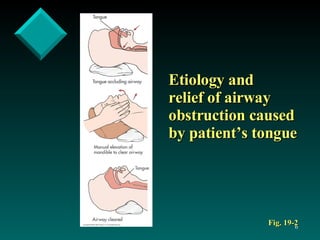
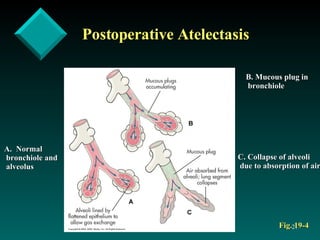
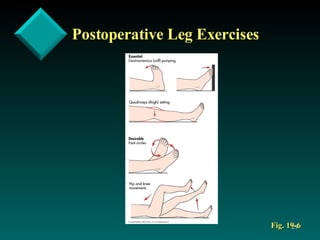
The document discusses postoperative care in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU). It outlines assessments and potential complications to monitor for various body systems, including respiratory (atelectasis, hypoxemia), cardiovascular (hypotension, arrhythmias), neurological, pain, hypothermia, nausea and vomiting. Nursing diagnoses and interventions are provided to manage complications and optimize recovery, such as deep breathing exercises to prevent atelectasis, monitoring vital signs and urine output, providing pain relief, and addressing psychological needs before discharge.