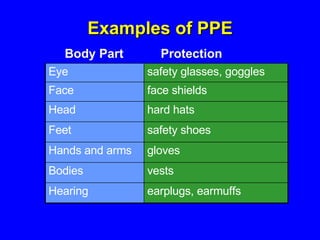
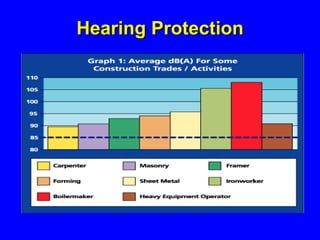
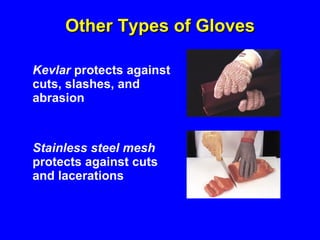
Employers must protect employees from workplace hazards through engineering and work practice controls or by providing personal protective equipment (PPE). They must assess the workplace for hazards, select appropriate PPE to address hazards that cannot be eliminated, and train employees on proper PPE use and care. PPE like hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and protective clothing aim to shield different body parts from hazards such as falling objects, chemicals, extreme temperatures, sharp edges, and more.