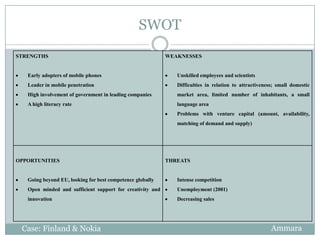
The document discusses Finland and Nokia. It provides background on how Finland transitioned to an innovation-driven economy in the 1980s and became a member of the European Union in the 1990s. It then focuses on Nokia, which accounted for 70-80% of Finland's exports and was the world leader in mobile phones. The Finnish government played an important role in supporting leading companies like Nokia. The document examines Finland and Nokia's relationship from 2001-2010 when the telecommunications sector experienced a slowdown globally.