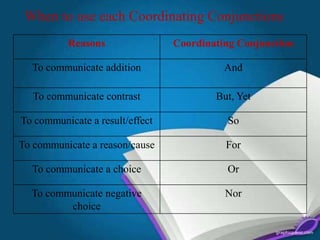
This document discusses conjunctions and their two types - coordinating and subordinating conjunctions. Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, and independent clauses, and include and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions introduce dependent clauses and express relationships between clauses, denoting time, reason, condition, contrast, or location. Examples are provided of conjunctions used correctly in sentences.