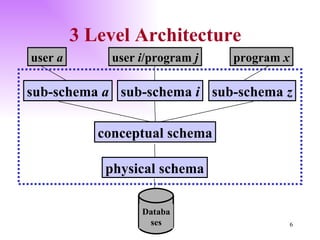
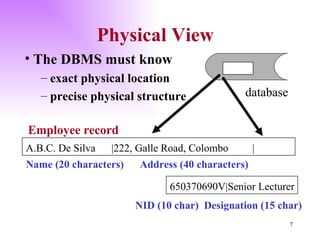
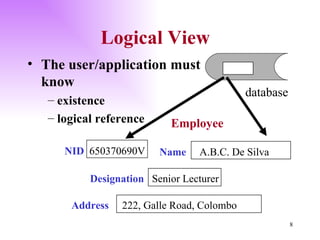
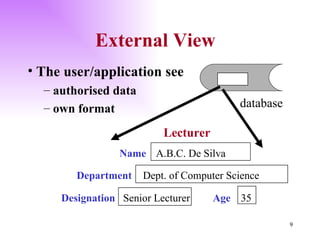
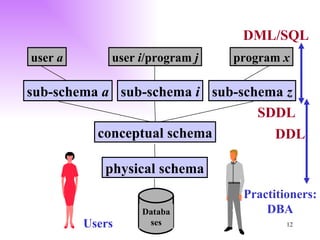
The document discusses the structure and architecture of database management systems, emphasizing the three-schema architecture which includes external, conceptual, and physical schemas. It details key components like data definition language (DDL), data manipulation language (DML), and the relational model, highlighting the importance of primary and foreign keys in establishing relationships between tables. It further explains the difference between external views, which provide customized user perspectives on data, and the conceptual model that represents the database's logical structure.
![IT2301 Database Management Systems [email_address] PREPARING FOR THE BIT Preparing for BIT 07/06/2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tv2001jun07it2301d-1230863180551062-1/75/Preparing-for-BIT-IT2301-Database-Management-Systems-2001d-1-2048.jpg)