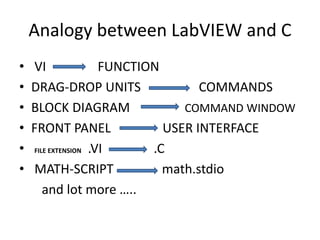
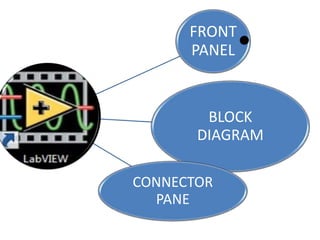
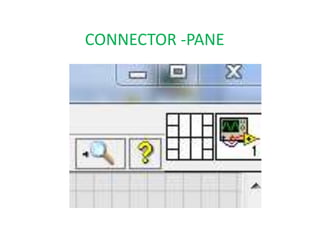
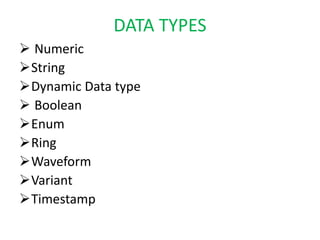
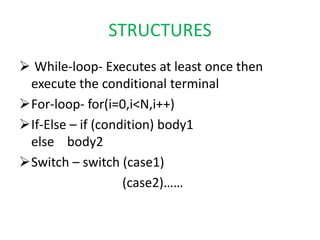
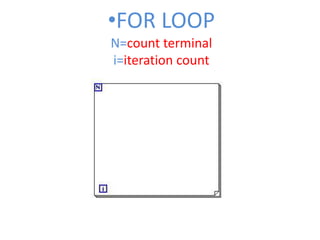
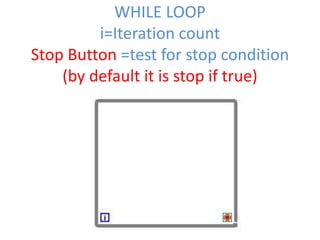
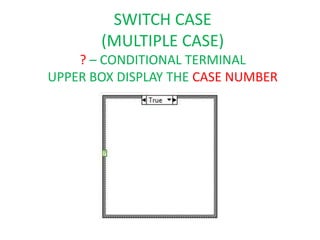
This document provides an overview of the LabVIEW environment and programming concepts. It describes LabVIEW as a graphical programming language where programs called VIs contain a front panel user interface and a block diagram with code. The block diagram uses dataflow programming with wires to connect functions and represents the execution of the program. Functions are selected from palettes and the connector pane allows passing data between VIs. Common LabVIEW constructs like while loops, for loops, and if/else statements are also covered.