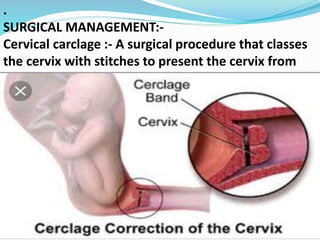
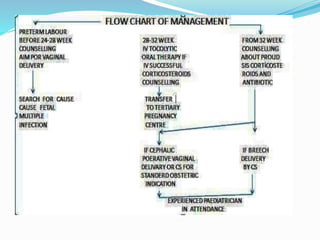
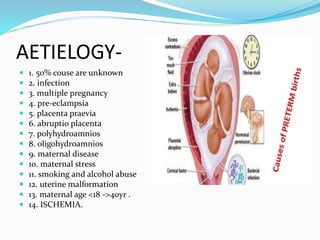
This document provides information about premature labor including its definition, incidence, etiology, risk factors, signs and symptoms, investigations, management, nursing management, prevention, and complications. Premature labor is defined as regular uterine contractions before 37 weeks of gestation. It affects about 5-18% of pregnancies in India. The causes are often unknown but can be due to infections, multiple pregnancies, pre-eclampsia, and other medical conditions. Management involves bed rest, tocolytic drugs, corticosteroids, and in some cases surgical cervical cerclage. Complications for the fetus include respiratory distress, brain injuries, and death. Nursing care focuses on monitoring the mother and fetus, administering prescribed treatments






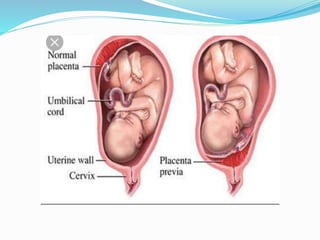

![SIGN / SYMPTOM-
1. back ache [lower back pain ]
2. contraction [every 10 min.]
3. cramping
4. fluid leaking from vagina
5.flu like symptom –Nousea ,
vomiting ,diarrhoea .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/savita-190401081625/85/premature-labor-12-320.jpg)

![MANAGEMENT -
Pharmacological management :-
1. maternal administration of corticosteroid is
advocated in the pregnancy is less then 34
wks
A. Beta methasone -2 dose :-12mg |IM |24 hr
B. Dexa methasone -4 dose:-6mg|IM|12 hr.
2.magnisium sulphate mgso4:- 4-6mg|IV
[20% solution]brain development
3. Antibiotic to reduce the infection .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/savita-190401081625/85/premature-labor-14-320.jpg)