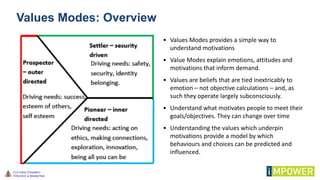
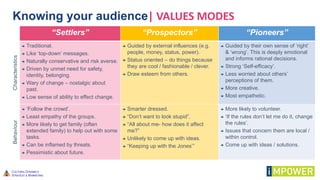
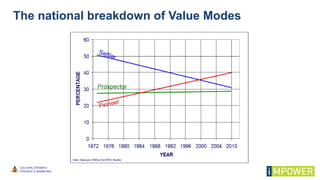
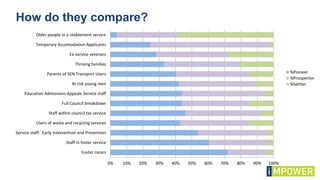
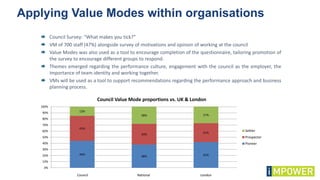
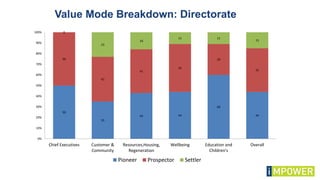
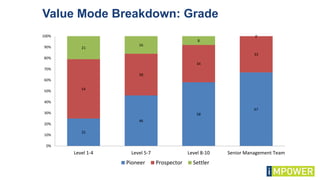
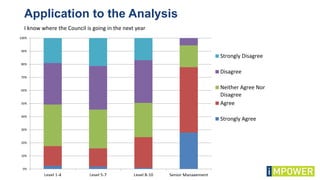
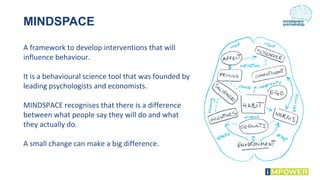
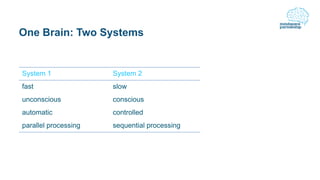
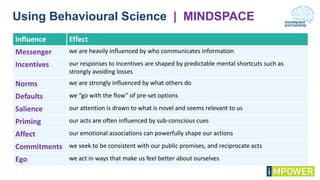
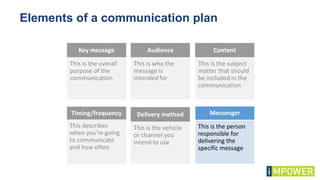
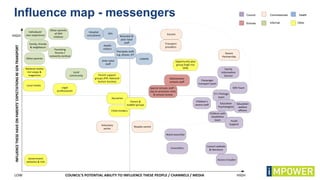
The document discusses effective workshop messaging strategies to influence behavior rather than just changing attitudes, utilizing the 'values modes' framework to understand audience motivations. It highlights different audience categories—settlers, prospectors, and pioneers—and explains how tailored messaging can impact engagement and service delivery across various sectors. Additionally, it introduces the 'mindspace' model which emphasizes behavioral science principles for effective communication and change implementation.



























![Results| Overview of trial results
- 63% of practitioners in the First Team [agreed
or strongly agreed that they have] changed the
way they have conversations*
- 64% of Care Direct call handlers have changed
the way they deal with calls*
‘’It’s a whole
mind-shift…”
(Practitioner - First Team
South)
‘’Made me see the person
differently…’’
‘’We talked about positive risk
taking where I normally wouldn’t
have.’’
‘’Made me see that the person had
a lot more going for them then I
would have normally realised.’’
(First Team South)
* Self reported via post trial surveys
Pioneers
72-77%
Prospectors
20-25%
Settlers
3%
77%
20%
3%
72%
25%
3%
Pioneers Prospectors Settlers
Managers All Staff](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/impower-ppmaseminar2016-160704134210/85/PPMA-Seminar-2016-Messaging-that-Makes-a-Change-42-320.jpg)