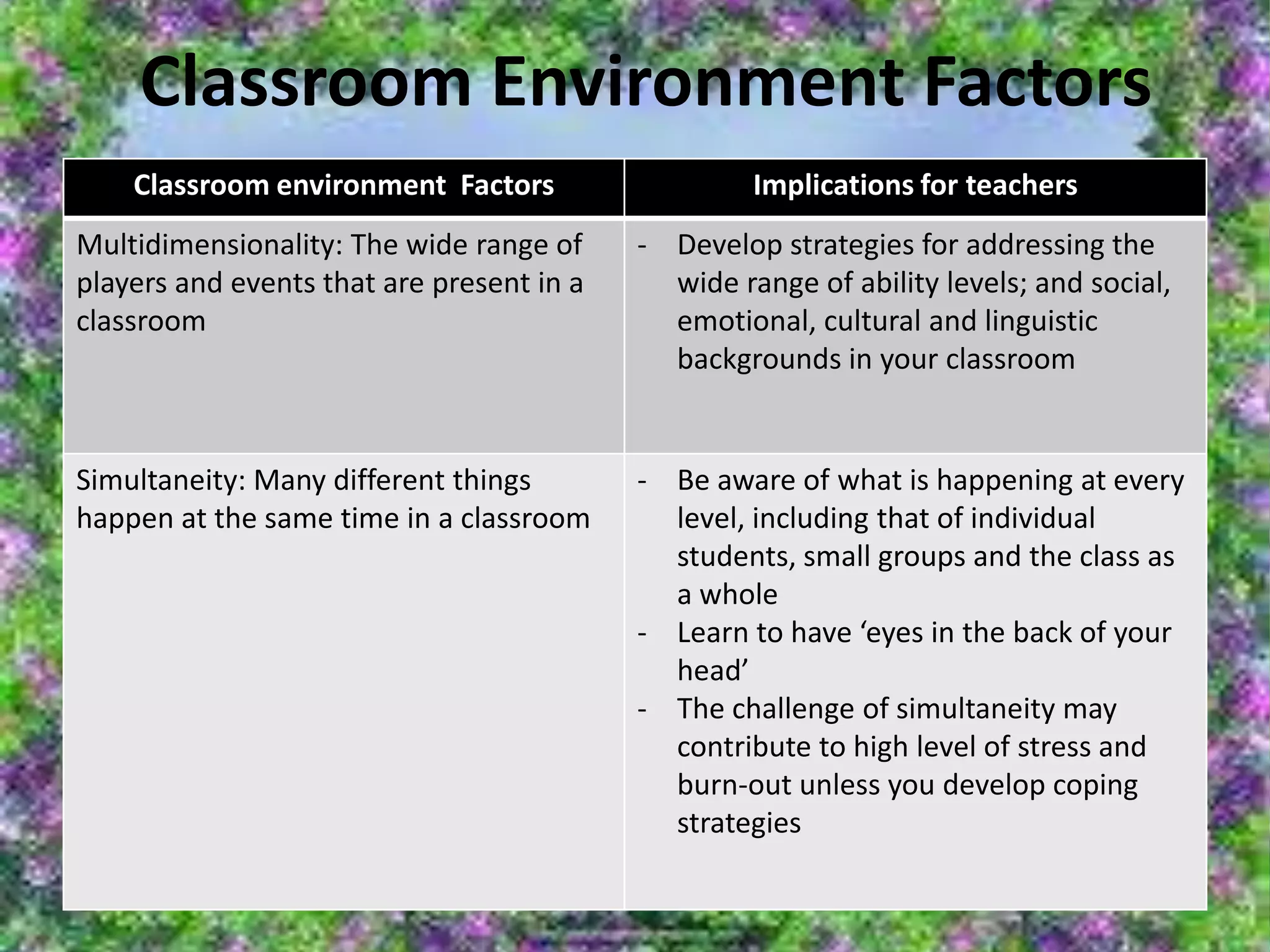
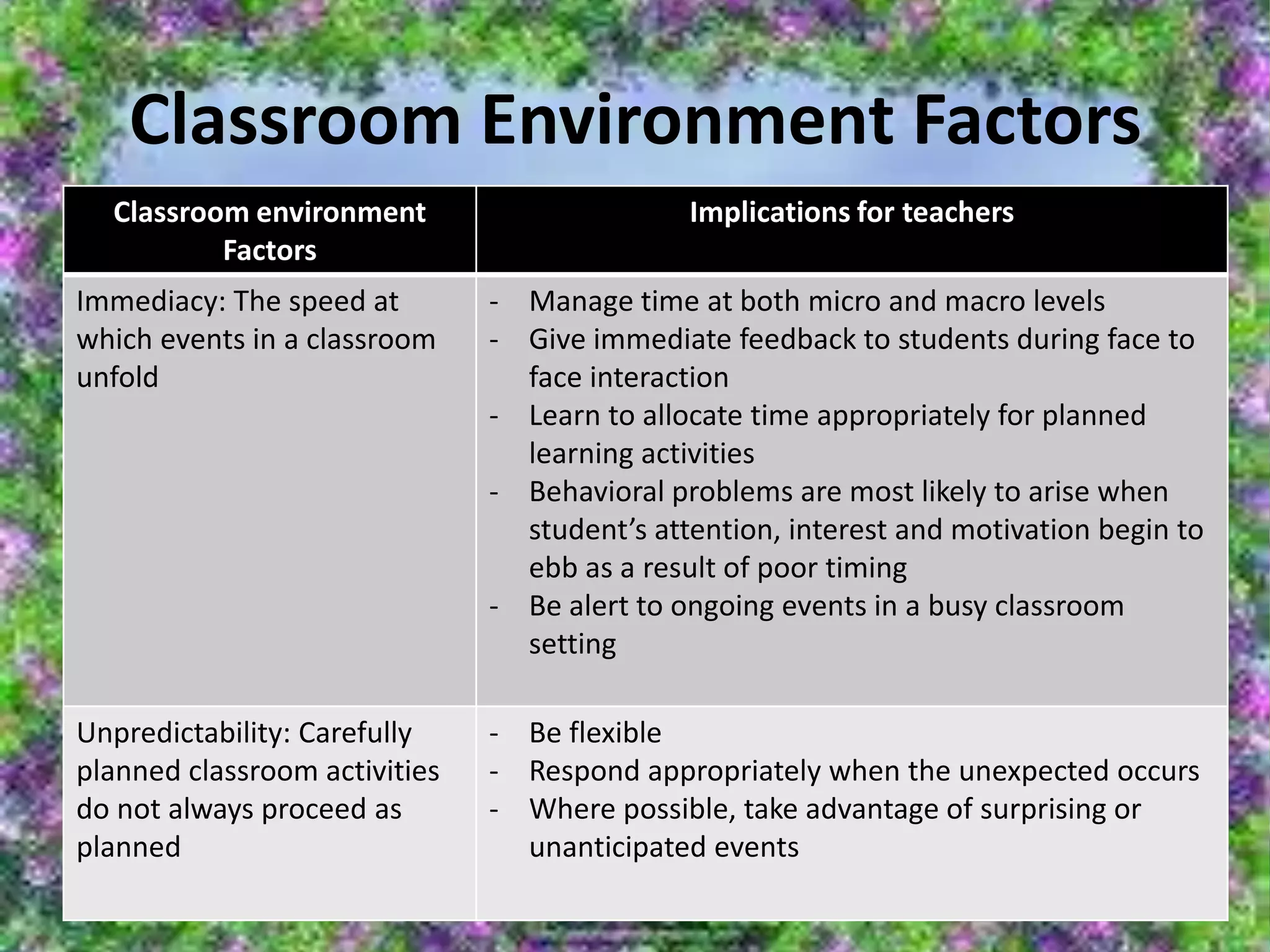
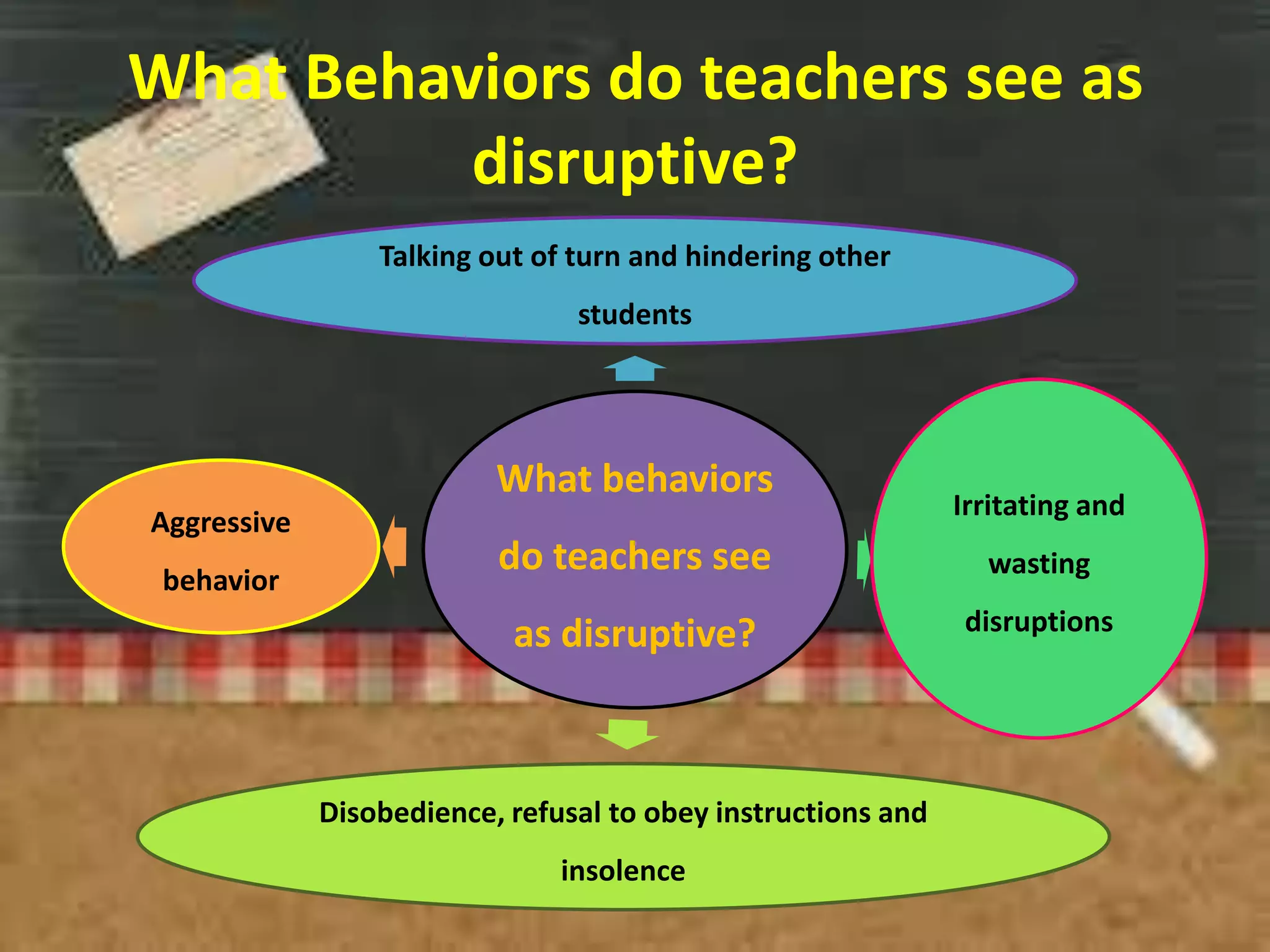
