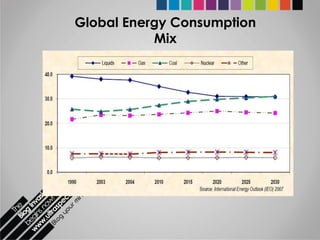
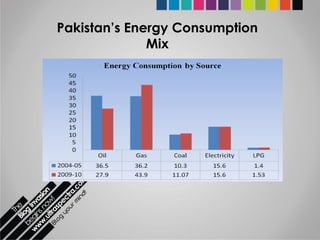
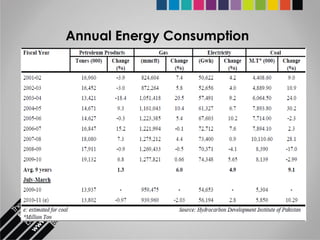
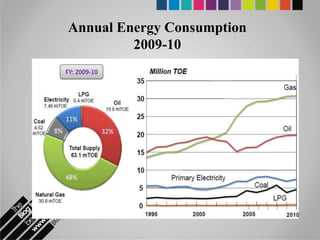
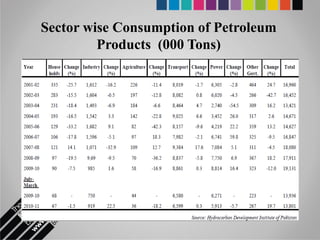
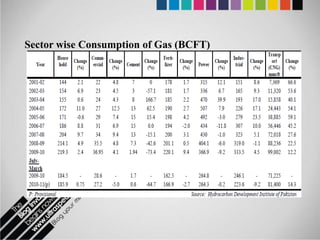
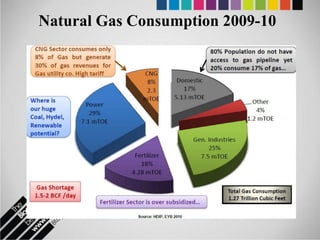
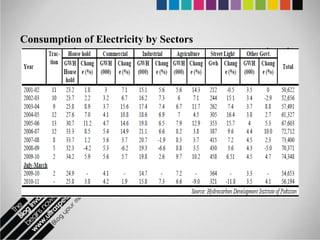
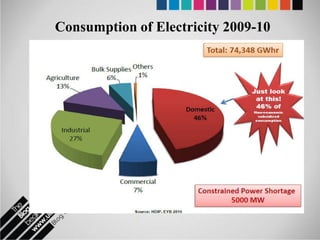
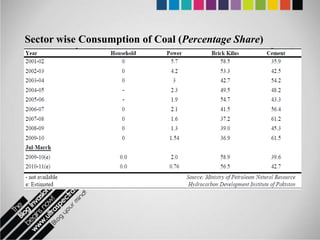
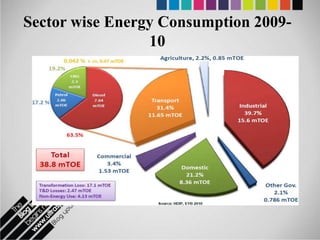
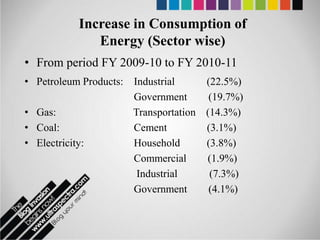
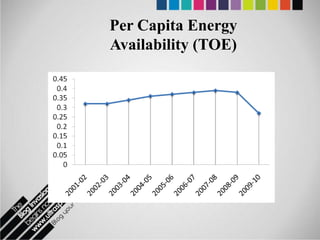
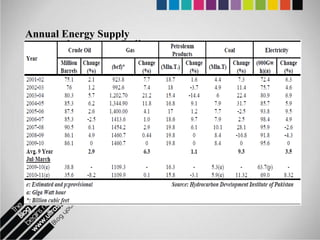
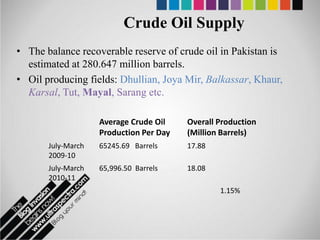
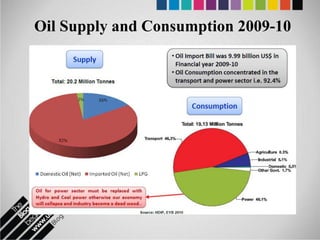
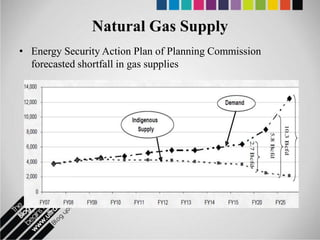
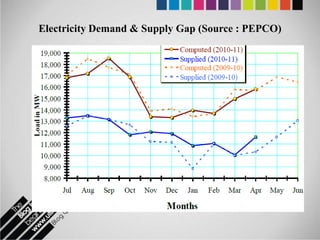
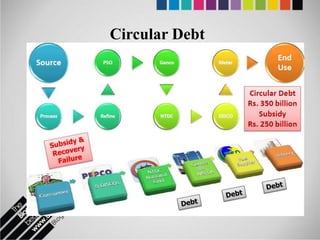
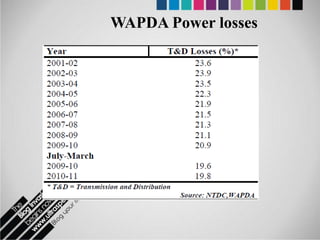
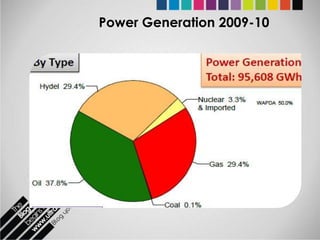
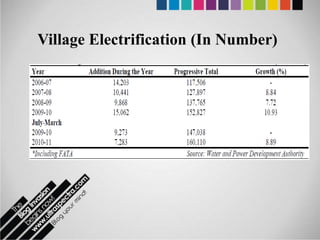
