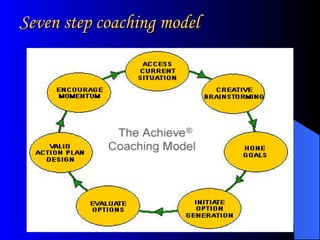
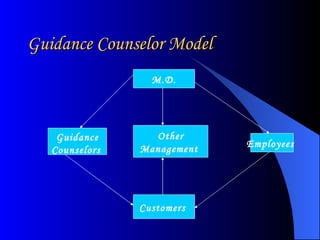
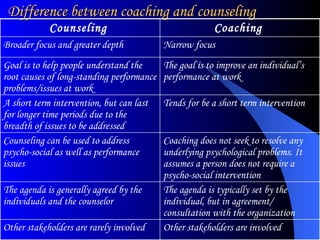
The document discusses the concepts of performance coaching and counseling, using a case study of an employee named Barry who has made costly errors in his new role. Coaching aims to enhance performance by setting specific goals, assessing current performance, and developing action plans, while counseling addresses underlying psychological issues. Barry's supervisor decides to provide both coaching and counseling to improve his performance in both the short and long term.