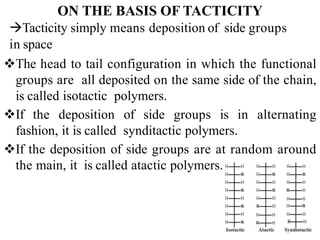
Polymers are large molecules formed by bonding many smaller molecules called monomers together in chains. There are natural, semisynthetic, and synthetic polymers classified based on origin. Polymers can also be classified based on monomer type, thermal response, formation method, structure, application, tacticity, and other parameters. Some important polymers include polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, nylon, and synthetic rubber.