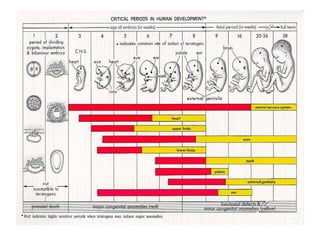
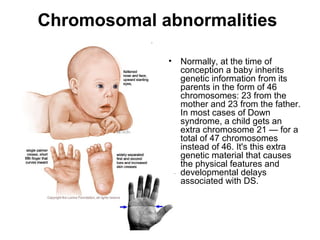
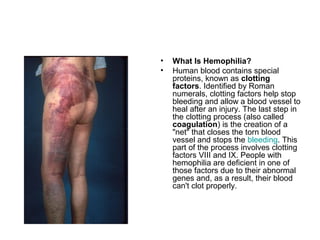
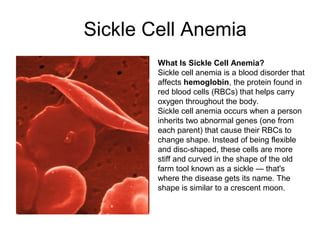
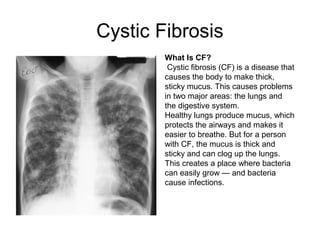
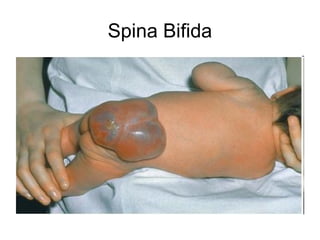
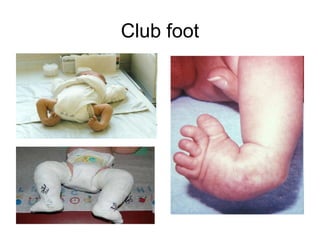
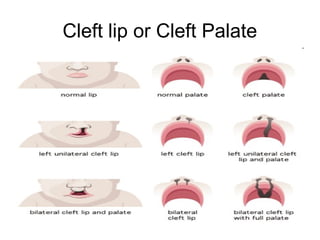
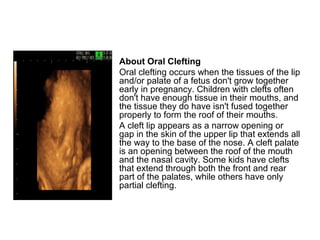
This document summarizes several common genetic disorders and birth defects that can occur during prenatal development. It describes chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome which is caused by an extra chromosome 21. It also discusses inherited disorders including sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, and hemophilia which result from abnormal genes passed down from parents. Specific physical birth defects that may have genetic and environmental causes are also outlined such as clubfoot, cleft lip, cleft palate, and spina bifida.