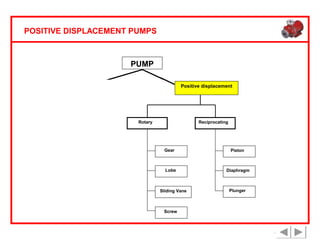
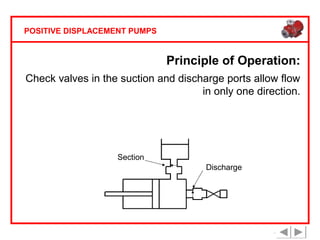
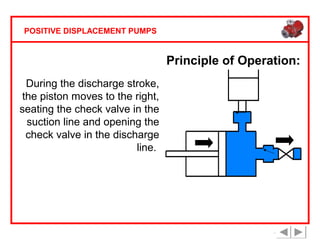
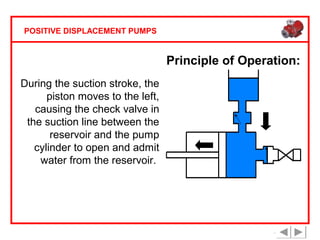
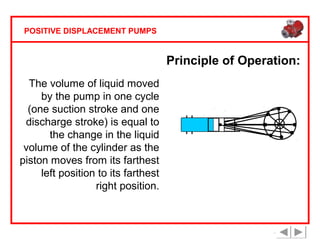
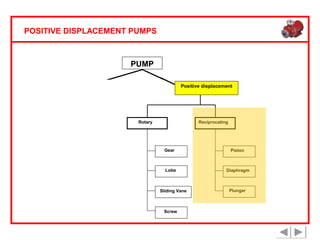
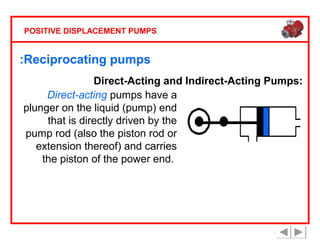
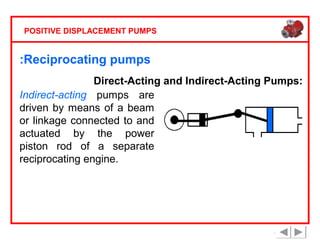
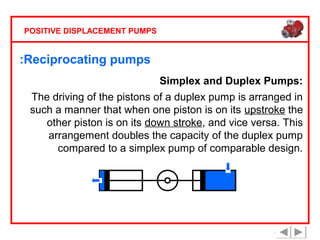
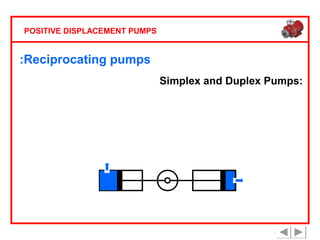
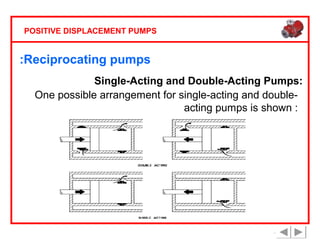
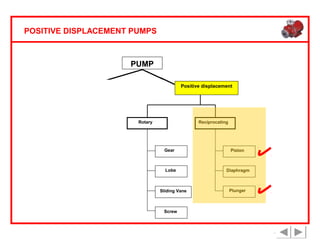
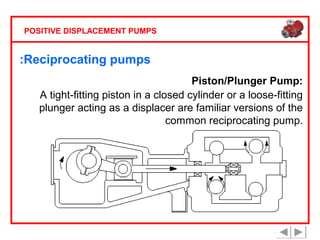
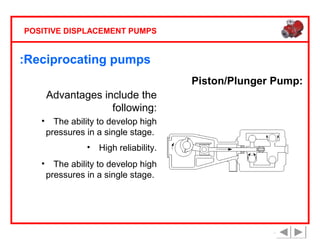
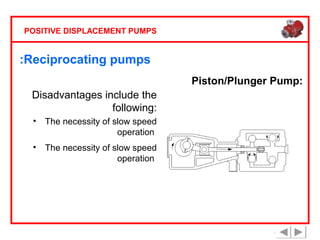
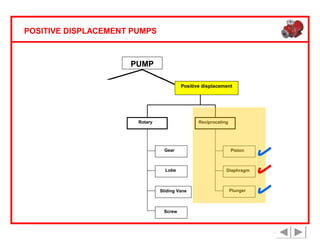
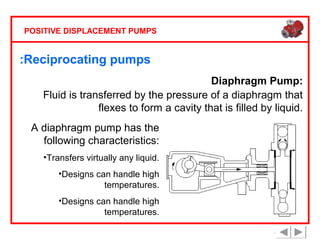
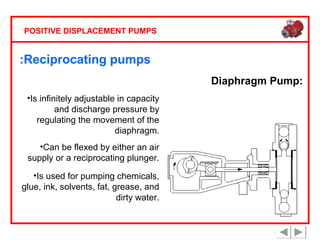
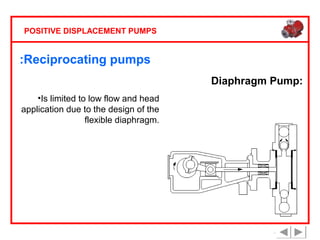
