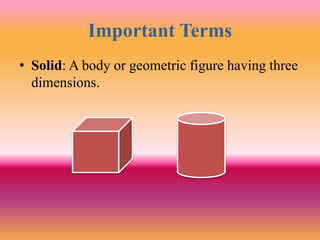
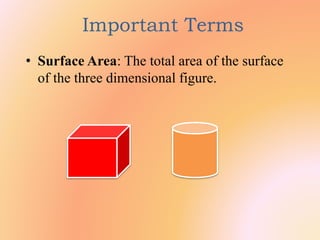
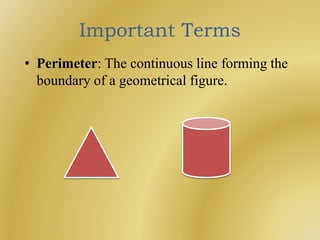
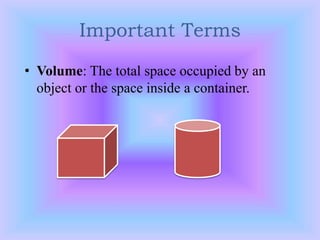
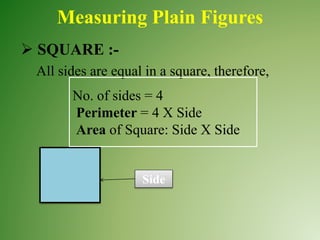
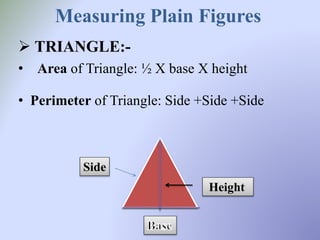
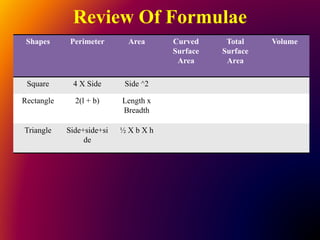
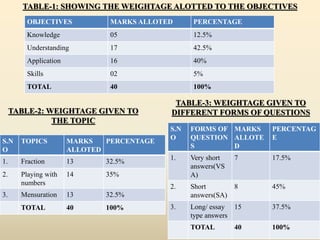
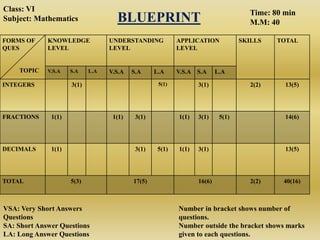
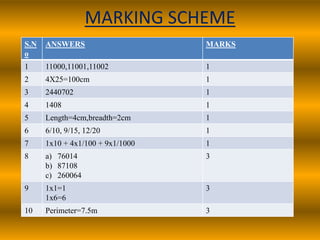
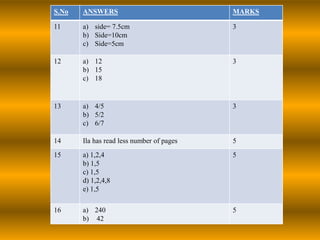
The document outlines a B.Ed. lesson plan on mensuration for 6th graders, detailing the teaching objectives, important terms, previous knowledge expected, and instructional content. It covers key concepts of calculating area and perimeter for various shapes, methodologies used, and includes evaluation and marking schemes for assessment. Additionally, it includes observations of student behavior during group activities, noting dynamics such as leadership and language use among peers.