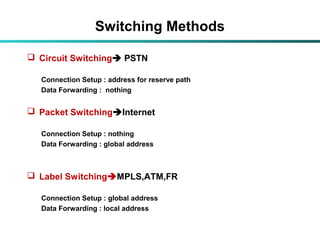
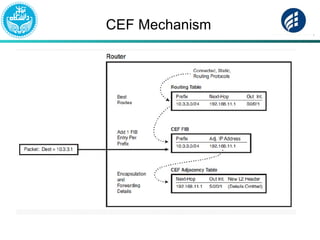
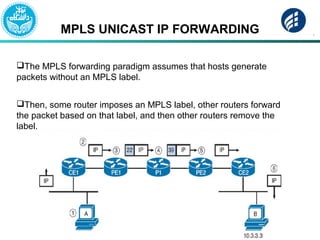
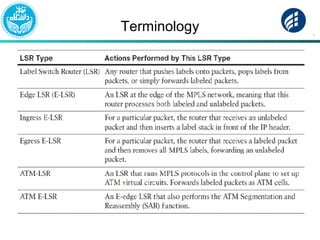
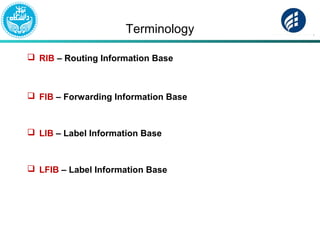
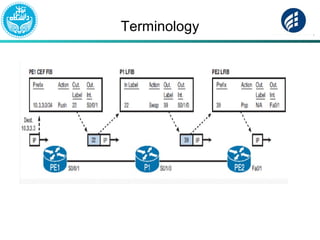
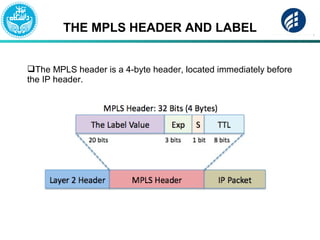
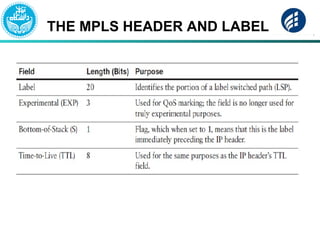
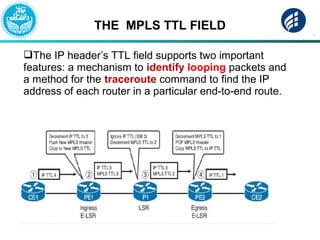
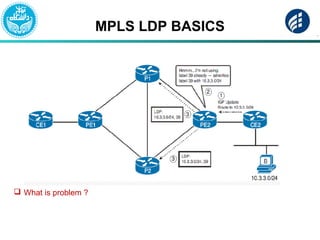
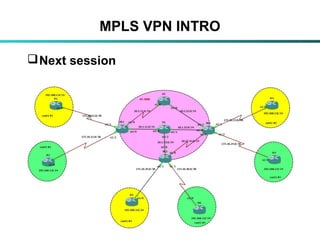
The document discusses Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS), highlighting its advantages over traditional routing methods, limitations, and various applications such as VPNs, Traffic Engineering (TE), and Quality of Service (QoS). It explains the role of label distribution protocols, especially LDP, in facilitating dynamic label distribution and emphasizes the importance of the MPLS header and the concept of penultimate hop popping (PHP). Key terminologies related to MPLS, including FIB and RIB, are also defined.