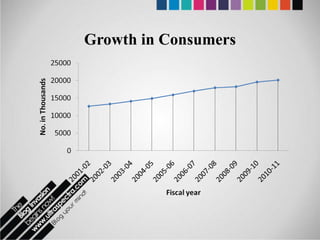
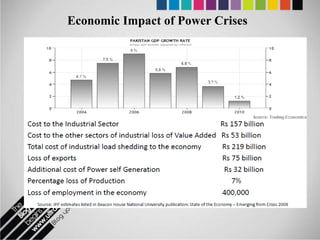
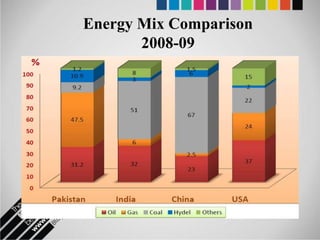
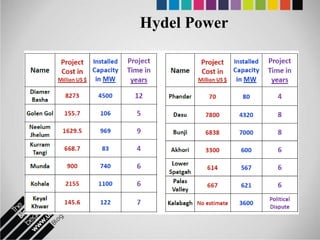
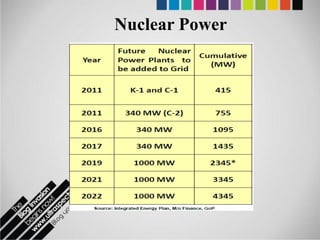
The document provides an overview of Pakistan's energy sector. It notes that energy is a key determinant of economic development. Pakistan's total energy consumption in 2009-10 was 63.1 million tons of oil equivalent. The majority of Pakistan's energy comes from natural gas and oil. However, there is a push to increase the use of domestic coal, hydropower, and renewables. Key challenges facing Pakistan's energy sector include a growing demand, reliance on imported fuels, underdevelopment of domestic resources, and poor governance. Addressing these issues through integrated energy planning and developing indigenous energy sources is seen as important for Pakistan's economic growth.