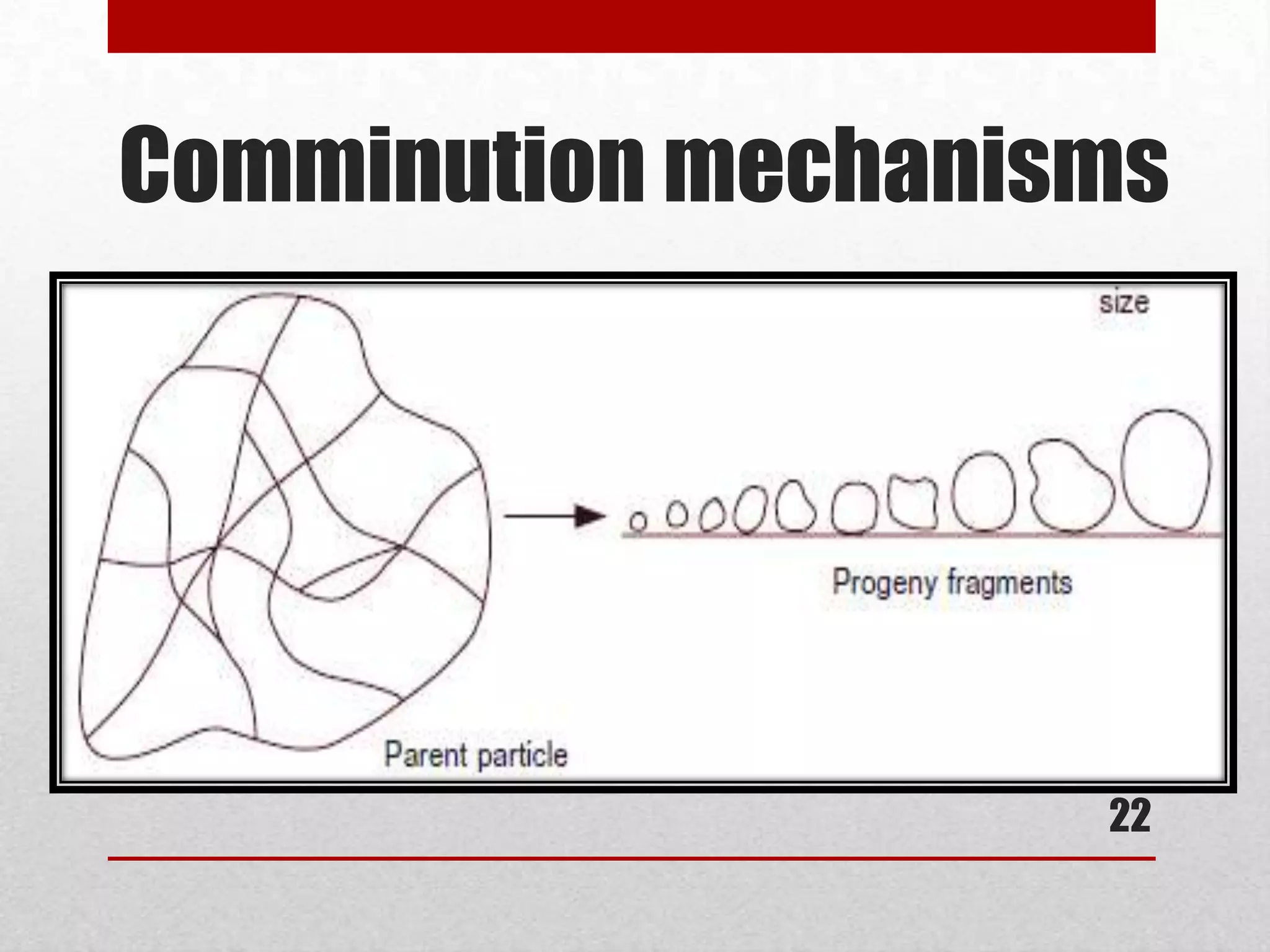
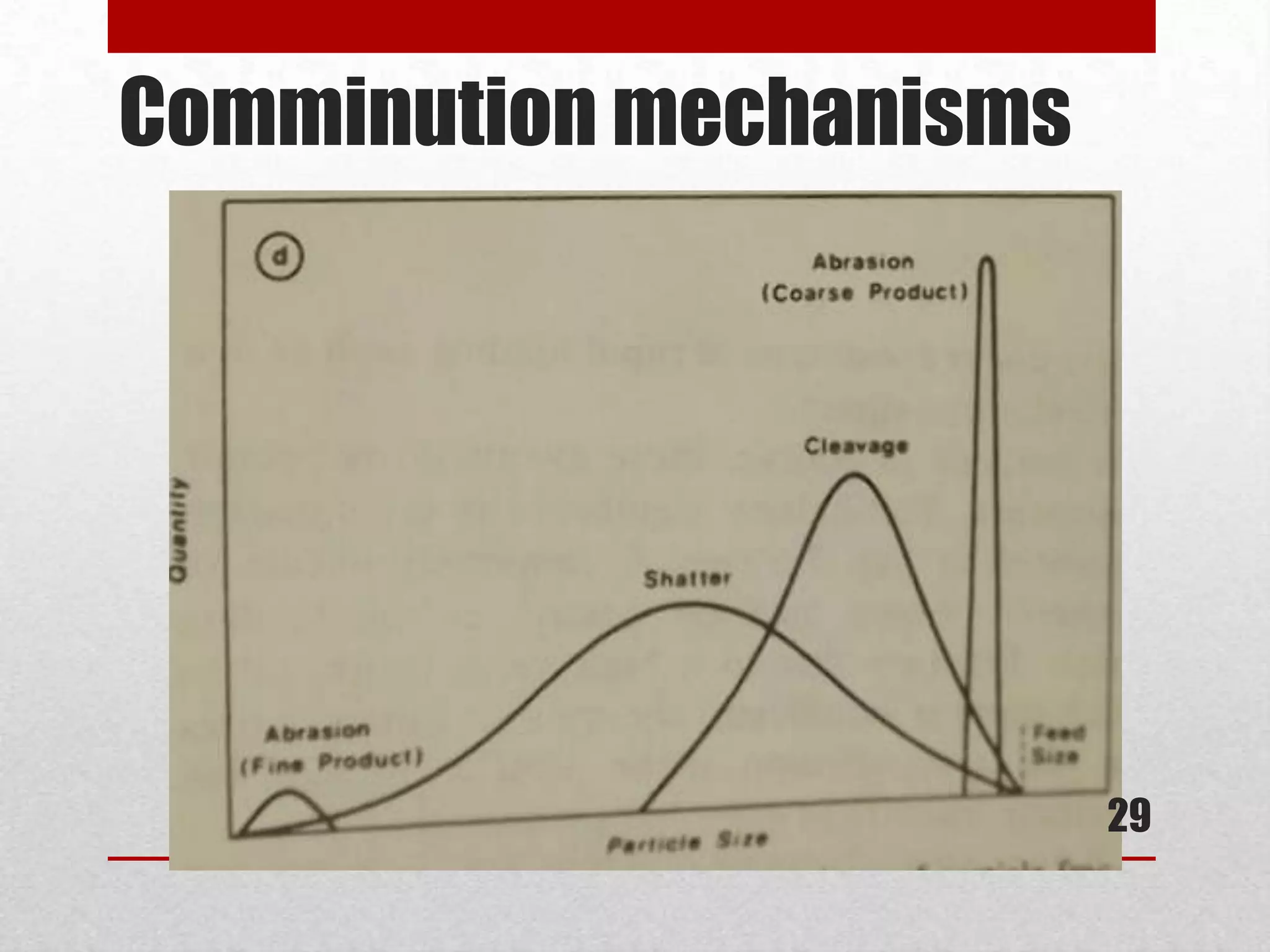
![Comminution mechanisms
• Shatter (impact):
• This mechanism of fracture is induced by rapid
application of compressive stress.
• high speed 10 – 2000 m.s-1 [10]
• A broad spectrum of product sizes is produced and this
process is unselective
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-20-2048.jpg)
![Comminution mechanisms
• shattering process consists of a series of steps in which the
parent particle is fractured and this is followed immediately
by the sequential fracturing of successive generations of
daughter fragments until all of the energy available for
fracture is dissipated.
