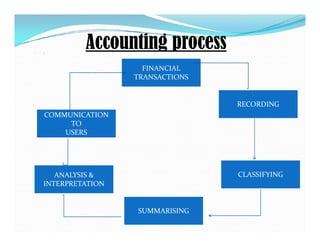
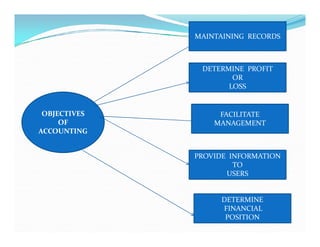
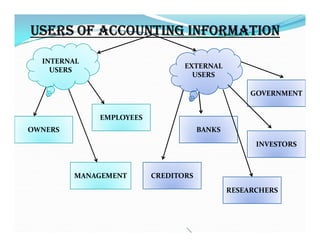
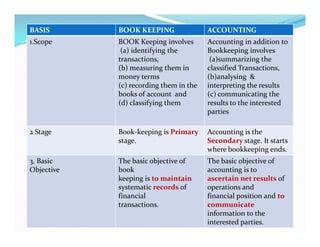
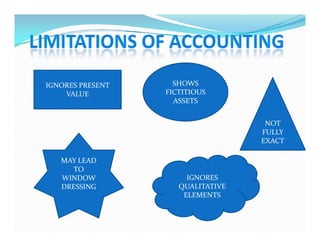
The document provides an overview of accounting, defining it as the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions while interpreting their results. It outlines the accounting process including recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and communicating financial information to various users such as management and external stakeholders. Additionally, it discusses the objectives, limitations, and qualitative characteristics of accounting, emphasizing the importance of reliable and relevant financial information for decision-making.