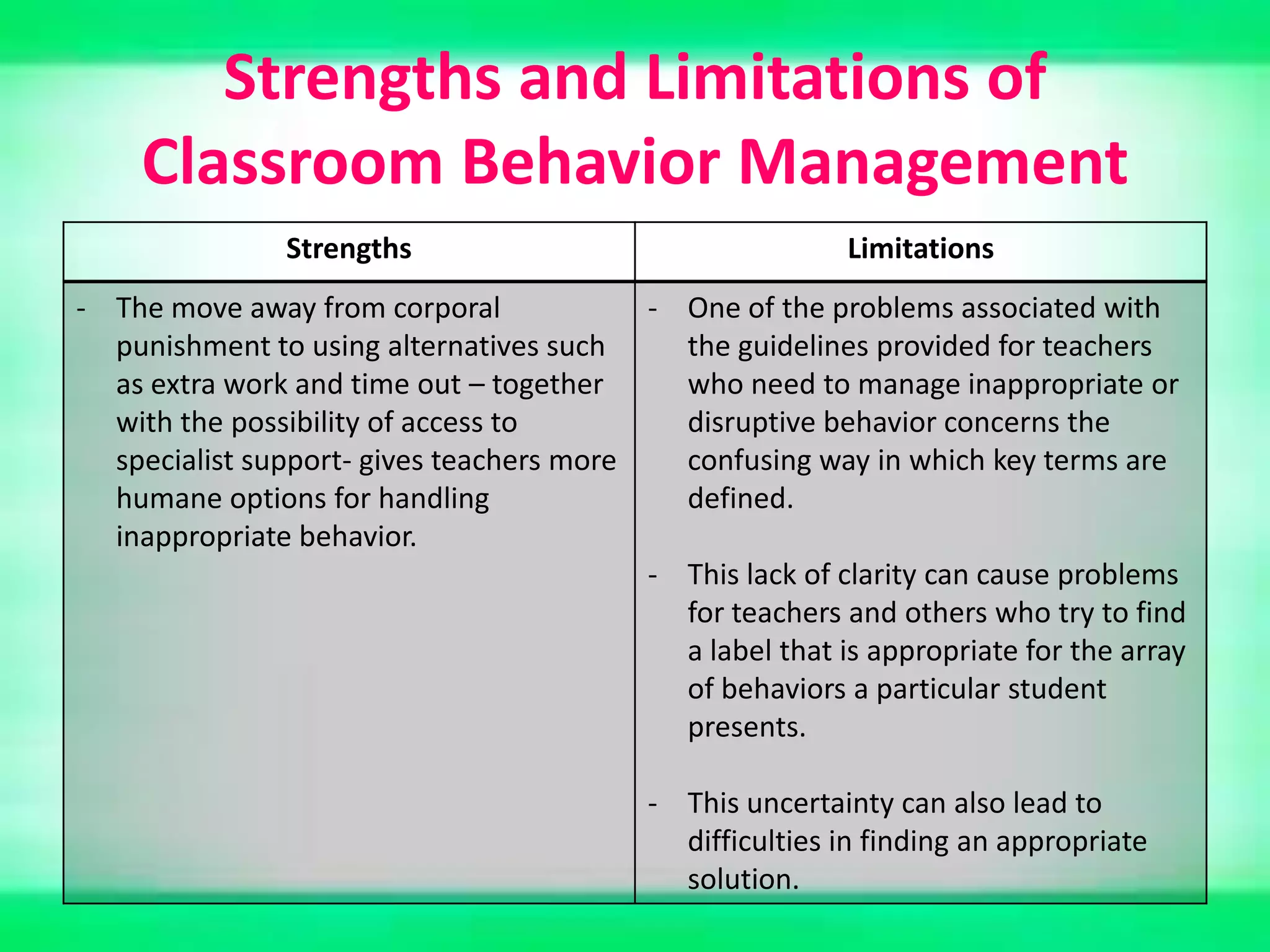
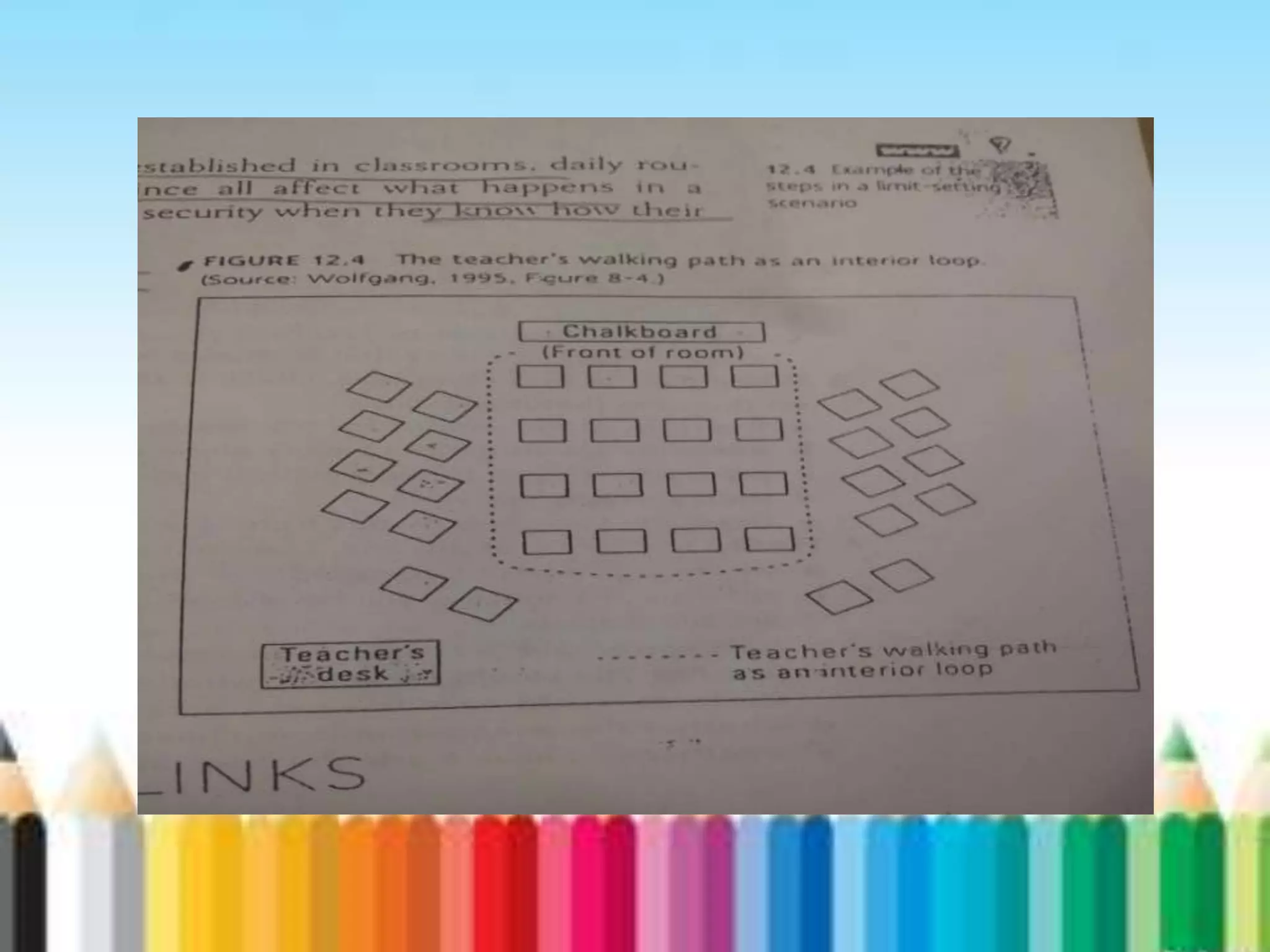
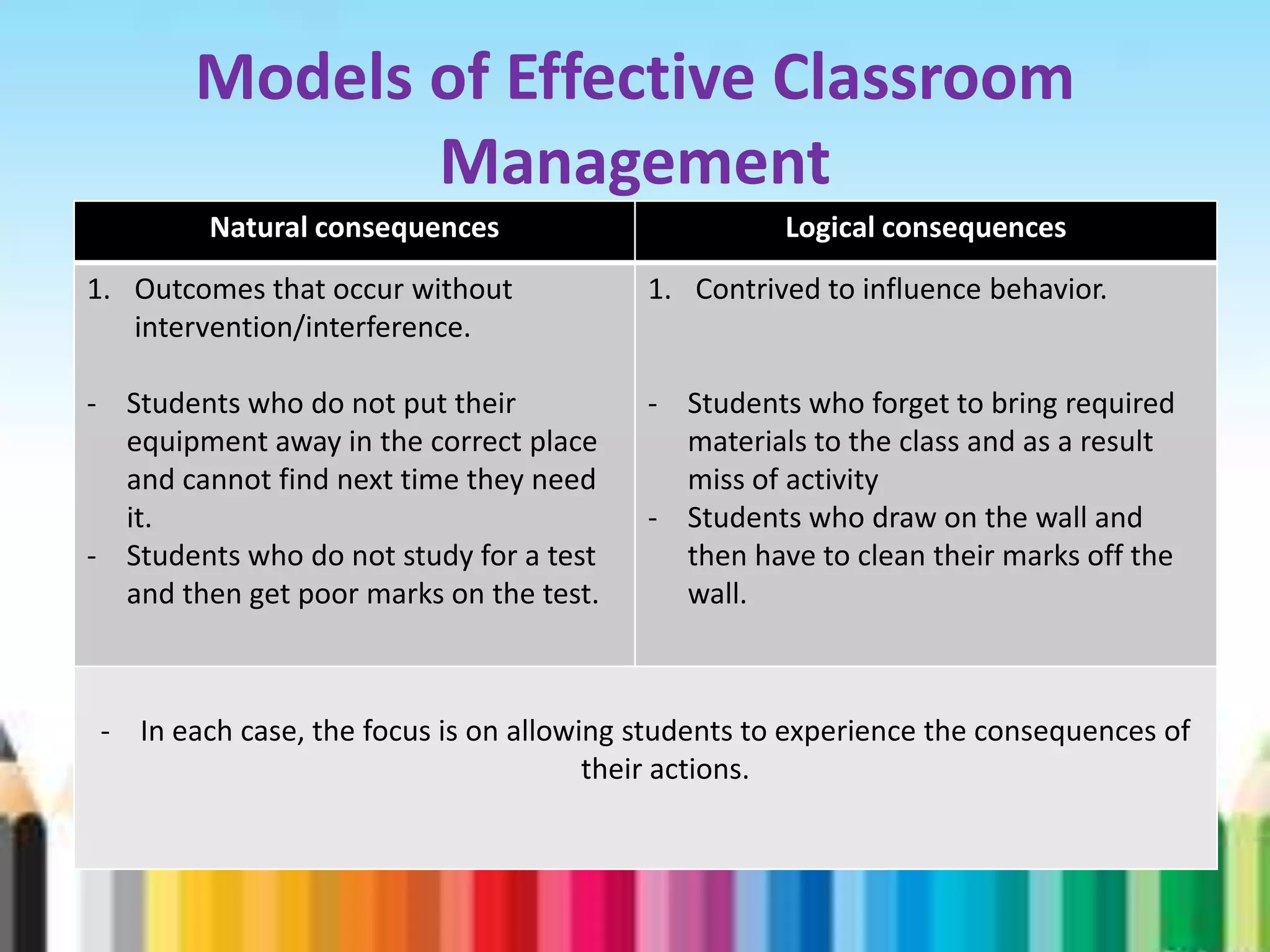
