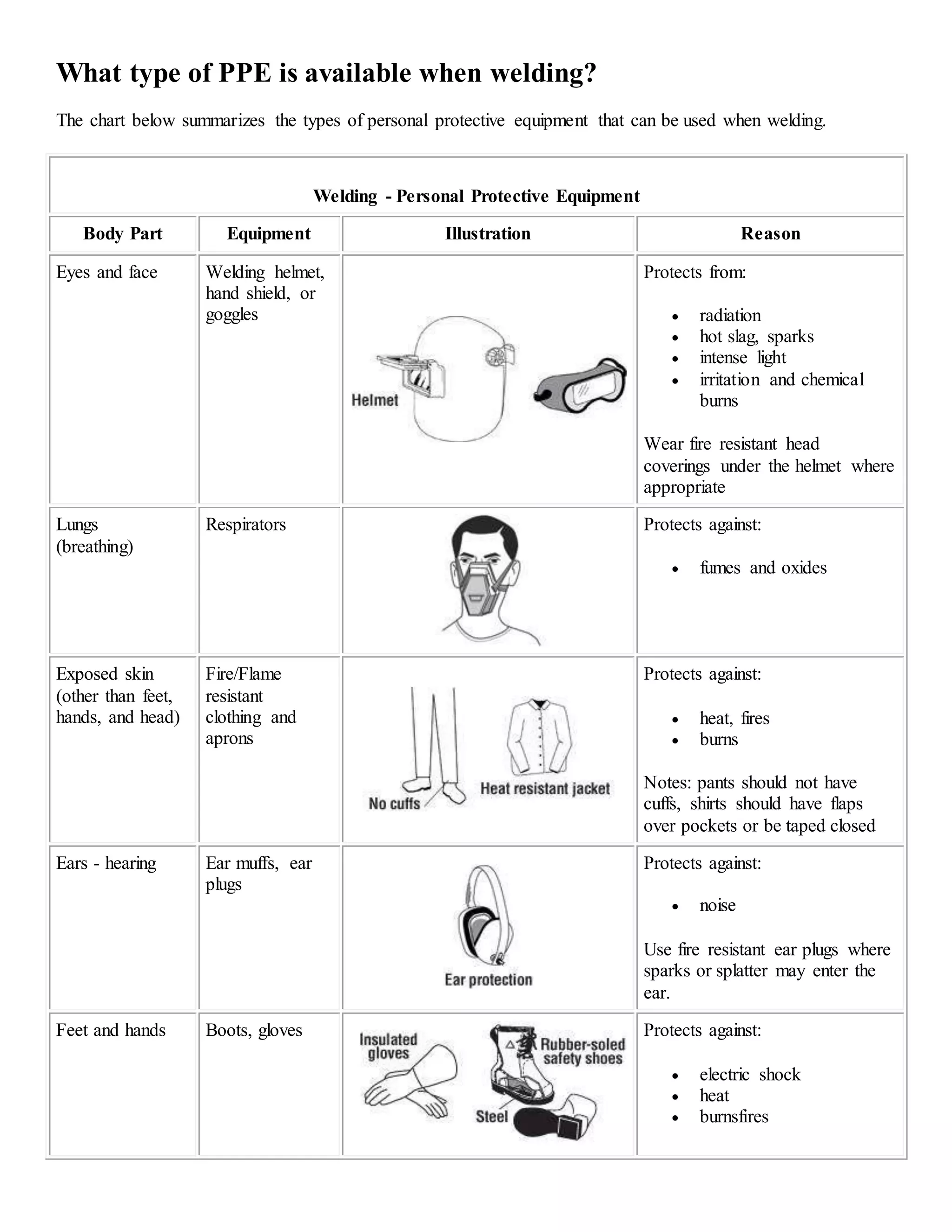
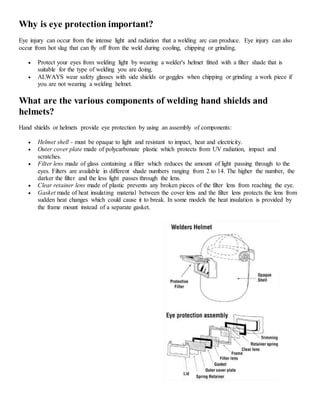
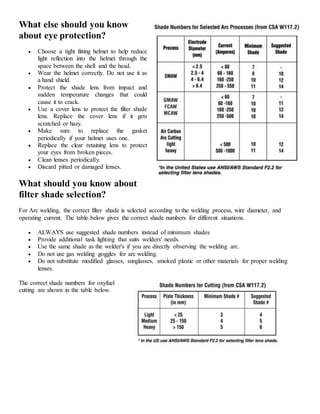
The document discusses personal protective equipment (PPE) used for welding. It provides a chart summarizing the types of PPE needed to protect different body parts, including eyes and face (welding helmet), lungs (respirators), exposed skin (fire resistant clothing and aprons), ears (ear muffs or plugs), and feet and hands (boots and gloves). The PPE protects welders from radiation, hot slag and sparks, intense light, fumes and oxides, heat, fires, burns, noise, and electric shock.