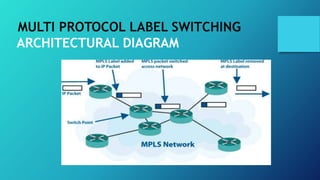
MPLS is a routing technique that establishes an end-to-end path between a source and destination using labels. It builds a connection-oriented service on IP networks by using labels to set up the path in a hop-by-hop manner. MPLS makes IP routing faster by reducing the number of routing lookups and eliminates the need to run routing protocols on all devices. It is protocol independent and maps IP addresses to fixed length labels to forward traffic.