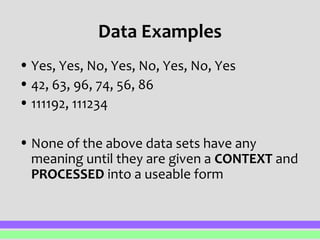
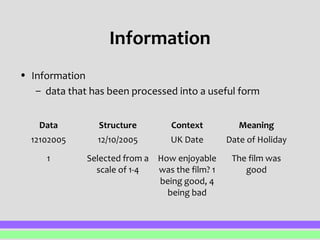
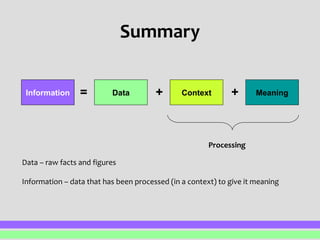
This document defines and distinguishes between data, information, and knowledge. Data refers to raw facts and figures that have not been processed and therefore have no inherent meaning. Information is data that has been processed and organized to give it context and meaning. Knowledge builds upon information by incorporating rules about how to apply and use that information. The key distinction is that data is raw facts, information provides meaning to data through context and processing, and knowledge applies rules to information.