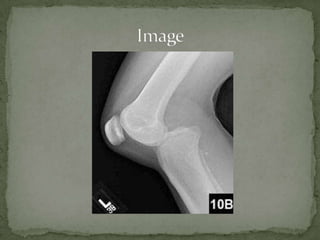
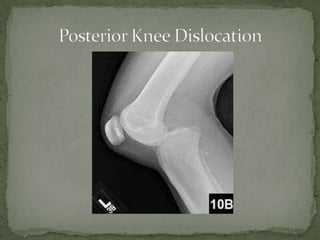
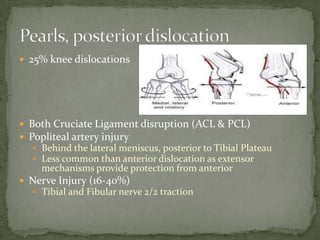
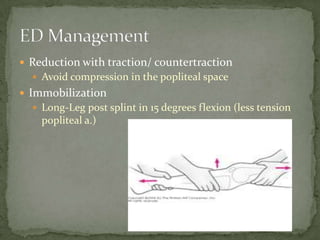
A 37-year-old female presented with left knee pain after being in a motor vehicle collision where her knee struck the dashboard. On examination, her left knee was grossly unstable and unable to extend with decreased sensation over the lateral foot. She likely suffered a posterior knee dislocation with injuries to both cruciate ligaments, the popliteal artery, and nerves. Treatment requires reduction, immobilization, assessment of vascular injury such as with CT angiography, and emergent orthopedic referral.