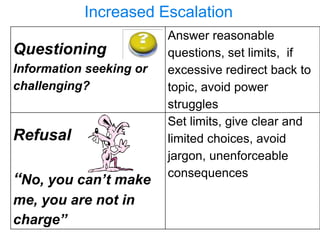
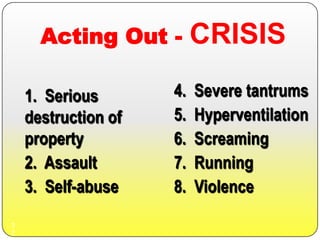
This document provides strategies for effective behavior management and supporting students in crisis. It begins by describing proactive behavior management and identifying causes of disruptive behavior. It then discusses strategies to decrease disruptive behavior and prevent crisis, including establishing clear expectations, teaching routines, and focusing on positive relationships with students. The document outlines signs that a student may be escalating and recommends response strategies, tools to reduce student stress, and techniques for calming a student in crisis and helping them regain control.