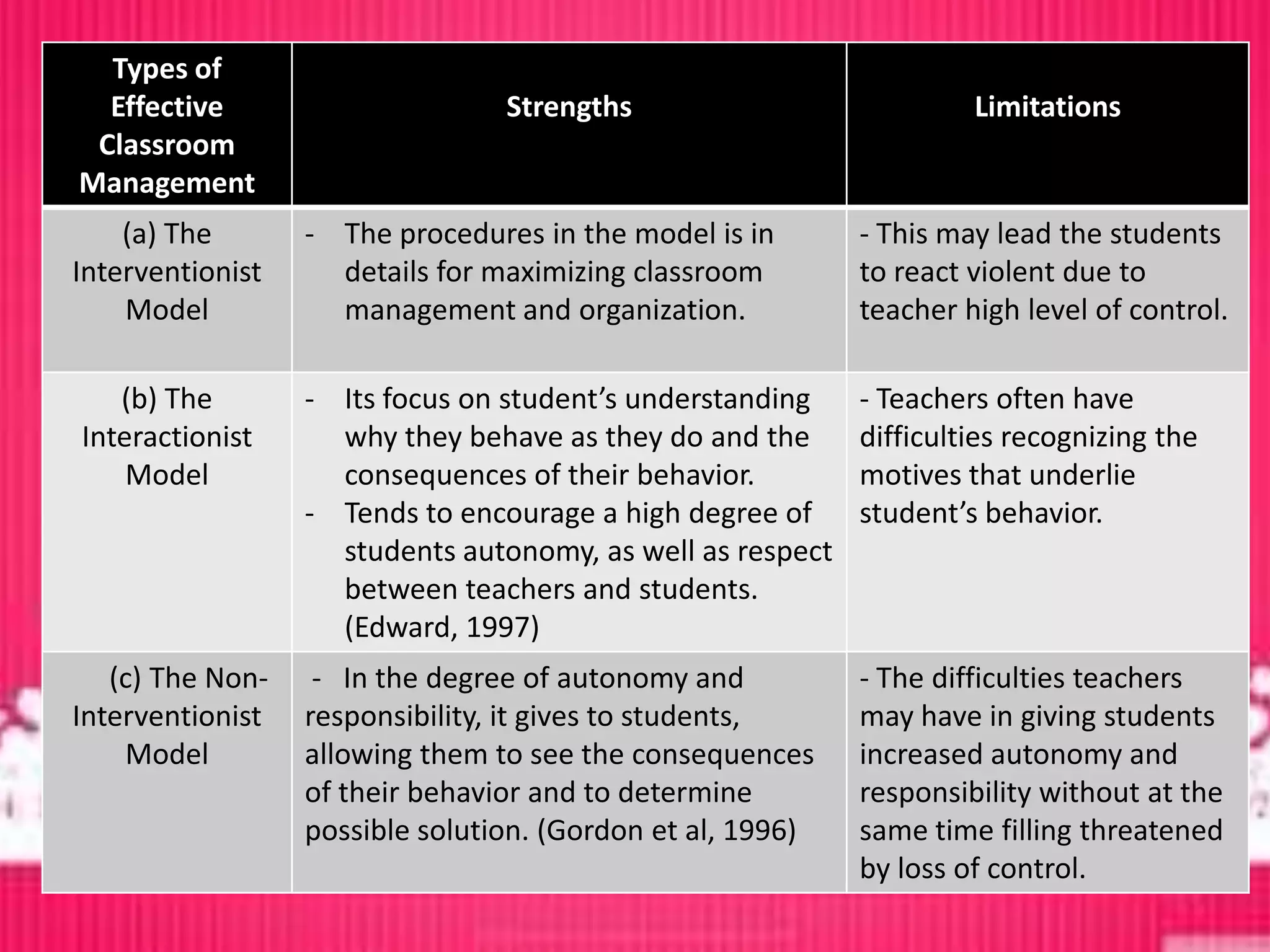
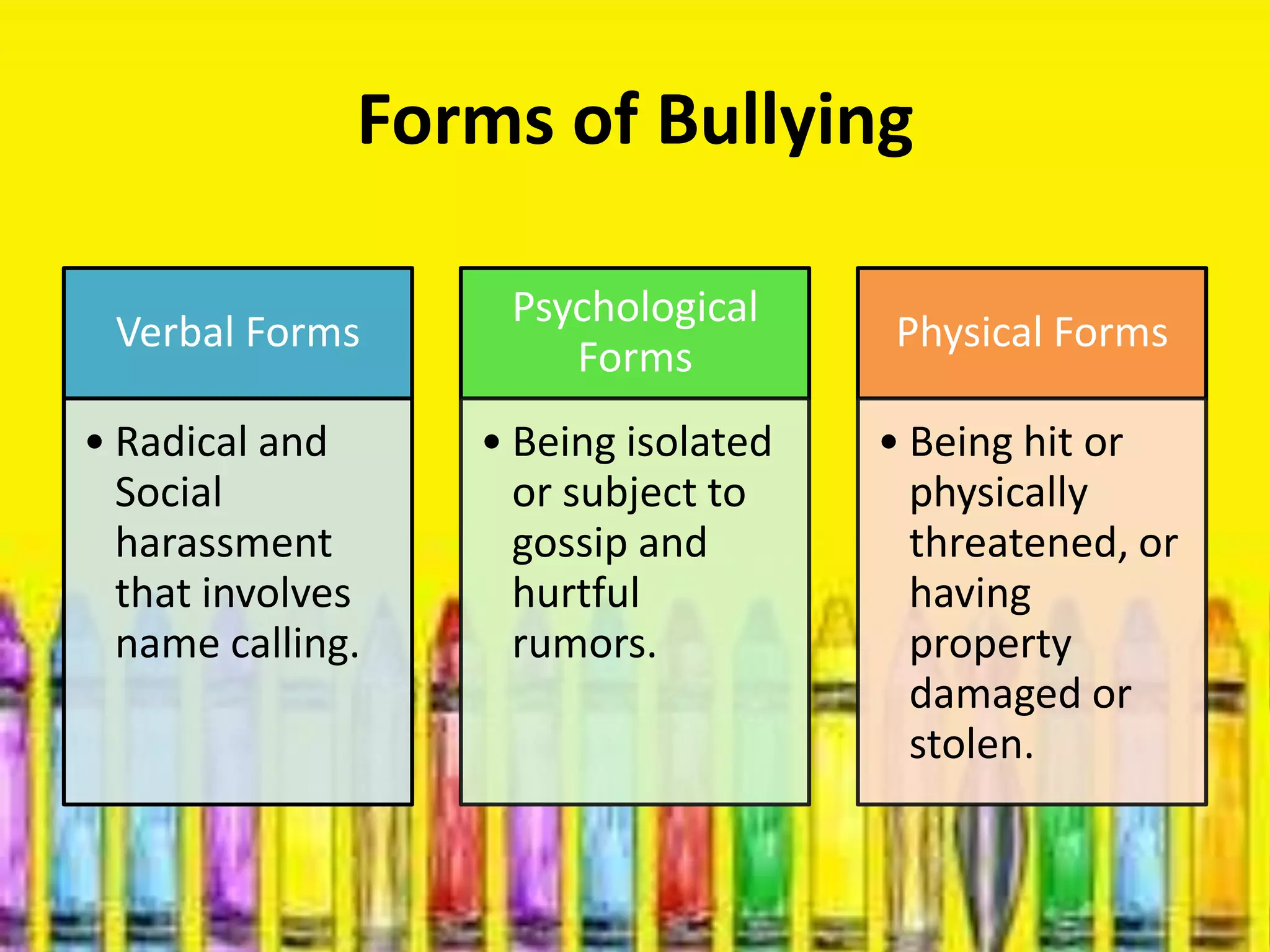
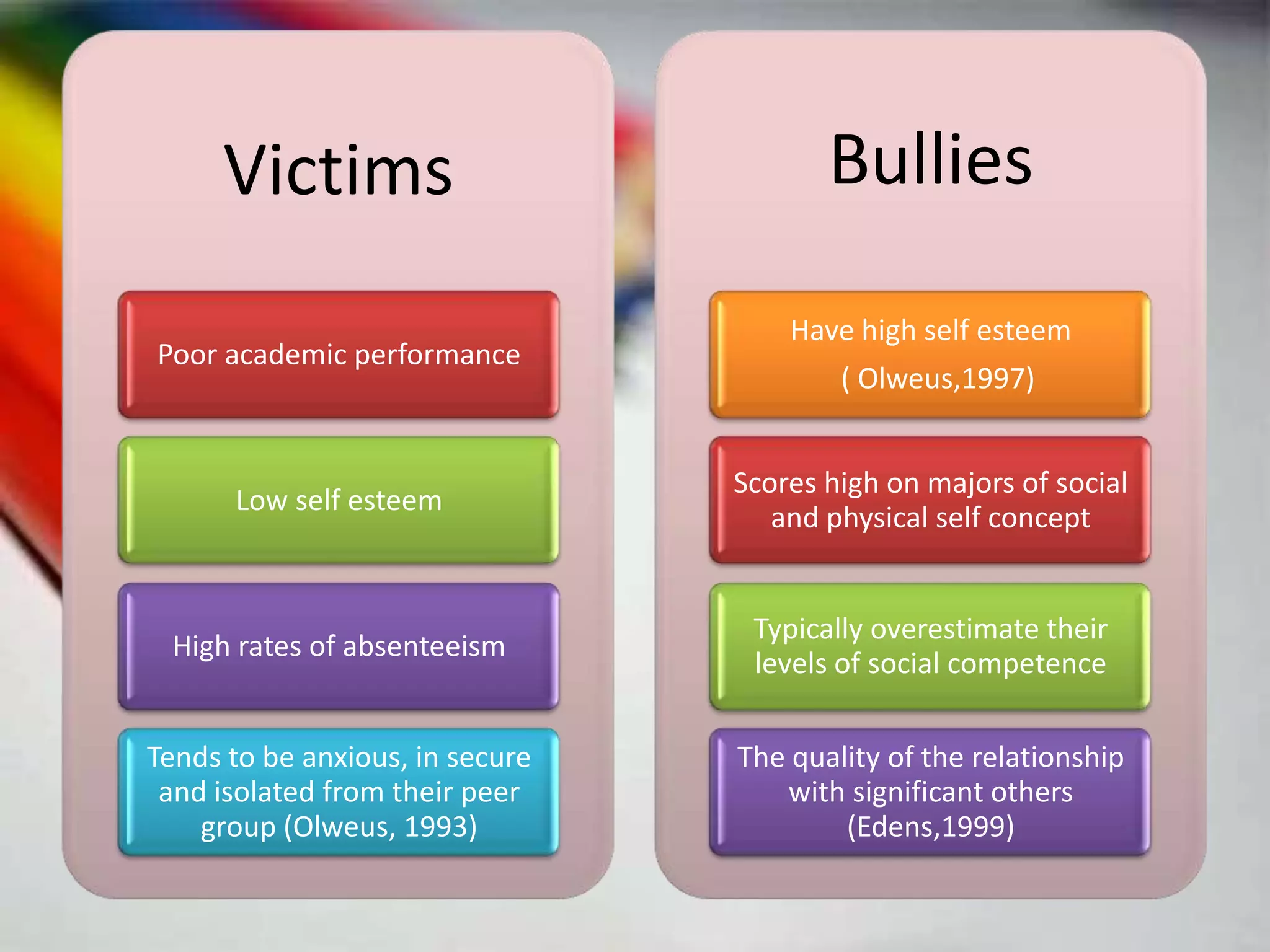
