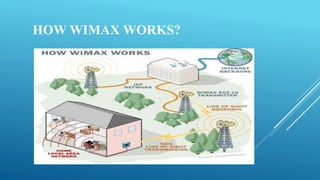
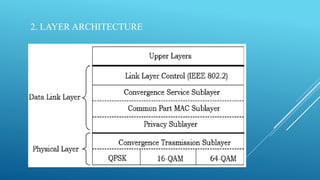
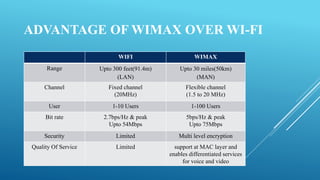
This document discusses WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) technology, which provides broadband wireless connectivity based on the IEEE 802.16 standard. It describes how WiMAX works using towers and receivers, its standards, architecture including physical and MAC layers, features like range and quality of service, advantages over WiFi, applications, and comparisons with 3G mobile networks. WiMAX allows high-speed wireless internet access over long distances at a lower cost than options like digital subscriber lines.