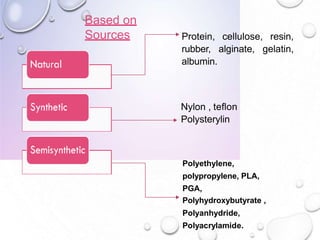
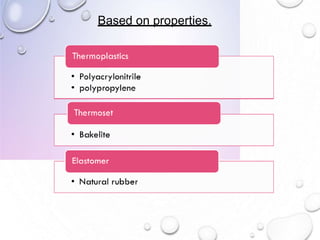
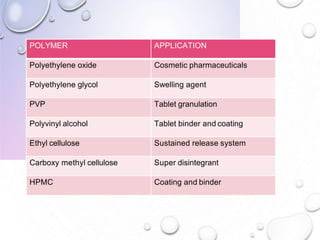
This document discusses polymers, including their definition as large molecules formed by linking repeating structural units. Polymers are classified in various ways, including by source, polymerization type, degradability, and properties. Ideal polymers are inert, non-toxic, easily administered, have good mechanical strength, and are biodegradable and biocompatible. Polymers have advantages like localized drug delivery and sustained release, while disadvantages can include dose dumping and low mechanical properties. The document outlines applications of polymers in drug delivery systems, including for controlled and sustained release, as well as in biomedical uses like tissue engineering and surgical adhesives.