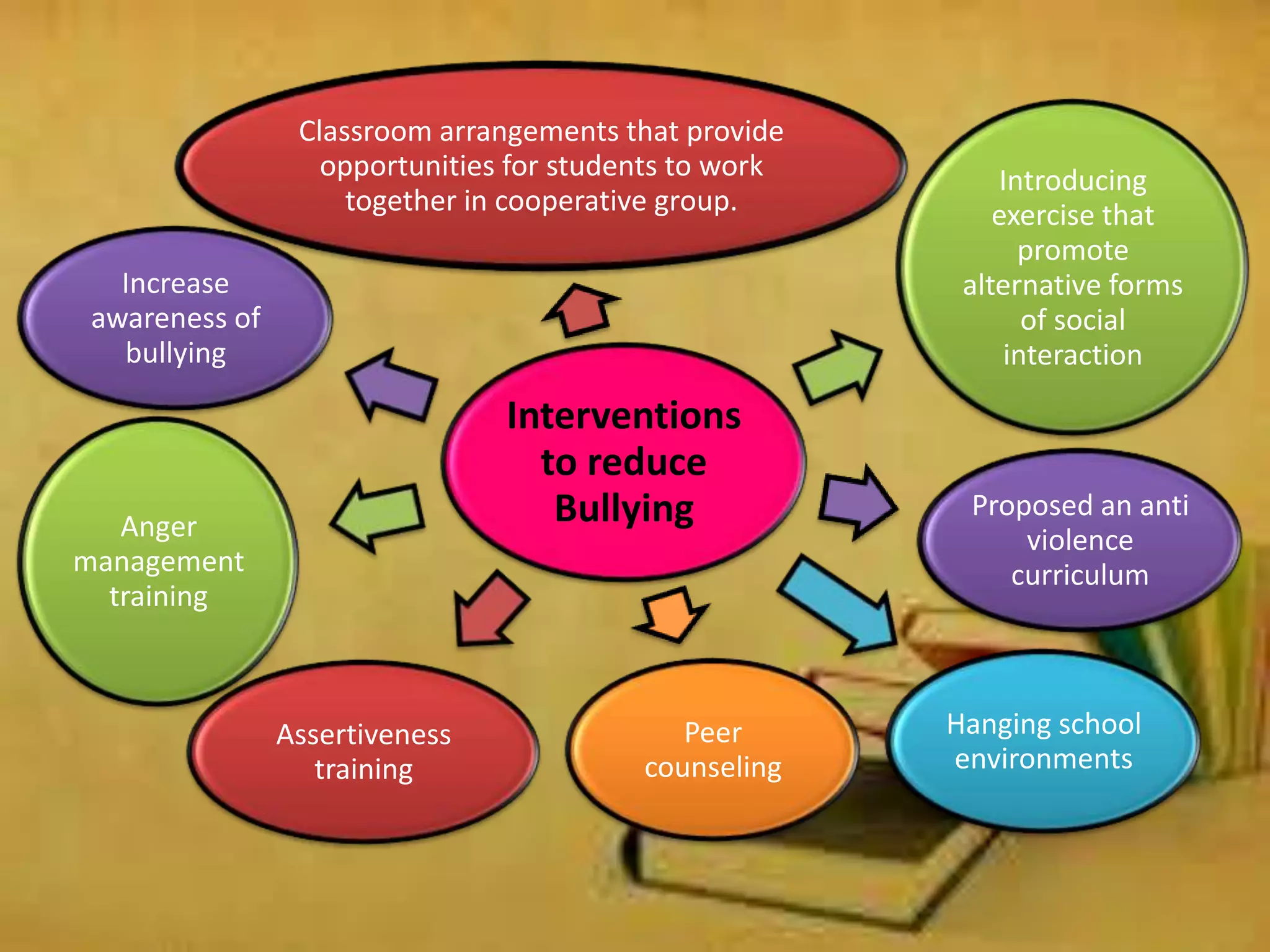
The document provides an overview of classroom management including definitions, models of effective classroom management, and strategies for managing disruptive behavior and bullying. It discusses three models of classroom management: interventionist, interactive, and non-interventionist. The interventionist model emphasizes teacher control while the non-interventionist model gives more autonomy to students. Effective behavior management requires understanding factors like student needs, consequences, and developing a structured classroom environment.