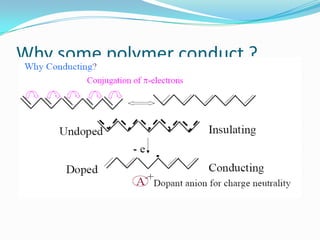
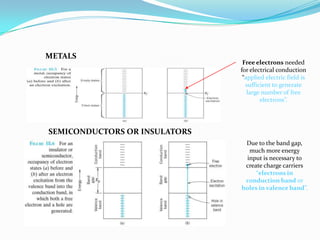
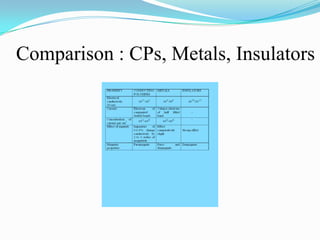
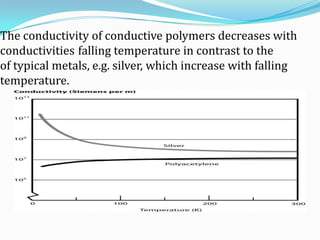
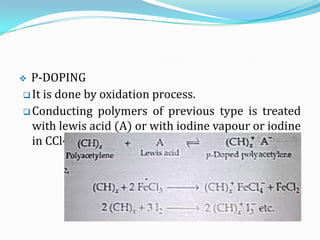
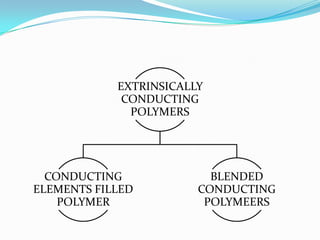
The document discusses conducting polymers and their properties and applications. There are four major classes of semiconducting polymers that have been developed: conjugated conducting polymers, charge transfer polymers, ionically conducting polymers, and conductively filled polymers. Conducting polymers can conduct electricity due to the presence of free electrons, holes, or charged atoms and molecules. They are unique in that they exhibit properties of both metals and plastics, making them promising for many technological uses. Common applications of conducting polymers include anti-static coatings, corrosion inhibitors, transistors, LEDs, solar cells, and smart windows.