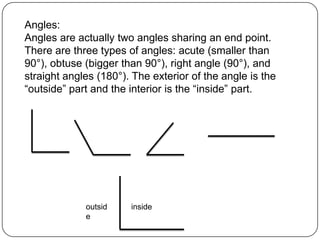
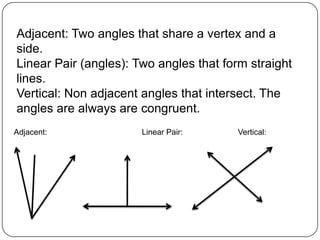
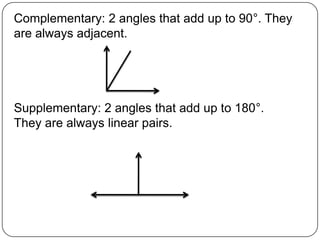
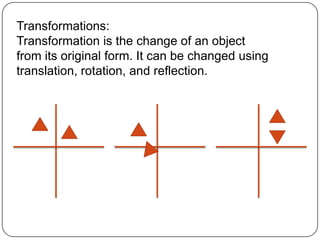
1) The document defines various geometric terms including points, lines, planes, collinear and coplanar points, segments, rays, intersections, angles, and transformations.
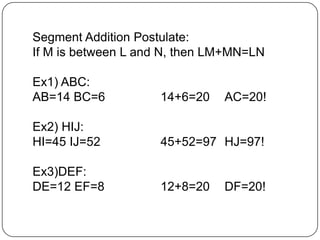
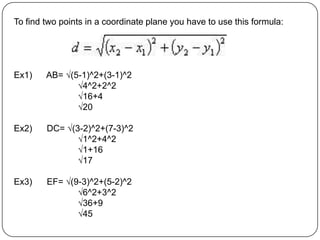
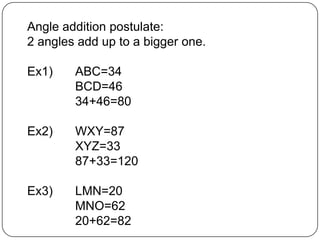
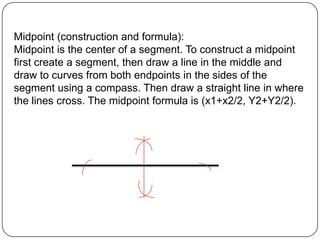
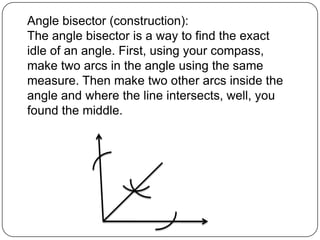
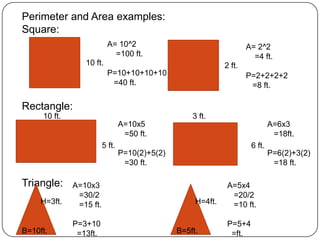
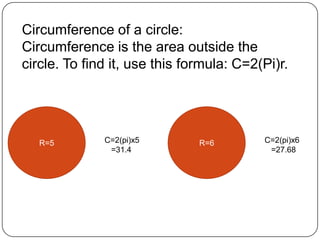
2) It provides examples of how to use formulas to find distances between points, add segments, use the Pythagorean theorem, find midpoints and angle bisectors, calculate perimeter and area of squares, rectangles, and triangles.
3) The five step problem solving process is outlined as read the problem, highlight important information, draw a picture, solve the equation, and answer the question.