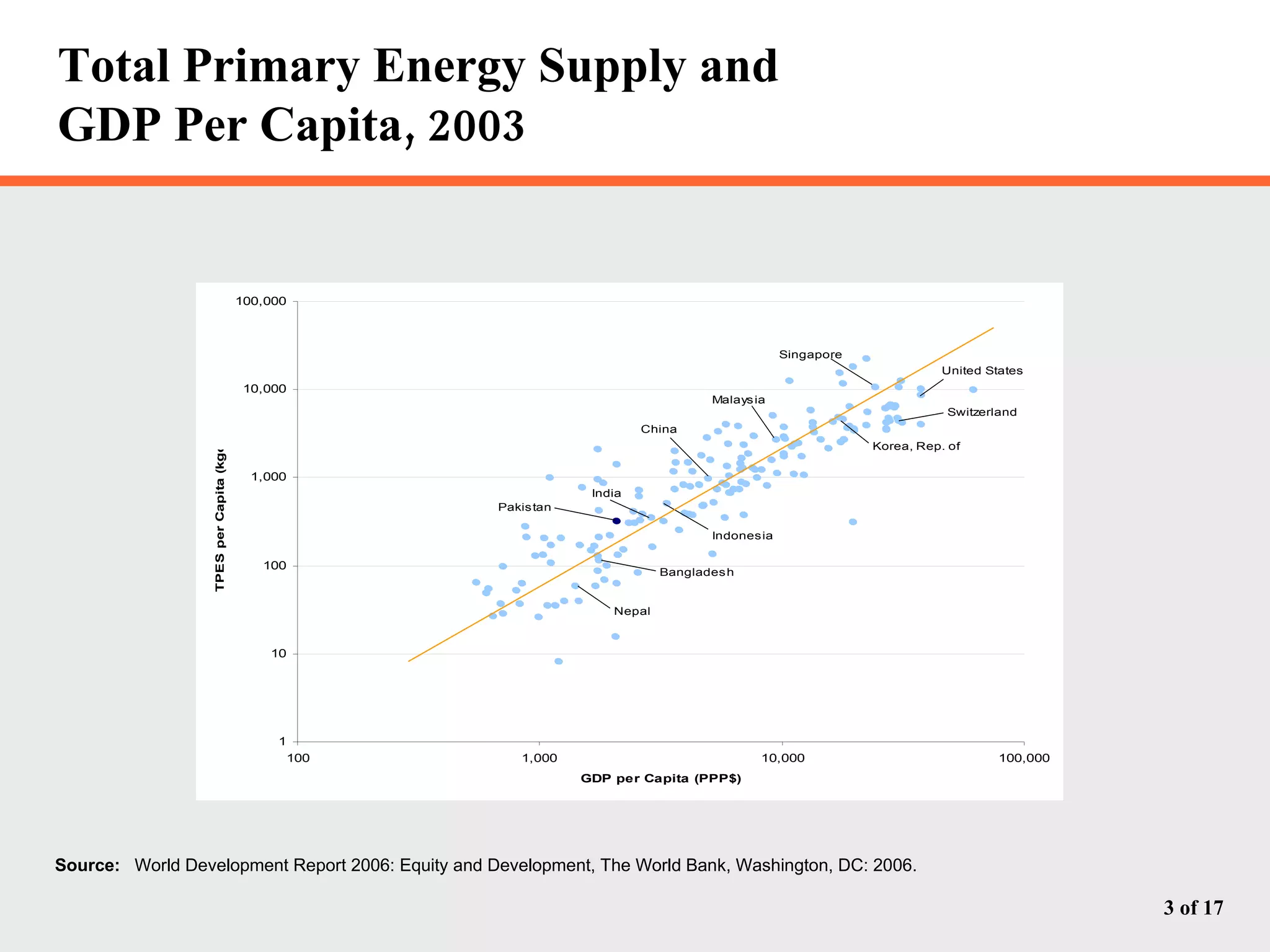
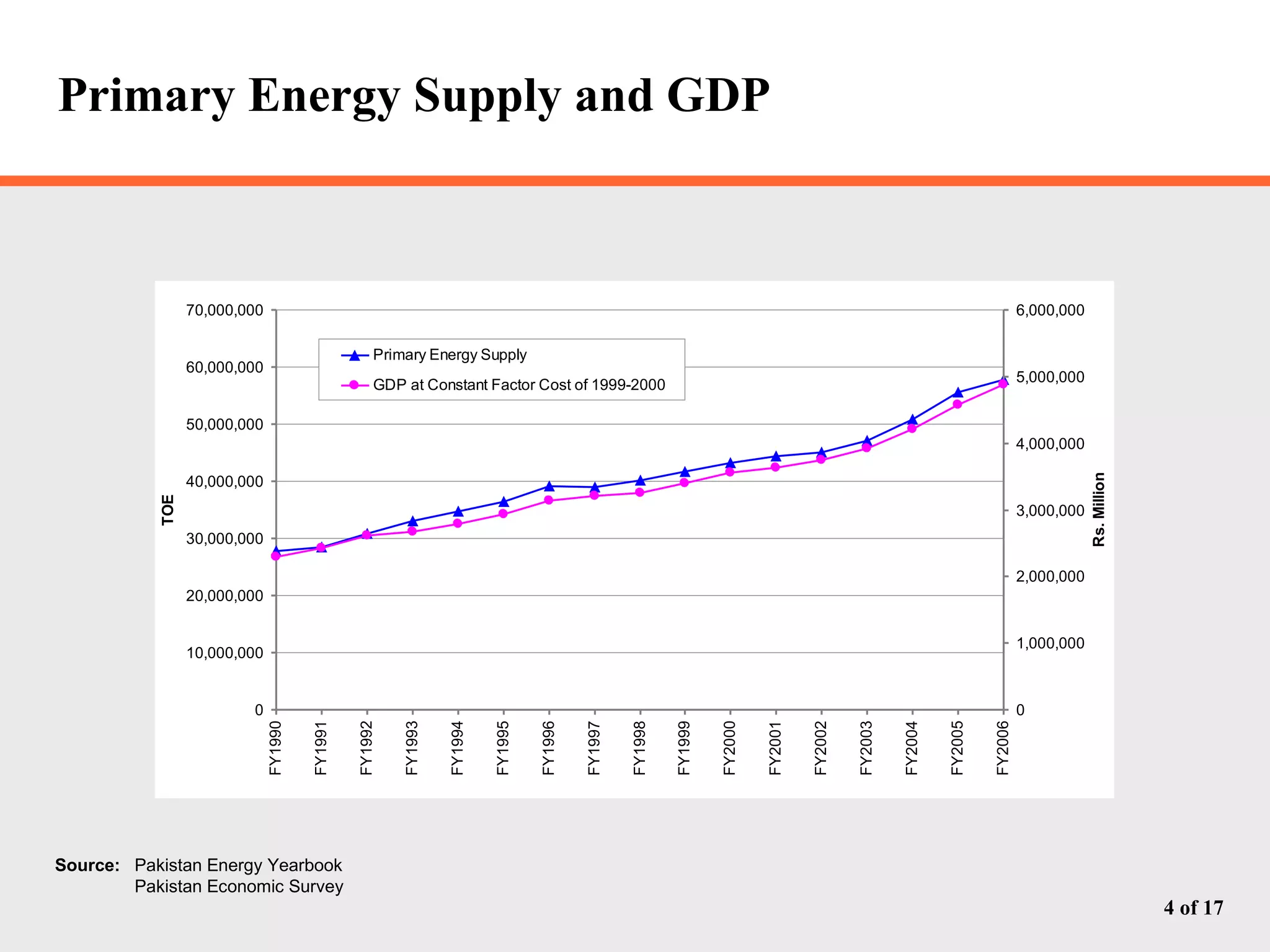
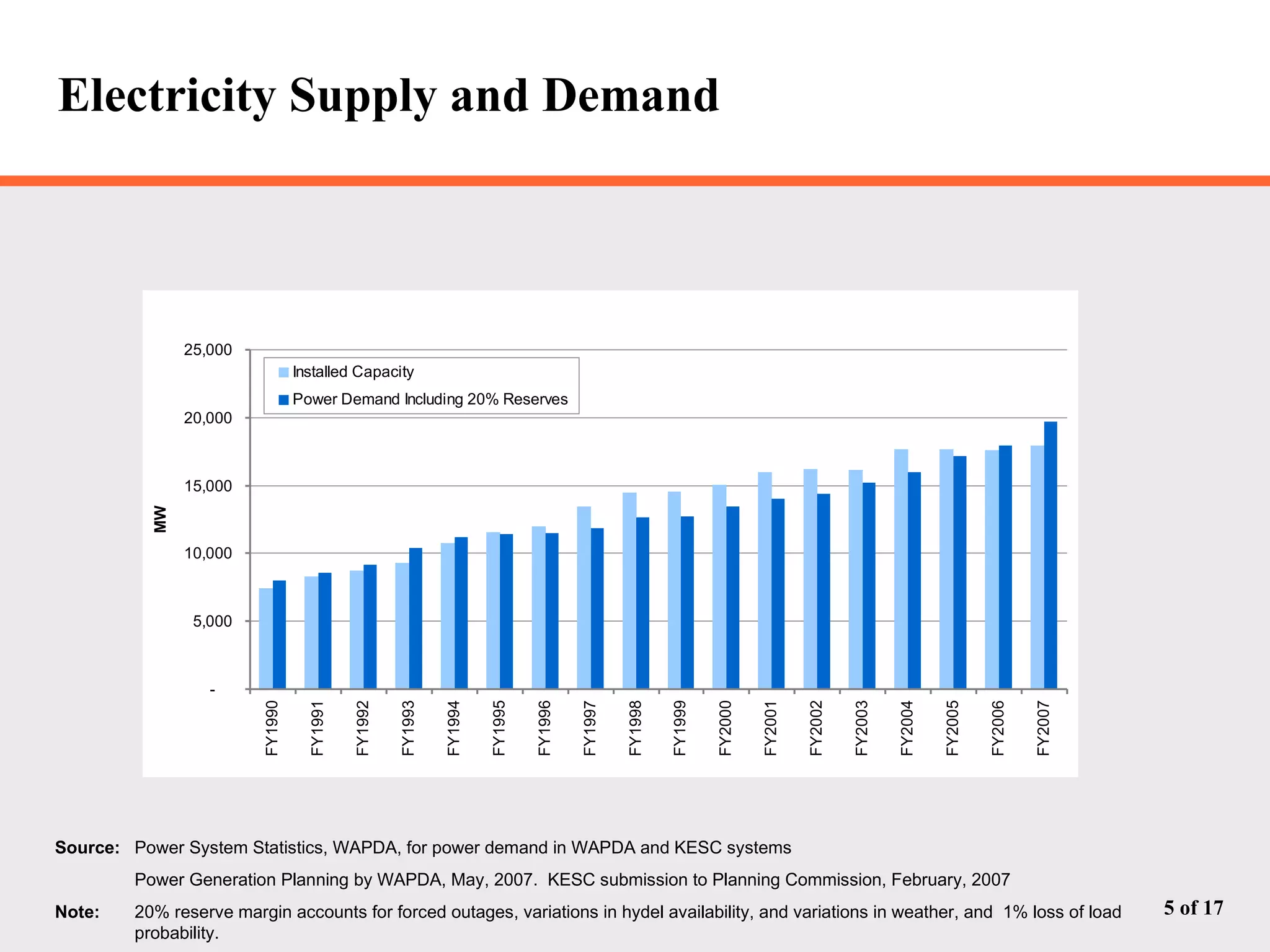