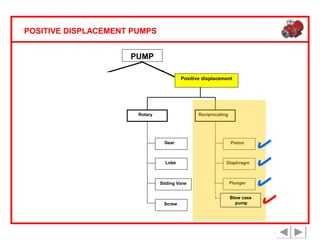
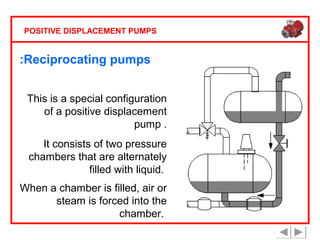
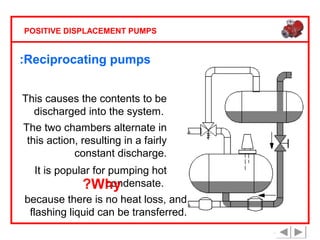
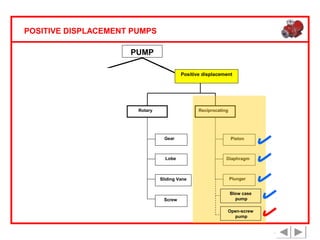
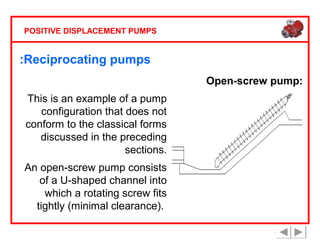
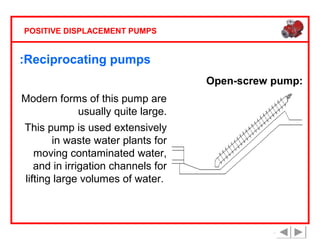
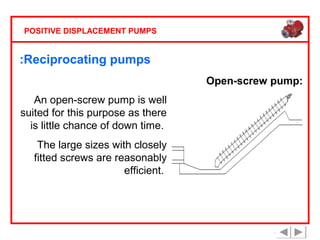
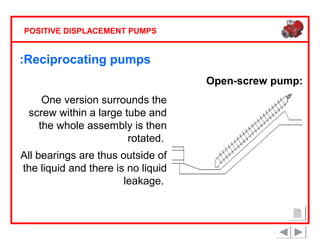
Positive displacement pumps are classified into three main categories: reciprocating, rotary, and diaphragm pumps, which deliver liquid in fixed volumes per operation cycle. These pumps operate by entraping a liquid quantity and using mechanisms such as pistons and check valves to facilitate flow in one direction. While they are capable of high pressures and flow rates, they may require slow speeds and have specific design characteristics that influence their application.