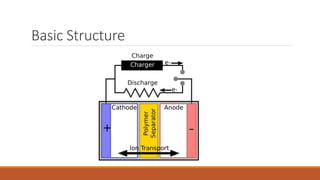
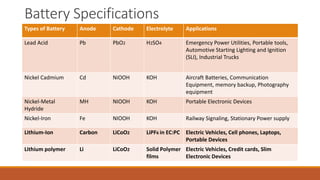
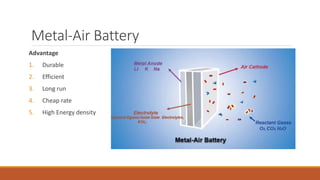
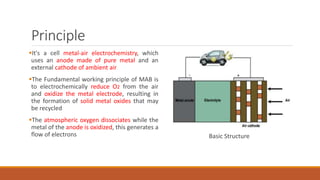
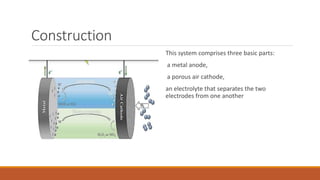
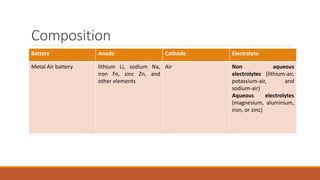
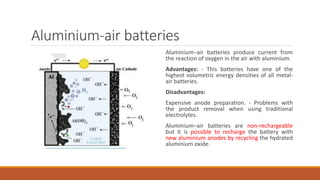
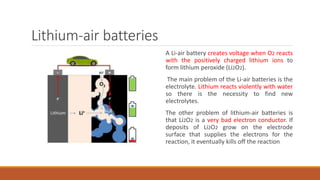
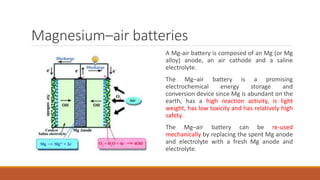
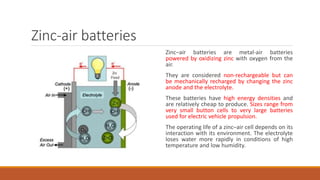
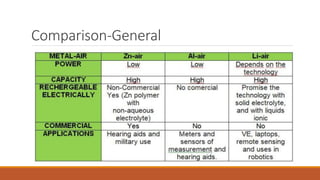
Batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. They consist of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. Primary batteries are non-rechargeable while secondary batteries are rechargeable. During discharge, oxidation occurs at the anode and releases electrons while reduction occurs at the cathode and consumes electrons. Common battery types include lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, nickel-metal hydride, and lithium-ion. Metal-air batteries have high energy density and use oxygen from the air as the cathode reactant, providing advantages over traditional batteries.