• Examples: industrial autogenous, rod and ball mills. [11]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-21-2048.jpg)
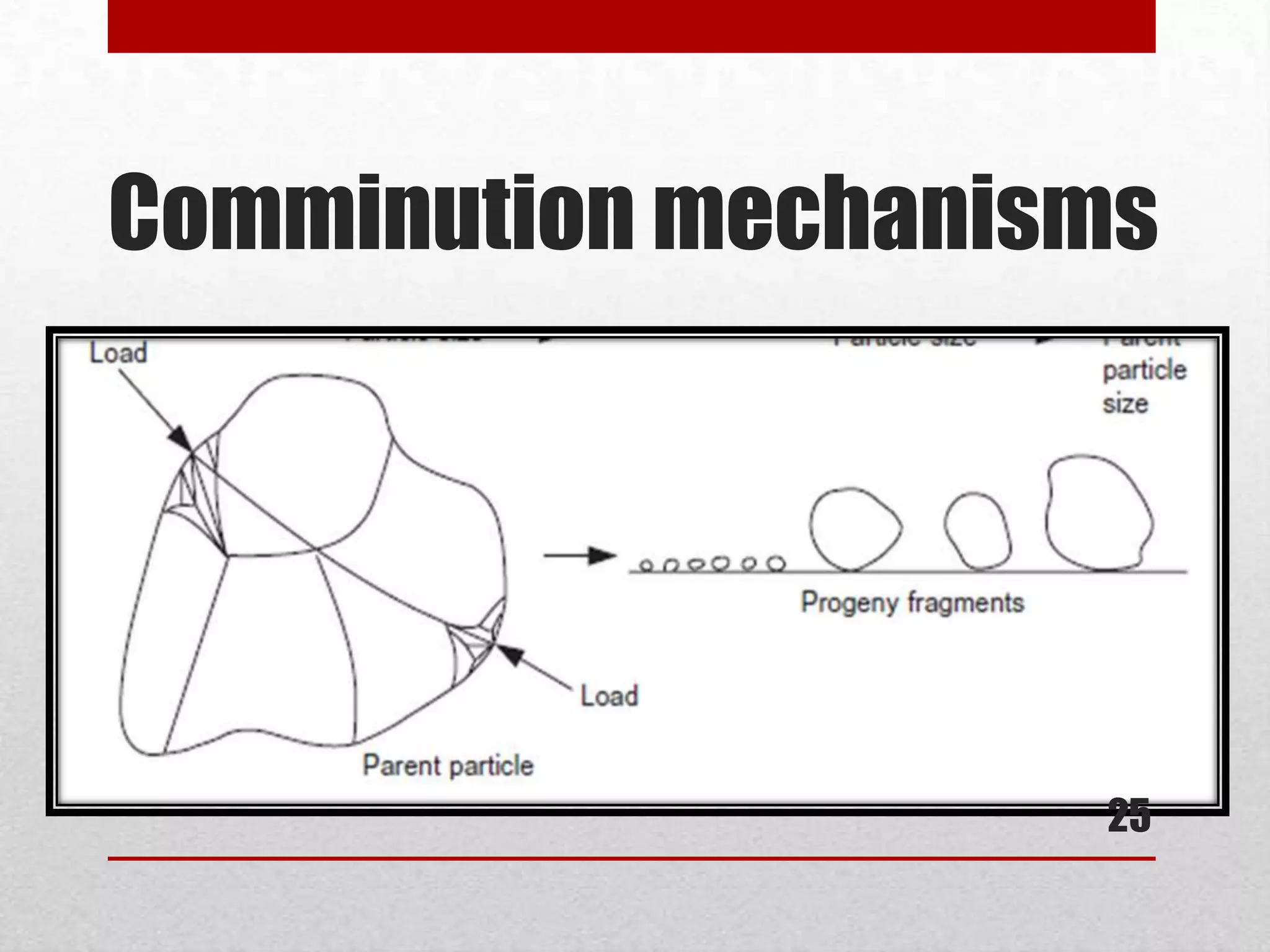
![Comminution mechanisms
• Cleavage: Strain is applied as compression stress
• Occurs when the energy applied is just sufficient to load
comparatively few regions of the particle to the fracture
point and only a few particles result. [7]
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-23-2048.jpg)
![Comminution mechanisms
• When the original solid has some preferred surfaces
along which fracture is likely to occur, cleavage results.
• The size distribution of the product particles is relatively
narrow [11]
• low speed 0,01 – 10 m.s-1
• Examples: jaw crushers, toggle crushers. [10]
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-24-2048.jpg)
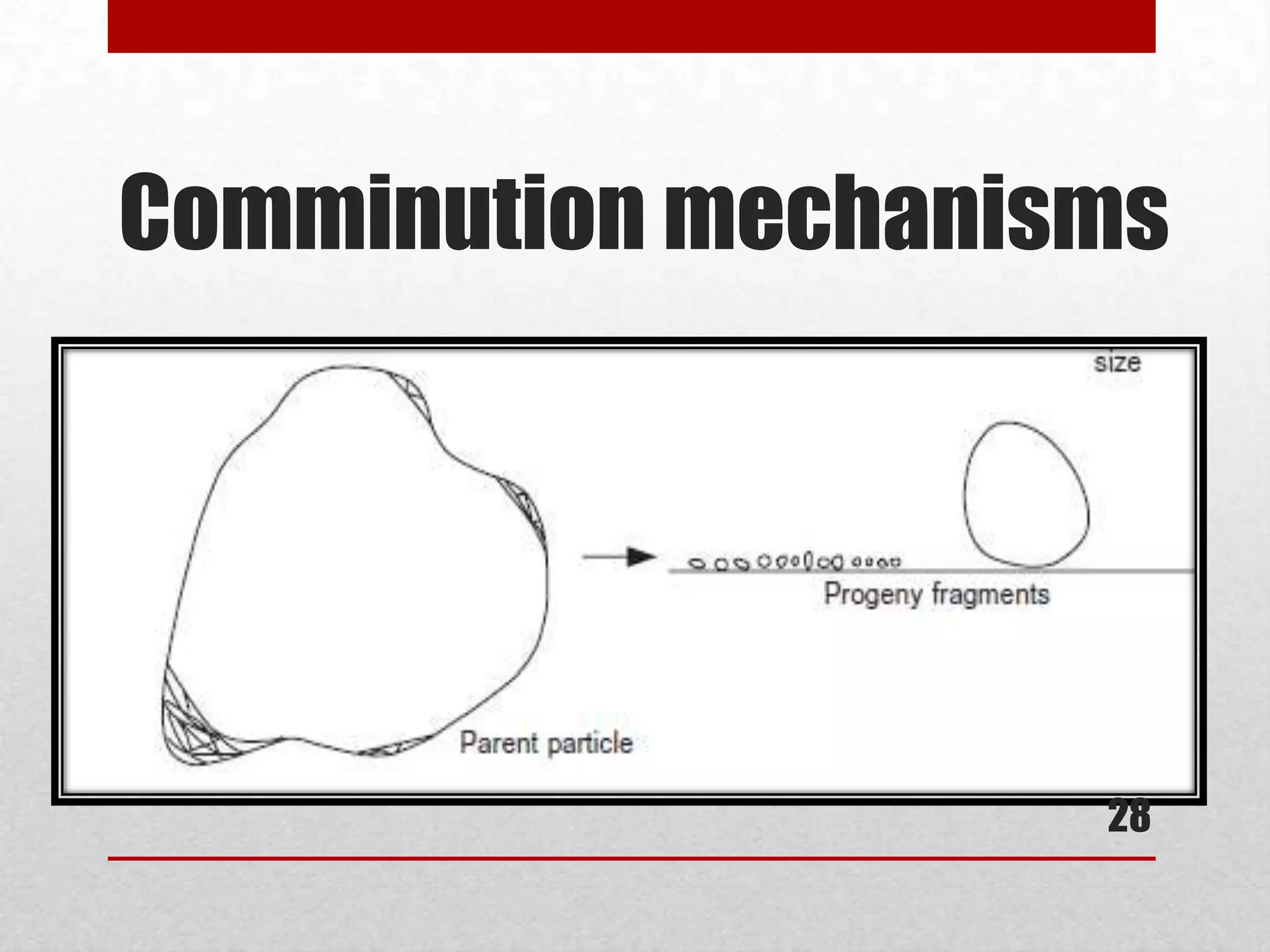
![Comminution mechanisms
• Attrition: Strain between two or more solid
surfaces as a result of shearing action[10]
• Attrition occurs when the particle is large and the stresses
are not large enough to cause fracture.
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-26-2048.jpg)
![Comminution mechanisms
• parent particle hardly changes size but the attrition
process generates a significant number of particles that
are much smaller than the parent size.
• Examples: occurs in autogenous mills where large
particles are present to act as media.[11], shearing action
between ring sieve and rotor in rotor beater mills, cross
beater mills, ultra-centrifugal mills, etc. [10]
