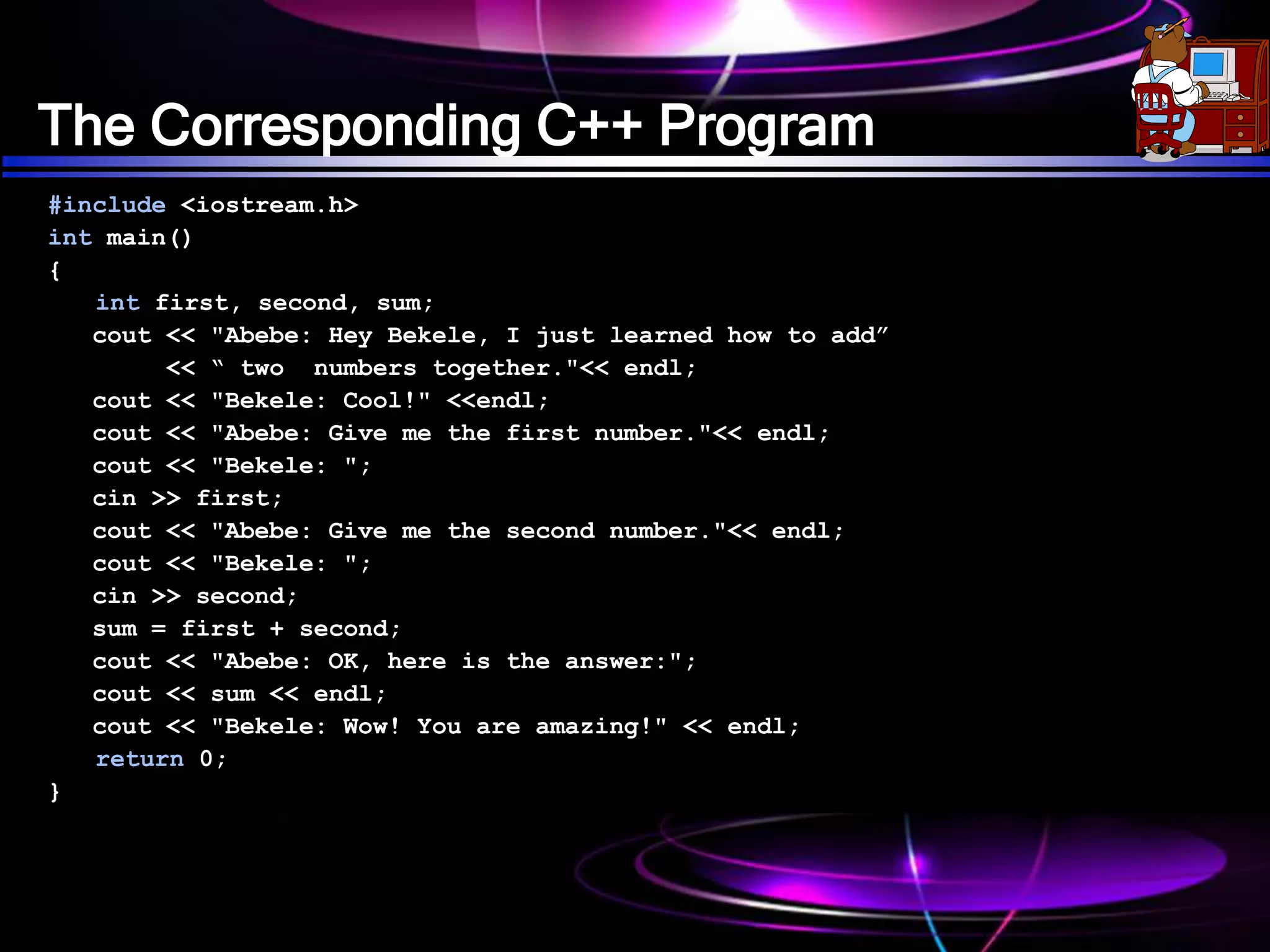
The document provides an overview of C++ operators and statements, including assignment, arithmetic, relational, logic, increment/decrement, conditional, type conversion, and compound assignment operators. It explains how to convert algebraic expressions to C++ code and outlines precedence rules for arithmetic operations. Additionally, it mentions various library functions and includes a quiz to reinforce understanding of the concepts covered.