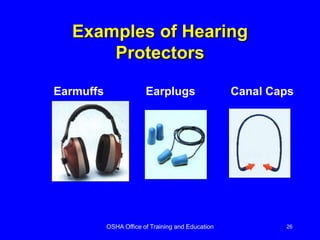
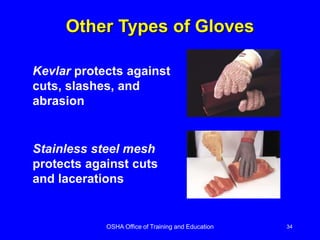
Employers must implement a PPE program to protect employees from workplace hazards. The program includes assessing hazards, using engineering and administrative controls first when feasible, and selecting and providing appropriate PPE to address remaining hazards. Employers must train employees on proper PPE use, care, and limitations. PPE like hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, steel-toed boots, and full body suits can protect against hazards such as falling objects, chemicals, extreme temperatures, cuts, impacts, and more.