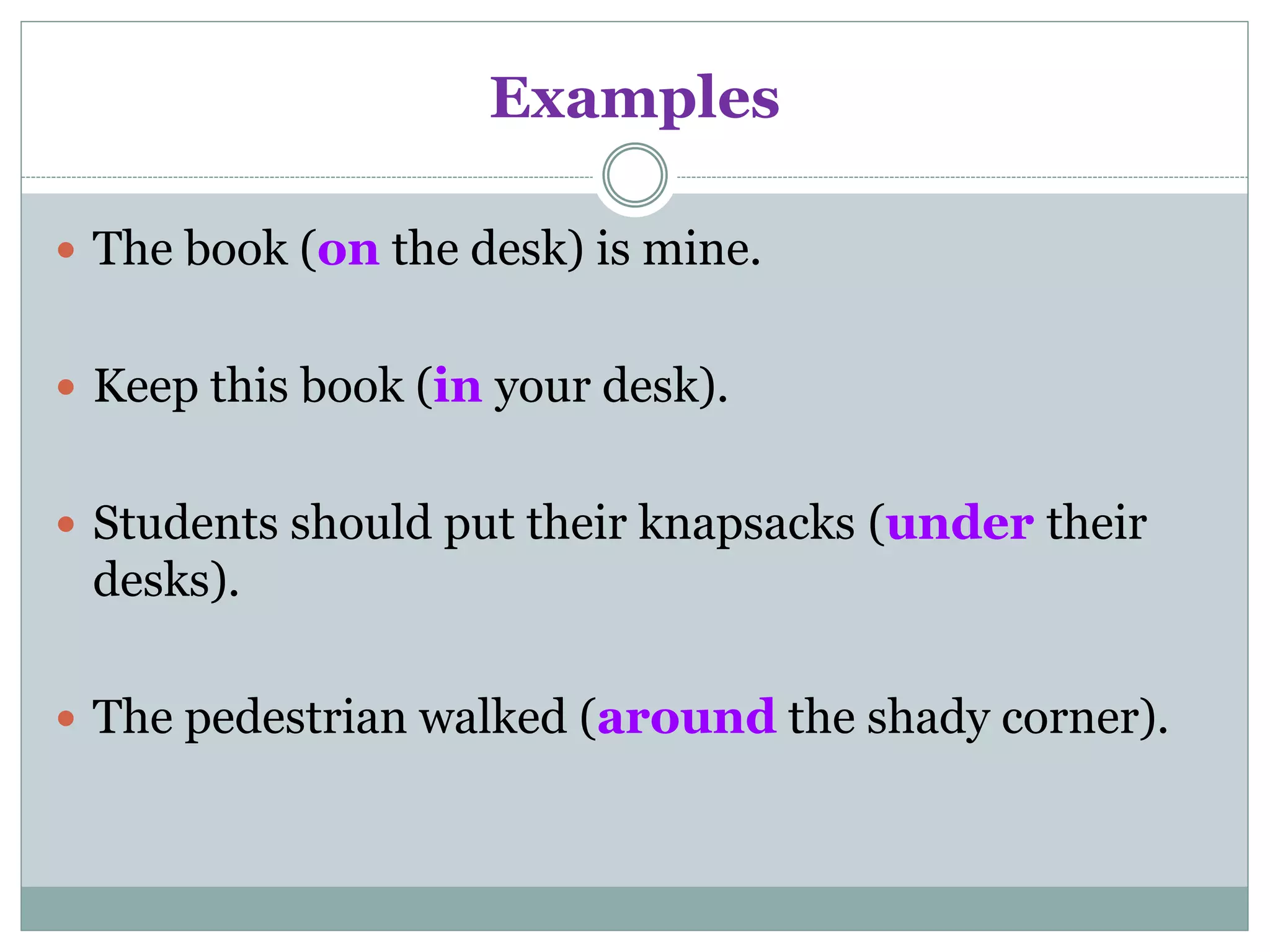
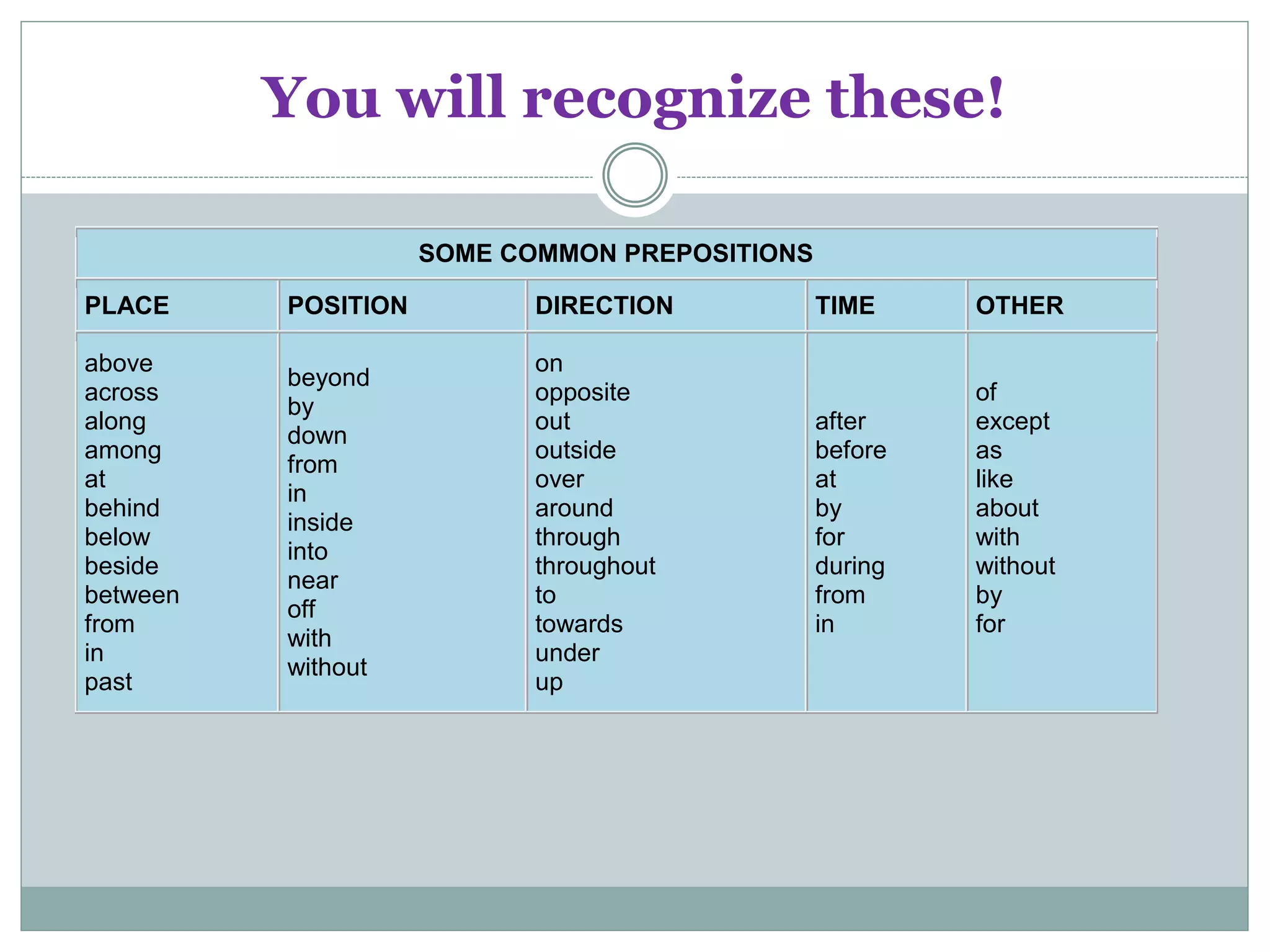
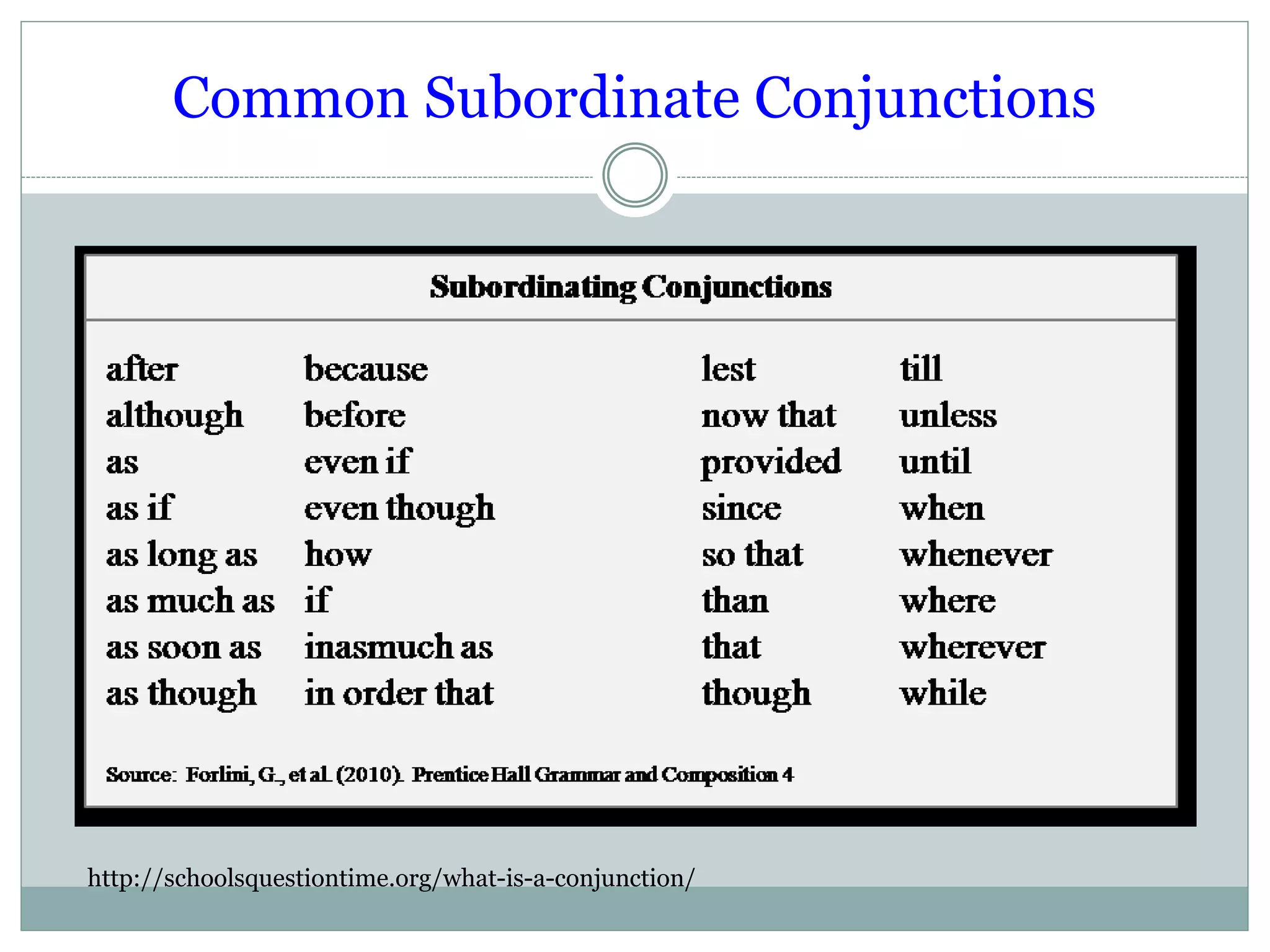
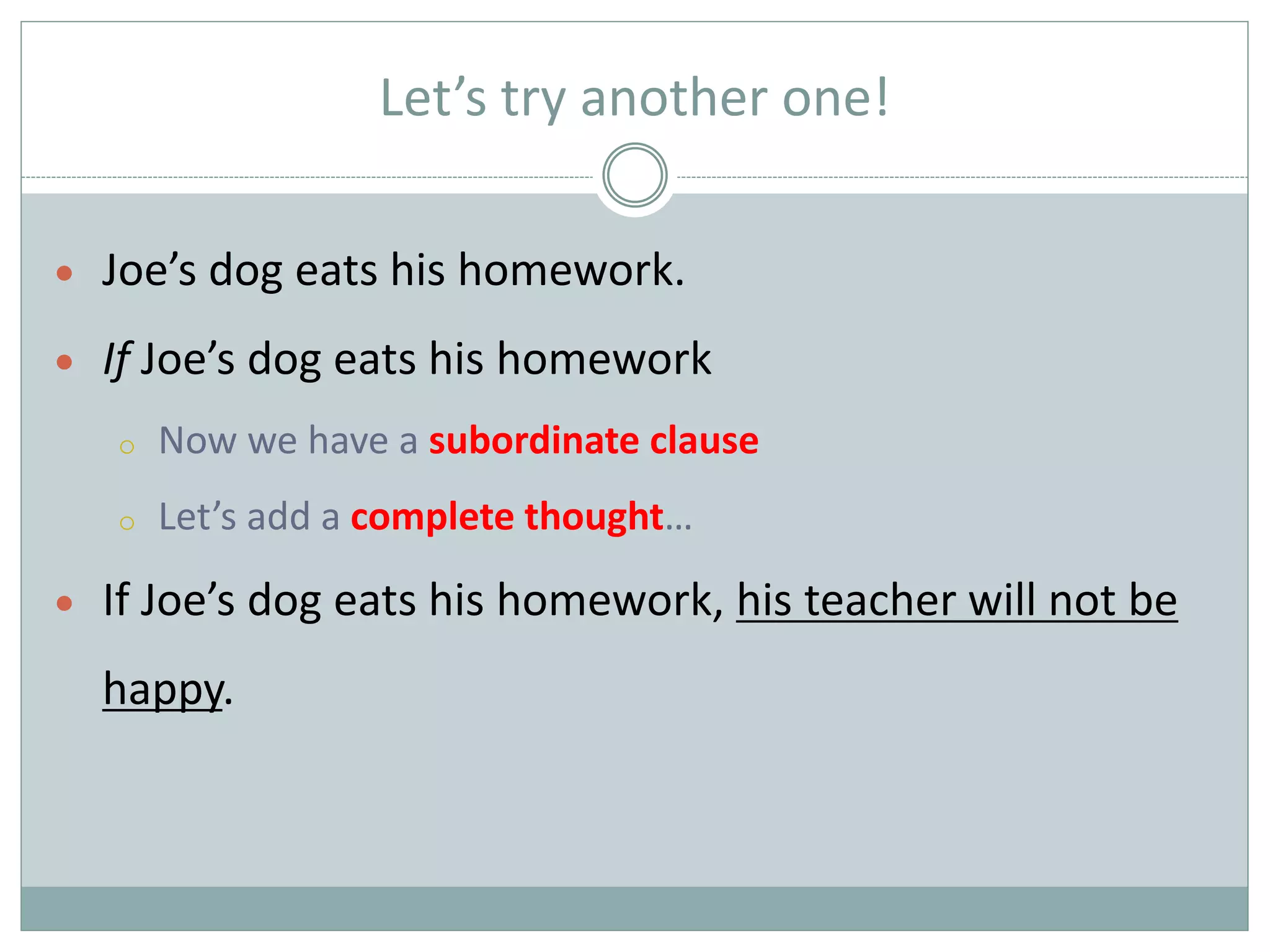
This document provides information about prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It defines prepositions as words that introduce a phrase and are followed by a noun or pronoun. Common prepositions indicating place, position, direction, time and other uses are listed. Conjunctions are defined as words that join words, phrases, or clauses. There are two types: coordinate conjunctions that join equal parts and are remembered with the acronym FANBOYS, and subordinate conjunctions that make a clause dependent on an independent clause. Examples of each type of conjunction are given. Interjections are defined as words that express strong feeling or emotion, usually beginning or ending a sentence followed by an exclamation point. Common interjections