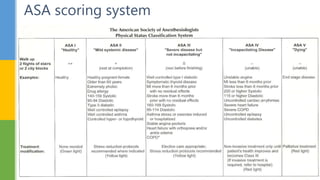
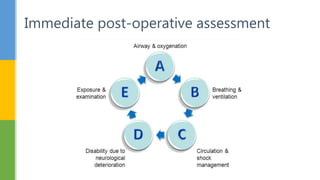
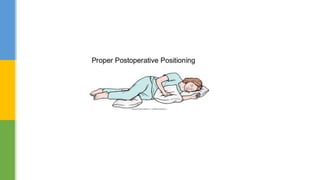
The document outlines the procedures and considerations for preoperative and postoperative assessments in surgical patients. It emphasizes the necessity of thorough medical evaluations to ensure patient safety and readiness for surgery, detailing various medical histories, medication management, and potential complications. Postoperative care is also covered, focusing on monitoring, pain management, and addressing complications to ensure recovery and discharge readiness.