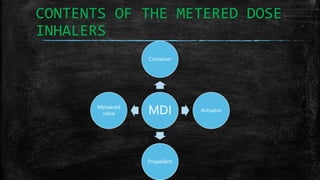
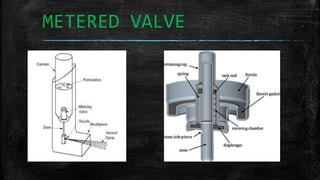
The document discusses metered dose inhalers (MDIs), which are devices that deliver a specific amount of medication to the lungs via a short burst of aerosolized medicine. MDIs are commonly used to treat asthma, COPD, and other respiratory diseases. The key components of an MDI are the container, actuator, propellant, and metered valve. When the metered valve is opened, the payload is forced out as an aerosol mist under pressure from the propellant. MDIs have advantages like delivering a low dose of medication in a portable and fixed amount, but also have disadvantages such as requiring coordination of inhalation and complex hand movements.