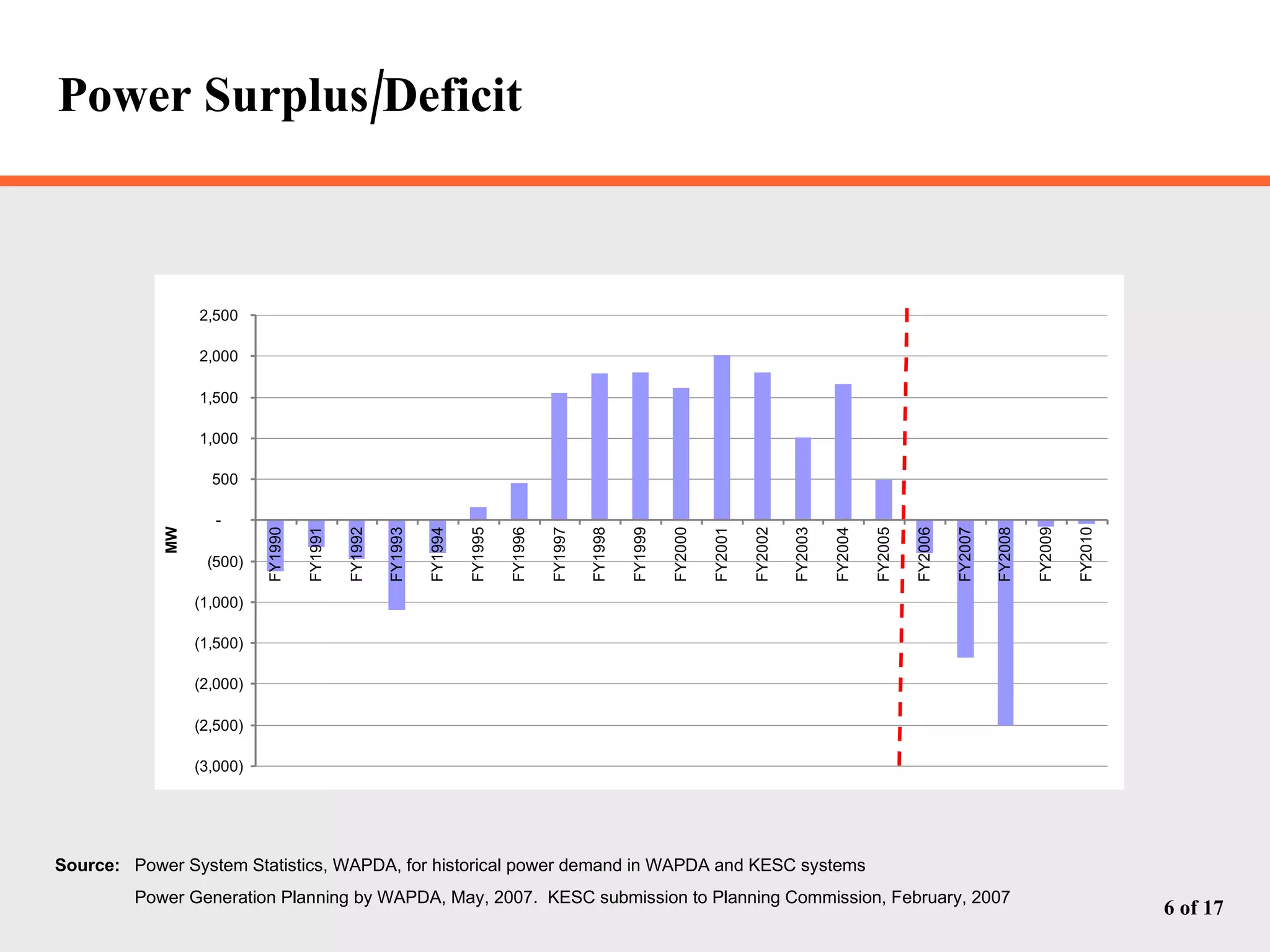
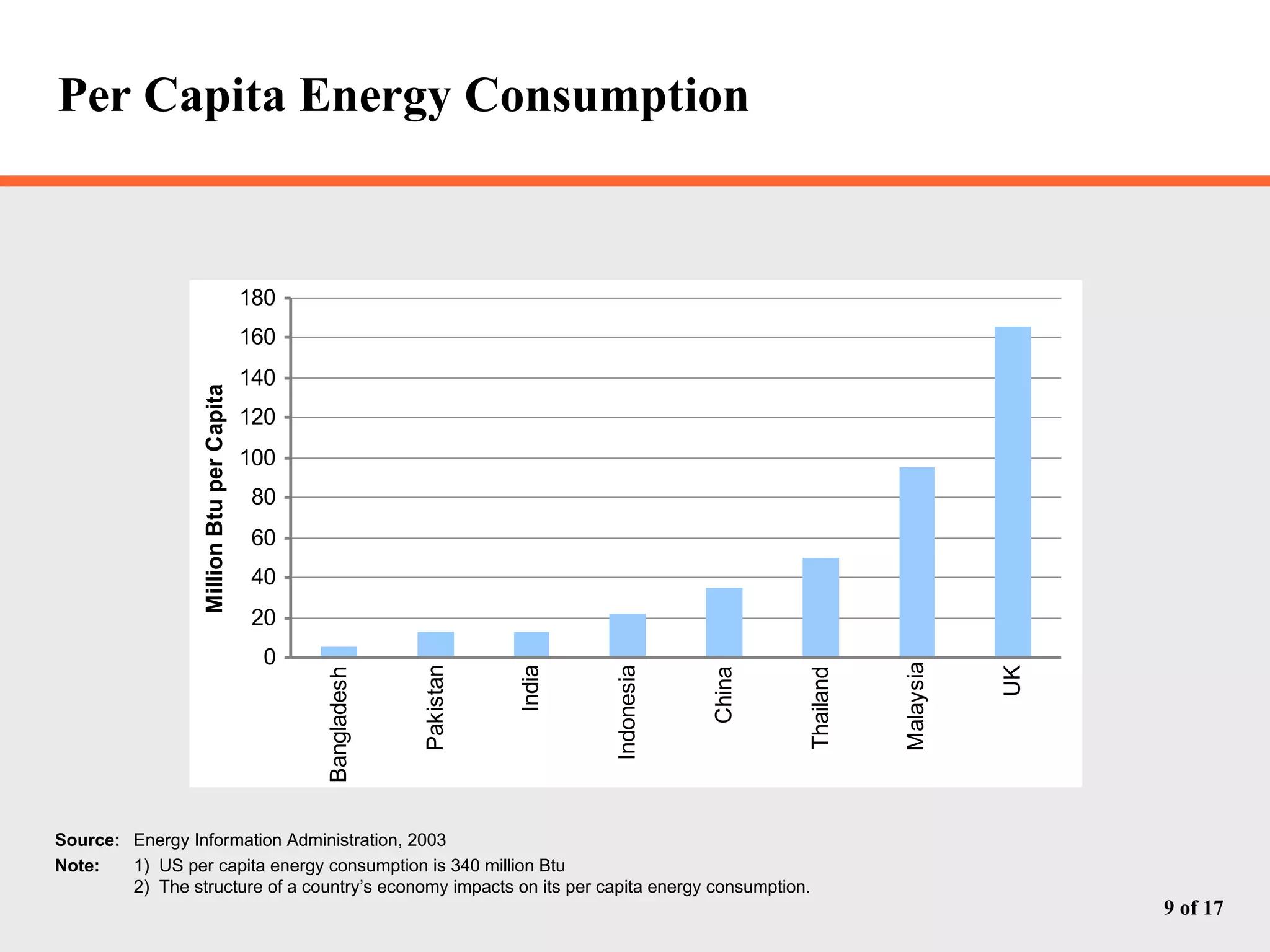
