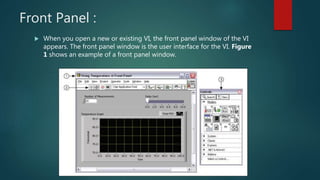
Sarith Wadkar completed a 6-week virtual internship at National Instruments Innovation Centre focused on LabVIEW. LabVIEW is a graphical programming language used for data acquisition, signal processing, and hardware control. It uses graphical block diagrams and front panels instead of text. A LabVIEW program, or VI, has three main parts: the front panel user interface, the block diagram code, and controls palette. Data flows between these elements through terminals. LabVIEW follows dataflow programming and is useful for applications like machine monitoring, research, and control system design.