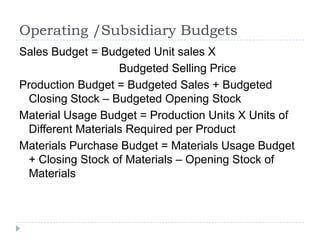
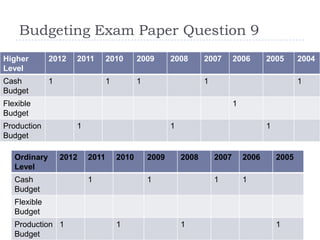
A budget is a financial plan for future costs and revenues over a specific period of time. Budgets have several purposes, including comparing planned costs to actual costs, controlling costs, planning production levels, and comparing performance over time. Operating budgets include sales, production, materials usage, and materials purchase budgets. Principal budgets include cash, master, and flexible budgets. A cash budget forecasts receipts and payments on a weekly or monthly basis. A master budget combines all subsidiary budgets into a projected income statement and balance sheet. A flexible budget allows comparisons of actual performance to the budget by adjusting for different activity levels and separating fixed and variable costs.