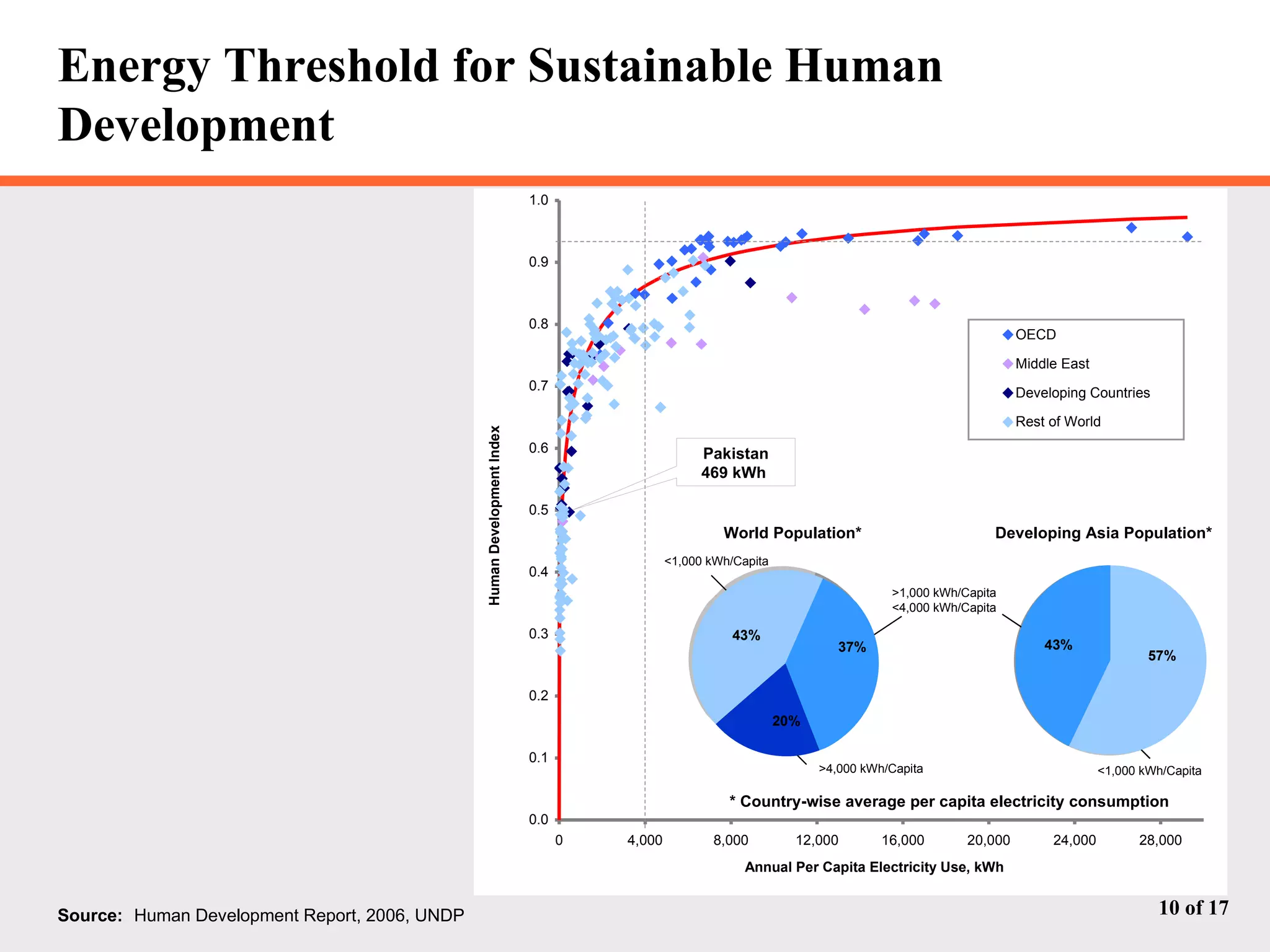
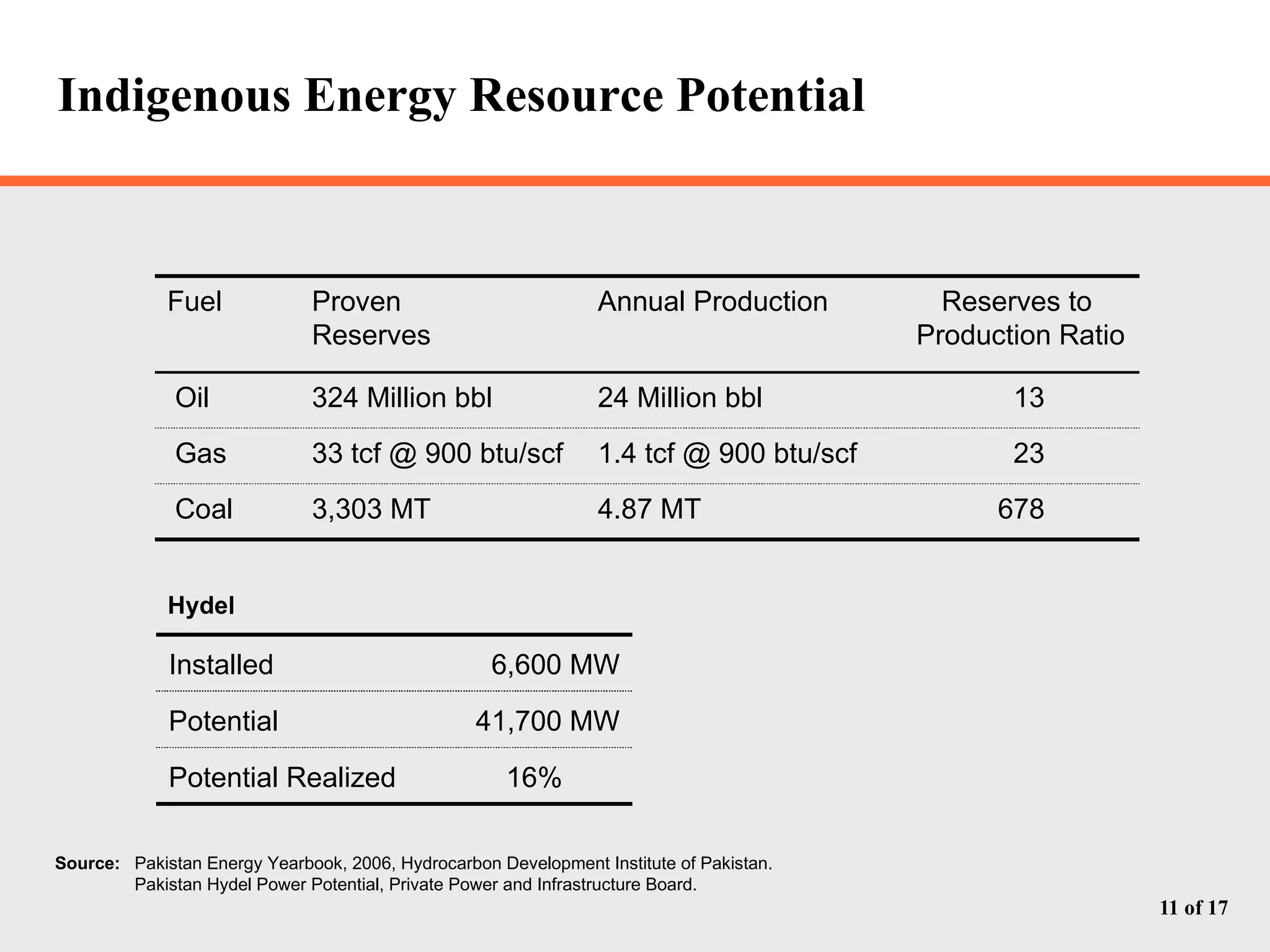
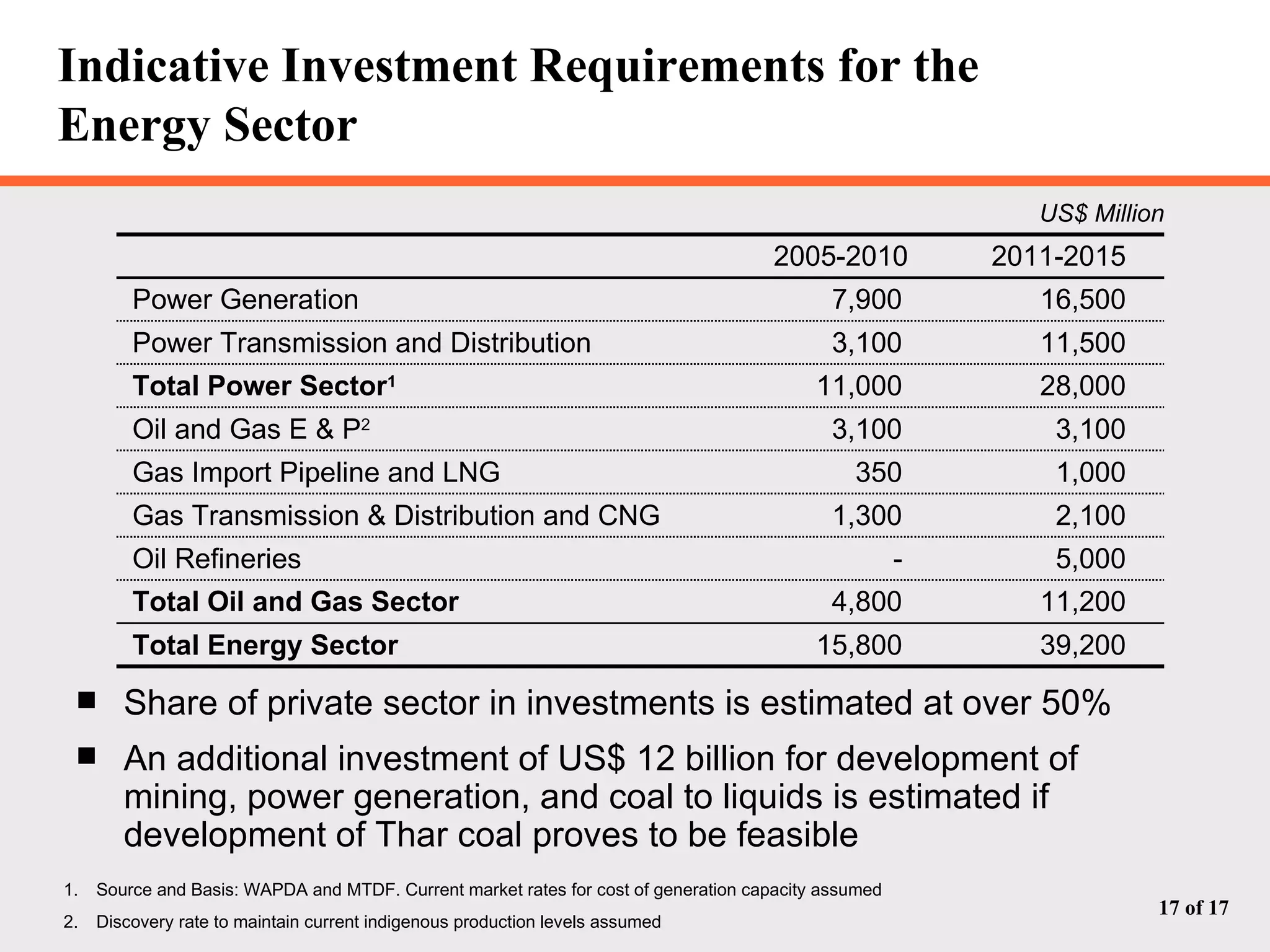
The document discusses Pakistan's growing energy needs to support its expanding economy. It outlines Pakistan's historical energy usage and projections showing increasing deficits if production and policy do not change. The government's energy sector action plan aims to boost oil, gas, coal, hydropower and nuclear production through public-private partnerships and integrated planning to meet demand sustainably. Significant investment estimated at $39.2 billion through 2025 will be required across the energy sector.