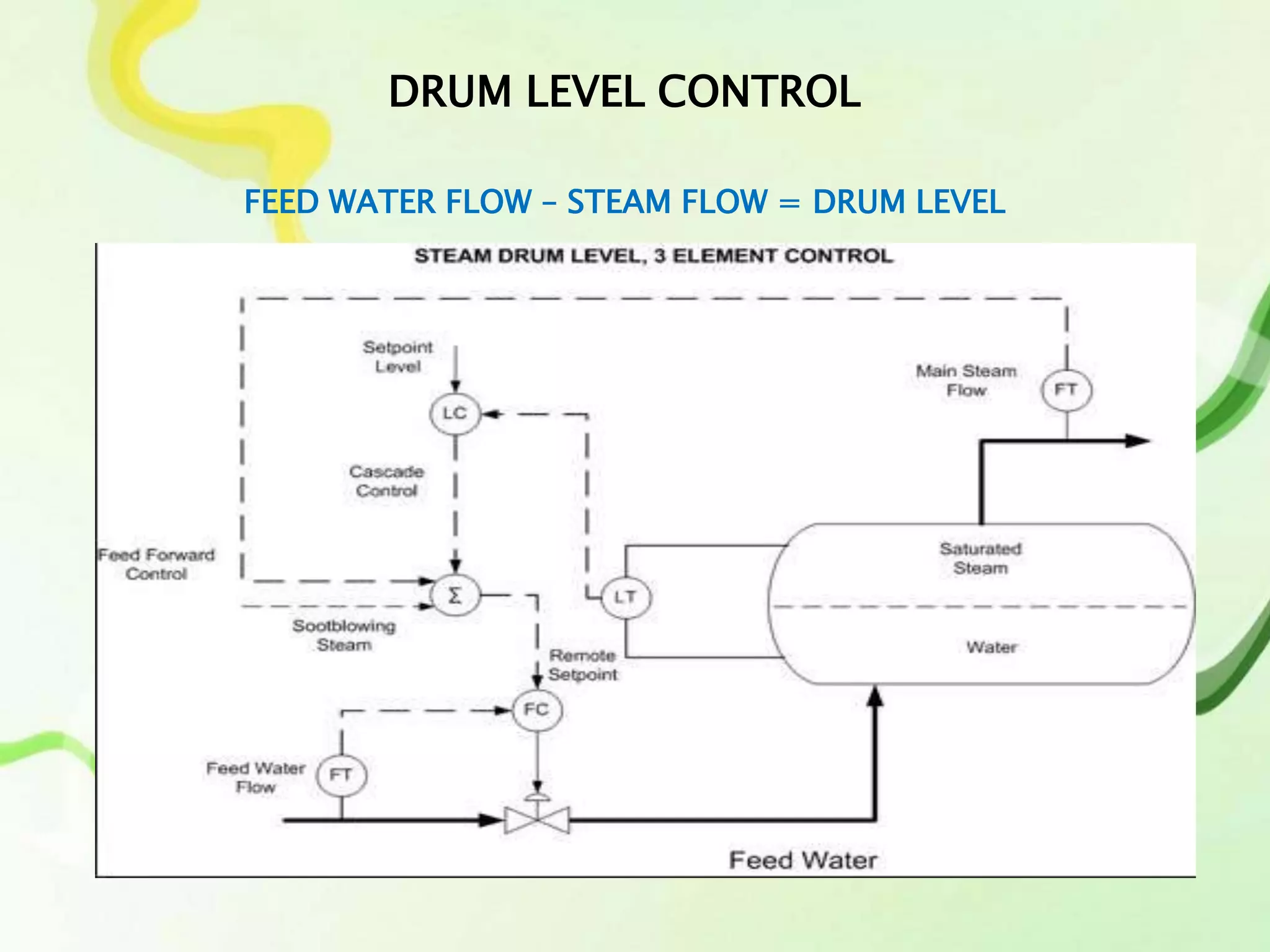
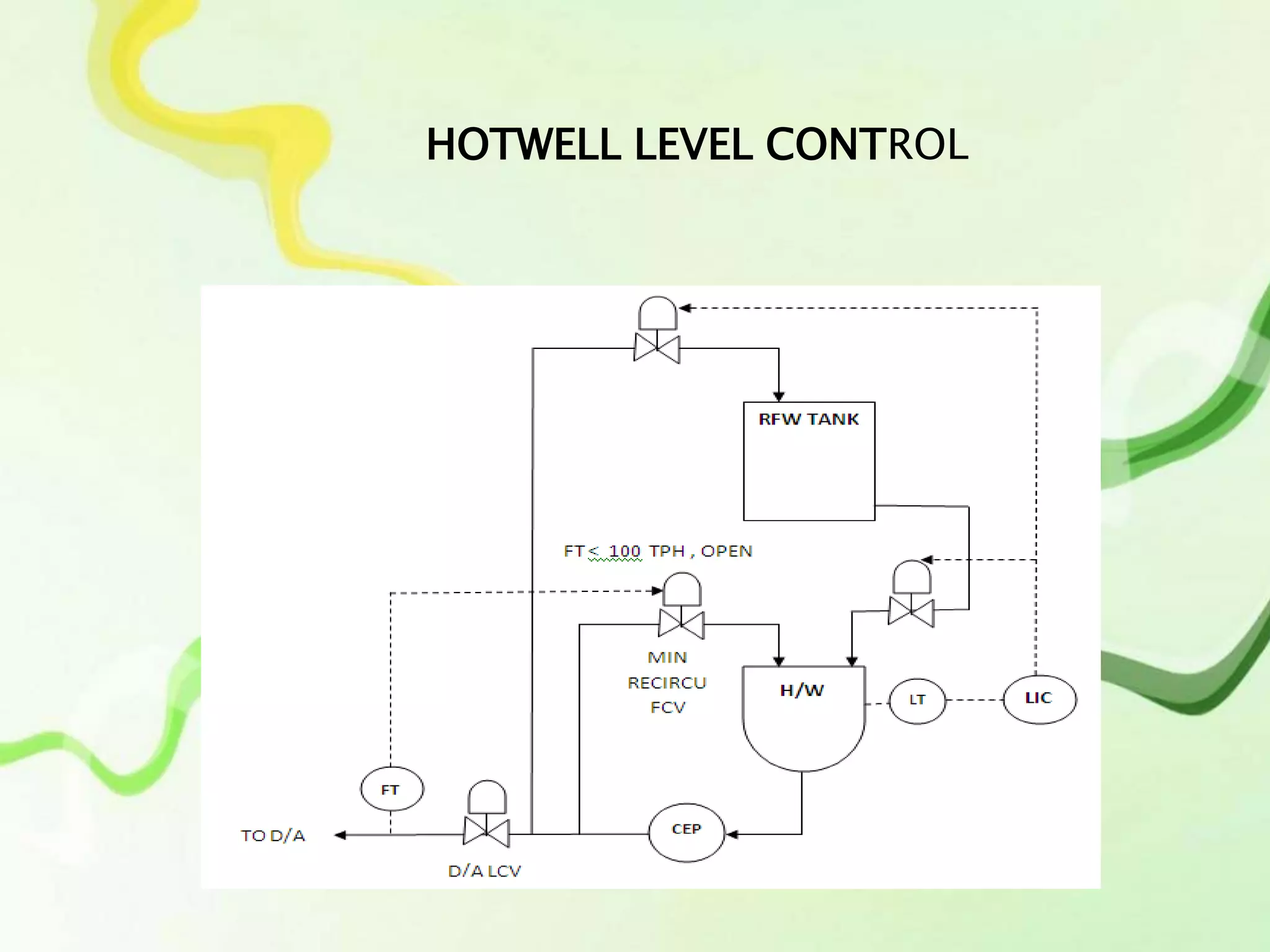
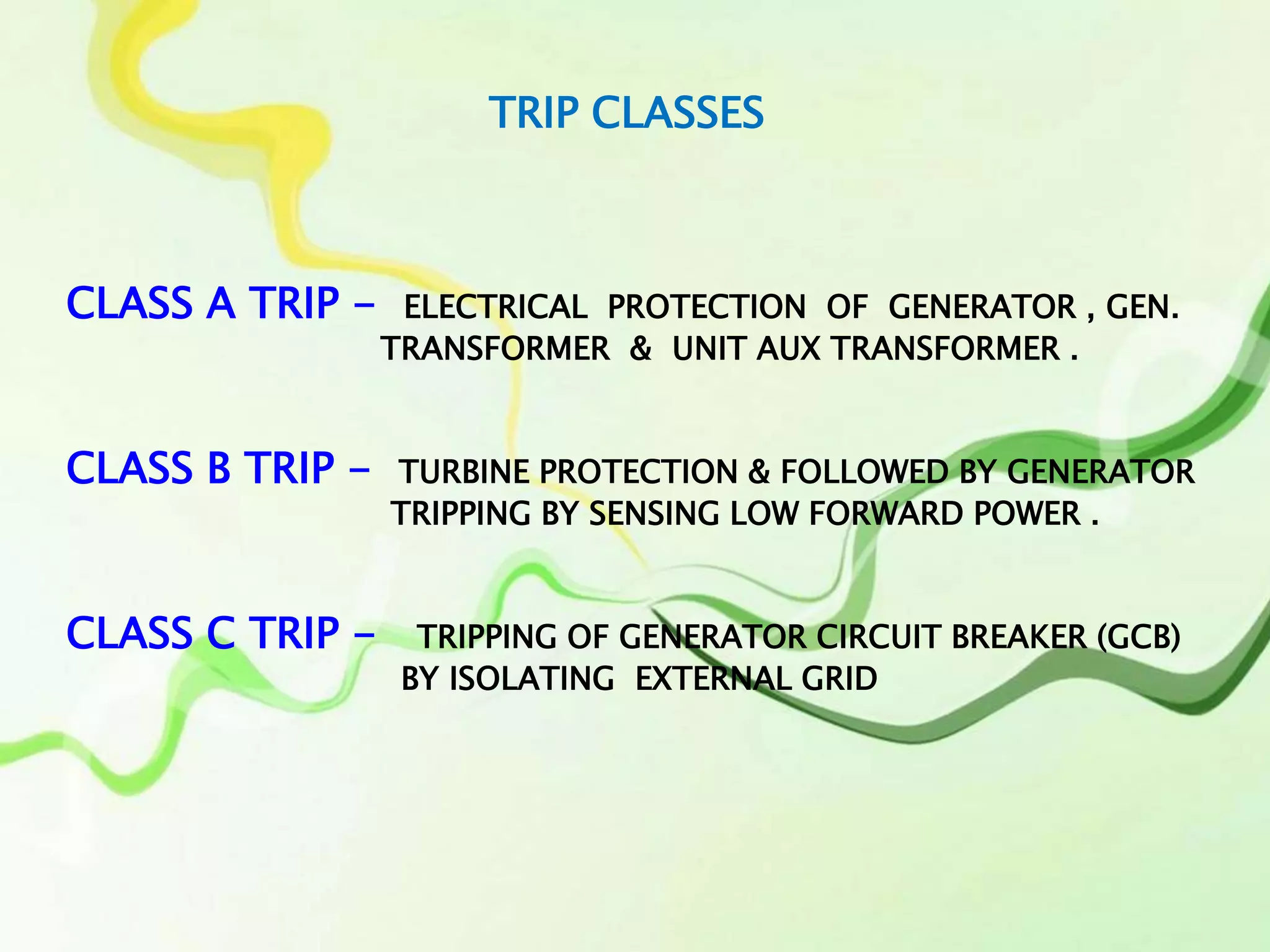
The document outlines the processes and instrumentation involved in power plant operation, focusing on control mechanisms like drum level control and turbine loops. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper water levels in condensers and details various trip classes for generator and turbine protection. Additionally, it describes control strategies such as feed forward control and three-element control to optimize performance and efficiency.