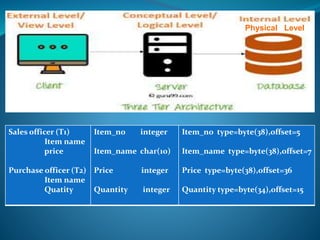
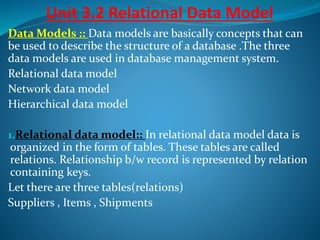
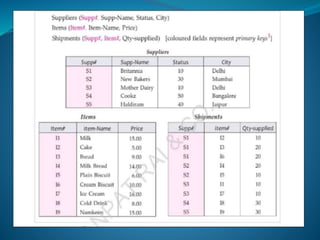
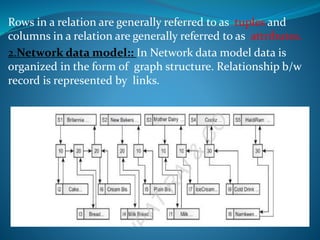
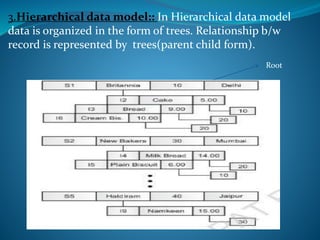
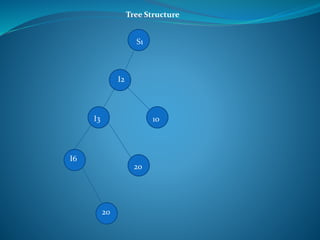
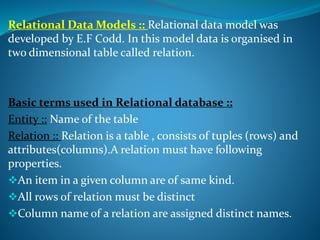
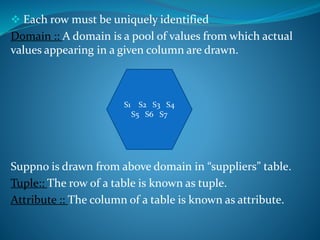
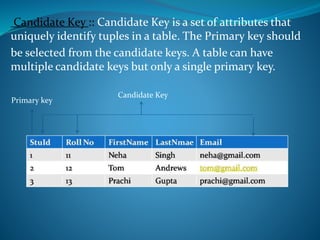
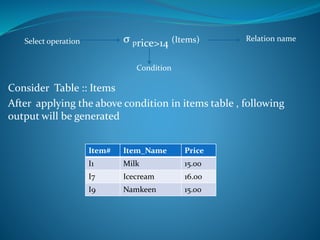
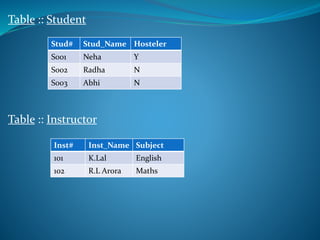
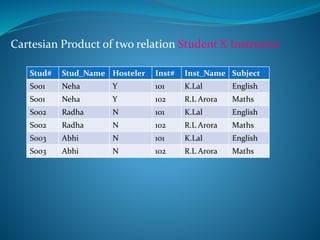
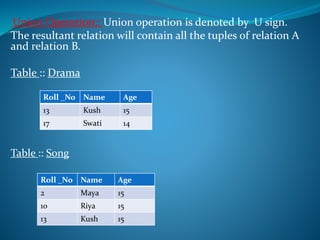
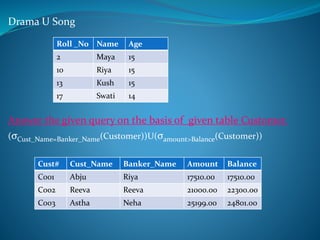
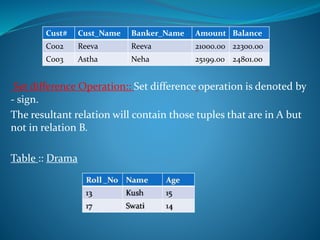
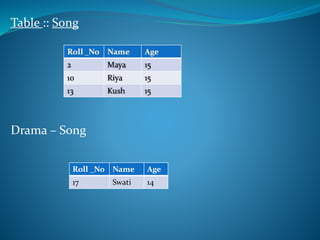
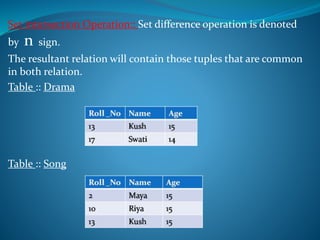
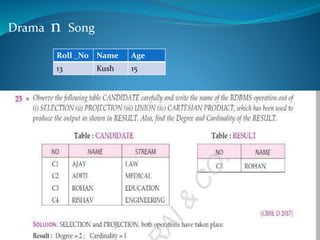
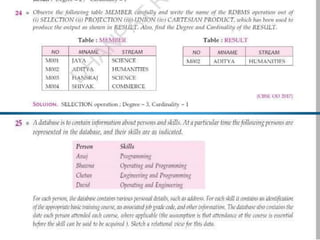
A DBMS is software that stores, maintains, and utilizes databases. It allows for organized data collection and sharing. Some examples of DBMS are MS Access, MySQL, SQLite, Oracle, and FoxPro. A DBMS reduces data redundancy and inconsistency, facilitates data sharing among users, enforces data standards, and ensures data security and integrity. The relational data model organizes data into tables with rows and columns and handles relationships between tables through primary and foreign keys. Relational algebra provides operations like selection and projection to manipulate the data in relational databases.