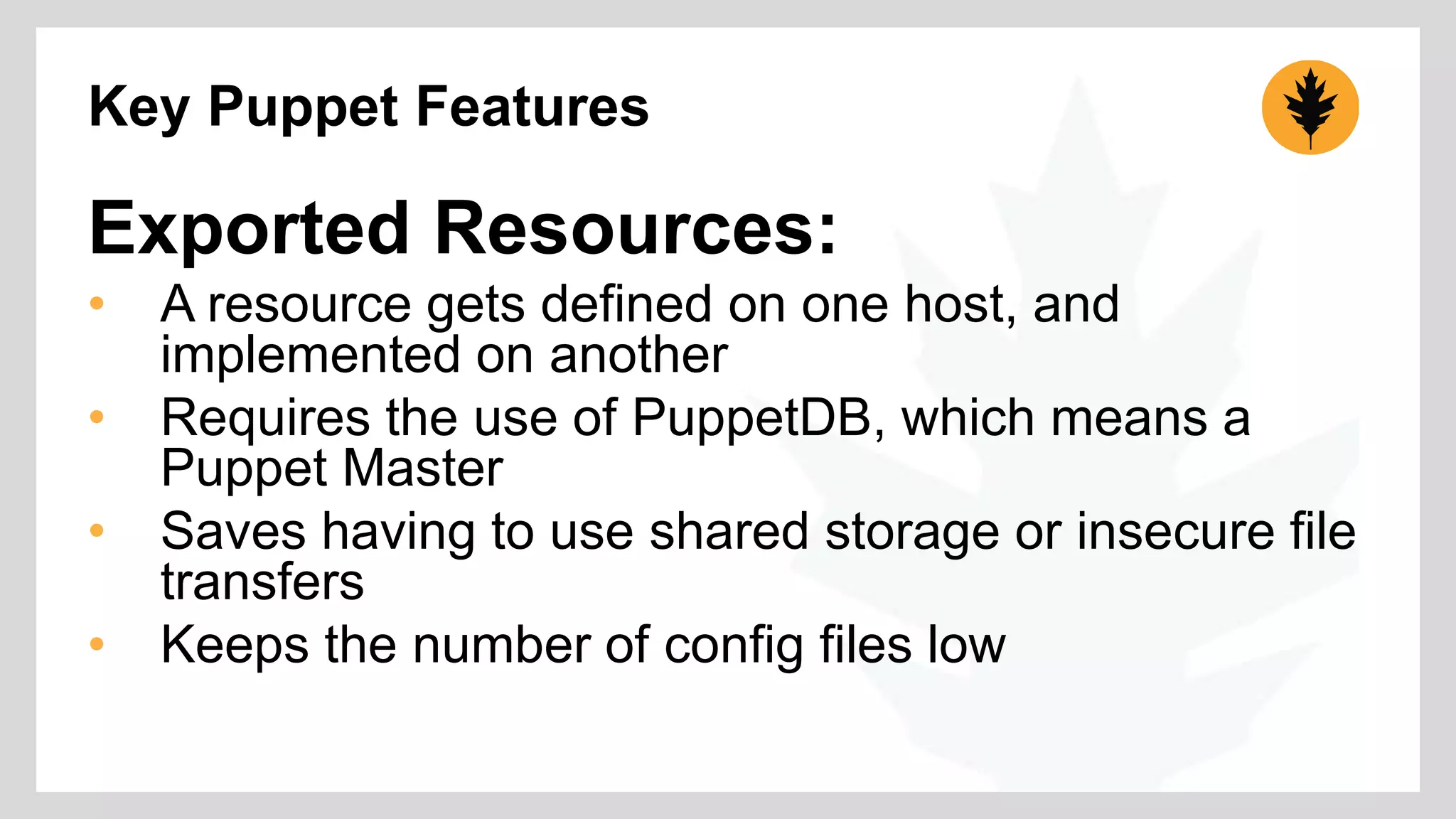
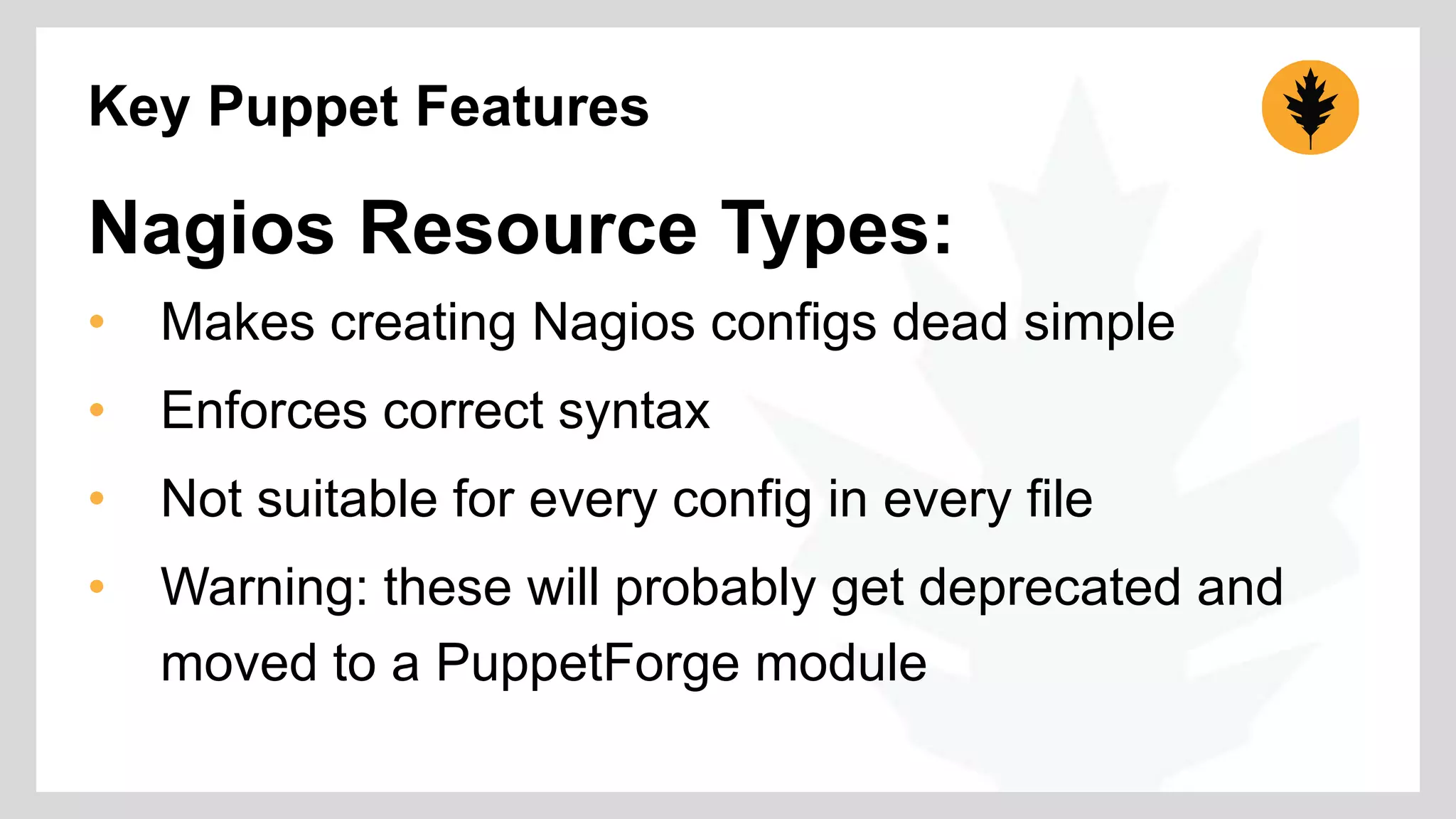
The document discusses the integration of Puppet with Nagios for configuration management, emphasizing why such systems are crucial in managing numerous nodes within IT operations. It highlights key features of Puppet such as exported resources, hiera, inline templates, and Nagios resource types which enhance monitoring capabilities and streamline the configuration process. Additionally, it outlines the use of a GitHub repository for testing Puppet code and invites contributions to develop a Puppet Forge module for improved provisioning and resource management.