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-27-2048.jpg)

![References
• [1] Progress in mineral processing technology, Halim Demirel and Salih
Ersayin, Hacettepe university,Ankara, 1994
• [2] an E-book chapter 10
• [3] http://www.ltu.se/centres/camm
• [4] http://www.chemeng.ed.ac.uk
• [5] Mineral Processing Technology, Recovery, by Barry A. Wills, Tim
Napier-Munn., Elsevier Science & Technology Books, October 2006
• [6] mineral crushing and grinding circuits, A.J. Lynch, Julius Kruttshnitt
Mineral Research Centre, department of mining and metallurgical
Engineering,university of Queensland, Australia, 1989
• [7] introduction to mineral processing, Errol G. Kelly, David J Spottswood
1989
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-31-2048.jpg)
![References
• [8] http://tresen.vscht.cz/kot/english/files/2012-03-particle-sizing-
comminution
• [9] www.scs.illinois.edu/~chem584/.../chem584.mechanicalfailure
• [10] Size reduction within the context of sample preparation, Helmut Pitsch,
Retsch Application Support
• [11] Modeling and Simulation of Mineral Processing Systems, R.P. King
Department of Metallurgical Engineering University of Utah, USA, 2001
• [12] Fracture toughness and surface energies of minerals: theoretical
estimates for oxides, sulphides, silicates and halides D. Tromans , J.A.
Meech, September 2002
• [13] Chemical Metallurgy, Chiranjib Kumar Gupta, 2003
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-130624080440-phpapp01/75/Comminution-mechanism-32-2048.jpg)