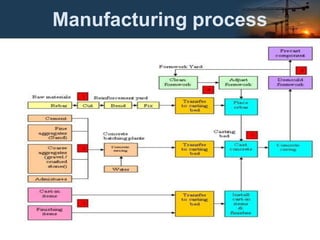
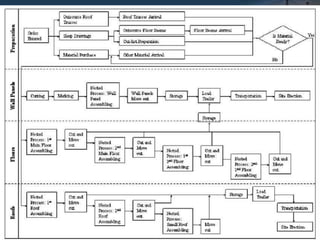
The document discusses prefabricated structures for use in emergency conditions. It defines prefabrication as assembling building components off-site and transporting them to the construction location. Prefabrication offers advantages like faster construction, improved quality control, minimized on-site work during bad weather. The document outlines the need for prefabrication, its advantages and limitations, different uses, principles, methods of prefabrication, production systems, and the prefabrication process from manufacturing to transportation and erection. It also discusses standardization and various machinery used in handling, transporting, and erecting prefabricated components.