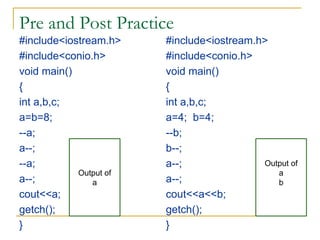
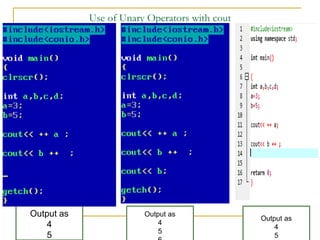
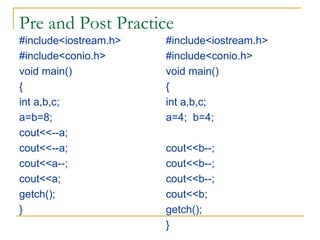
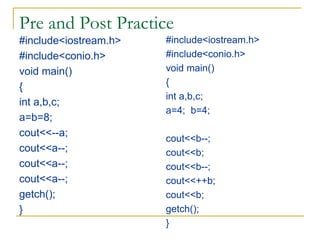
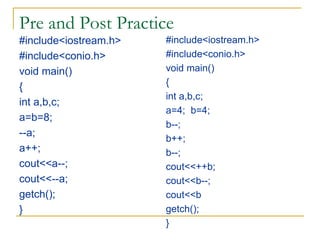
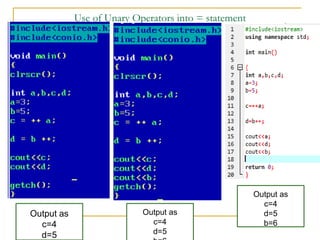
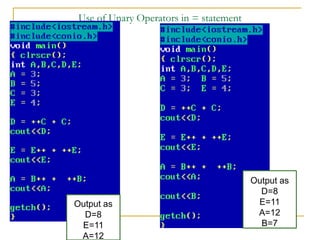
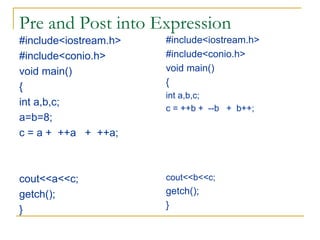
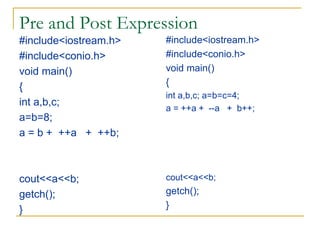
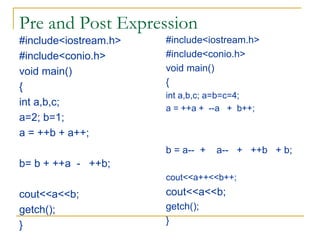
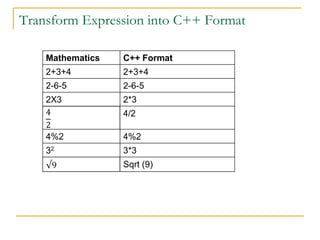
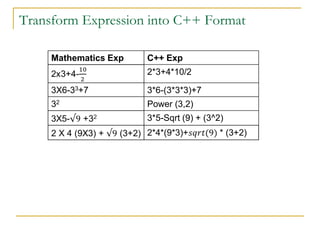
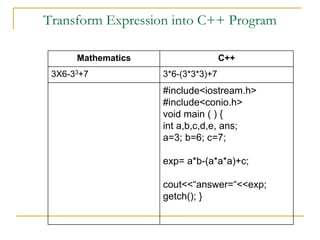
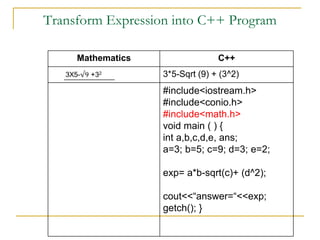
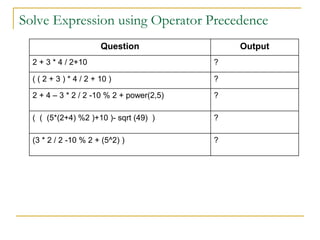
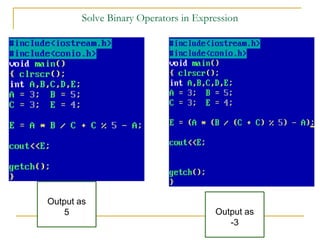
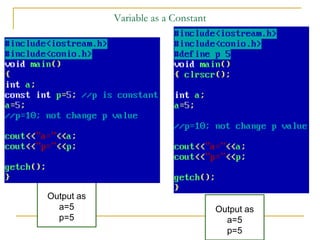
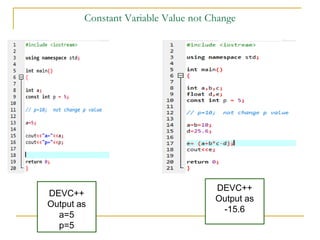
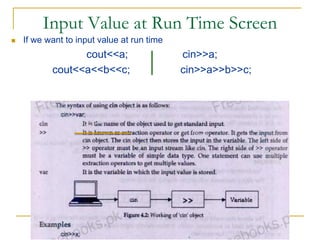
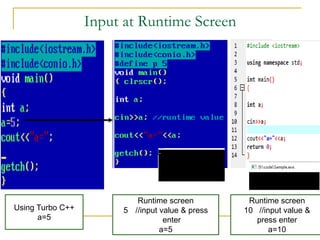
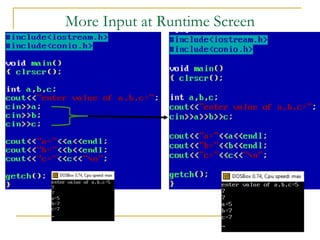
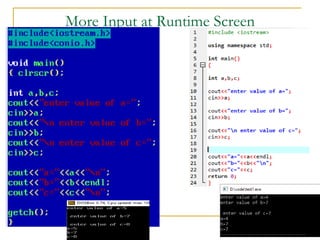
The document contains a series of C++ programming exercises focusing on unary and binary operators, including pre/post-increment and decrement practices, along with operator precedence and variable assignments. It provides example code snippets that demonstrate the effects of these operators when executed, aiming to illustrate fundamental C++ concepts through practical examples. Additionally, the document touches on mathematical operations and expressions transformed into C++ syntax.